Abstract
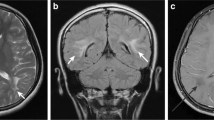
We report brain MRI findings in four patients with typical Kearns-Sayre syndrome (KSS) and correlate them with clinical manifestations. MRI was interpreted as normal in two patients; cerebral and cerebellar atrophy was seen in the other two. On T2-weighted spin-echo images, two patients had high-signal lesions bilaterally in subcortical white matter, thalamus and brain stem. In one patient, the white matter lesion extended into the deep cerebral white matter and the cerebellum was also affected. The other also had bilateral high-signal lesions in the globus pallidus. There was little correlation between neurological deficits and MRI findings. A review of the literature revealed that 10 of the 13 patients with typical KSS previously studied had bilateral subcortical white-matter lesions on T2-weighted images; at least 7 also had high-signal lesions in the brain stem, globus pallidus, thalamus or cerebellum. Although MRI may be normal or show atrophy, the characteristic finding in KSS is a combination of the high-signal foci in subcortical cerebral white matter and in the brain stem, globus pallidus or thalamus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 23 October 1998 Accepted: 8 February 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, B., Terae, S., Takahashi, C. et al. MRI of the brain in the Kearns- Sayre syndrome: report of four cases and a review. Neuroradiology 41, 759–764 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050838
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050838