Abstract
Purpose
New software solutions emerged to support radiologists in image interpretation in acute ischemic stroke. This study aimed to validate the performance of computer-aided assessment of the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT score (ASPECTS) for detecting signs of early infarction.
Methods
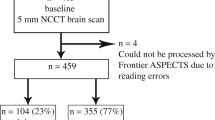
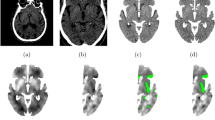
ASPECT scores were assessed in 119 CT scans of patients with acute middle cerebral artery ischemia. Patient collective was differentiated according to (I) normal brain, (II) leukoencephalopathic changes, (III) infarcts, and (IV) atypical parenchymal defects (multiple sclerosis, etc.). ASPECTS assessments were automatically provided by the software package e-ASPECTS (Brainomix®, UK) (A). Subsequently, three neuroradiologists (B), (C), and (D) examined independently 2380 brain regions. Interrater comparison was performed with the definite infarct core as reference standard after best medical care (thrombolysis and/or thrombectomy).
Results
Interrater comparison revealed higher correlation coefficient of (B) 0.71, (C) 0.76, and of (D) 0.80 with definite infarct core compared to (A) 0.59 for ASPECTS assessment in the acute ischemic stroke setting. While (B), (C), and (D) showed a significant correlation for individual patient groups (I), (II), (III), and (IV), except for (D) (II), (A) was not significant in patient groups with pre-existing changes (II), (III), and (IV). The following sensitivities, specificities, PPV, NPV, and accuracies given in percent were achieved: (A) 83, 57, 55, 82, and 67; (B) 74, 76, 69, 83, and 77; (C) 80.8, 85.2, 76, 84, and 80; (D) 63, 90.7, 82, 79, and 80, respectively.
Conclusion
For ASPECTS assessment, the examined software may provide valid data in case of normal brain. It may enhance the work of neuroradiologists in clinical decision making. A final human check for plausibility is needed, particularly in patient groups with pre-existing cerebral changes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feigin VL, Forouzanfar MH, Krishnamurthi R, Mensah GA, Connor M, Bennett DA, Moran AE, Sacco RL, Anderson L, Truelsen T, O'Donnell M, Venketasubramanian N, Barker-Collo S, Lawes CMM, Wang W, Shinohara Y, Witt E, Ezzati M, Naghavi M, Murray C (2014) Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990–2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 383:245–254
Rai AT, Seldon AE, Boo S, Link PS, Domico JR, Tarabishy AR, Lucke-Wold N, Carpenter JS (2017) A population-based incidence of acute large vessel occlusions and thrombectomy eligible patients indicates significant potential for growth of endovascular stroke therapy in the USA. J Neurointerv Surg 9:722–726
Albers GW, Marks MP, Kemp S et al (2018) Thrombectomy for stroke at 6 to 16 hours with selection by perfusion imaging. N Engl J Med 378:708–718. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1713973
Raul G, Nogueira MD, Ashutosh PJ et al (2018) Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct. N Engl J Med 378:11–21
Von Kummer R, Allen KL, Holle R et al (1997) Acute stroke: usefulness of early CT findings before thrombolytic therapy. Radiology 205:327–333
Tomura N, Uemura K, Inugami A, Fujita H, Higano S, Shishido F (1988) Early CT finding in cerebral infarction: obscuration of the lentiform nucleus. Radiology 168:463–467
Srinivasan A, Goyal M, Al Azri F, Lum C (2006) State-of-the-art imaging of acute stroke. RadioGraphics 26:S75–S95
Barber PA, Demchuk AM, Zhang J et-al. (2000) Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. ASPECTS Study Group Alberta Stroke Programme Early CT Score. Lancet 355:1670–1674
Pexman JH, Barber PA, Hill MD et-al. (2001) Use of the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) for assessing CT scans in patients with acute stroke. AJNR 22:1534–1542
Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, Roy D, Jovin TG, Willinsky RA, Sapkota BL, Dowlatshahi D, Frei DF, Kamal NR, Montanera WJ, Poppe AY, Ryckborst KJ, Silver FL, Shuaib A, Tampieri D, Williams D, Bang OY, Baxter BW, Burns PA, Choe H, Heo JH, Holmstedt CA, Jankowitz B, Kelly M, Linares G, Mandzia JL, Shankar J, Sohn SI, Swartz RH, Barber PA, Coutts SB, Smith EE, Morrish WF, Weill A, Subramaniam S, Mitha AP, Wong JH, Lowerison MW, Sajobi TT, Hill MD, ESCAPE Trial Investigators (2015) Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372:1019–1030
Jovin TG, Chamorro A, Cobo E, de Miquel MA, Molina CA, Rovira A, San Román L, Serena J, Abilleira S, Ribó M, Millán M, Urra X, Cardona P, López-Cancio E, Tomasello A, Castaño C, Blasco J, Aja L, Dorado L, Quesada H, Rubiera M, Hernandez-Pérez M, Goyal M, Demchuk AM, von Kummer R, Gallofré M, Dávalos A, REVASCAT Trial Investigators (2015) Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372:2296–2306
MD*Calc (medical app); online site: https://www.mdcalc.com/alberta-stroke-program-early-ct-score-aspects#creator-insights (accessed 02/2018).
Syngo.via Frontier ASPECT Score Prototype V1_2_0. Siemens Healthcare GmbH®, Erlangen, Germany. https://www.healthcare.siemens.de/medical-imaging-it/advanced-visualization-solutions/syngo-via-frontier/use. (accessed 02/2018).
e-ASPECTS. Brainomix®, Oxford, UK. https://www.brainomix.com/ (accessed 02/2018).
Forsting M (2017) Machine learning will change medicine. J Nucl Med 58:357–358
Nagel S, Sinha D, Day D, Reith W, Chapot R, Papanagiotou P, Warburton EA, Guyler P, Tysoe S, Fassbender K, Walter S, Essig M, Heidenrich J, Konstas AA, Harrison M, Papadakis M, Greveson E, Joly O, Gerry S, Maguire H, Roffe C, Hampton-Till J, Buchan AM, Grunwald IQ (2017) e-ASPECTS software is non-inferior to neuroradiologists in applying the ASPECT score to computed tomography scans of acute ischemic stroke patients. Int J Stroke 12:615–622
Pfaff J, Herweh C, Schieber S, Schönenberger S, Bösel J, Ringleb PA, Möhlenbruch M, Bendszus M, Nagel S (2017) e-ASPECTS correlates with and is predictive of outcome after mechanical thrombectomy. AJNR 38:1594–1599
Herweh C, Ringleb PA, Rauch G et al (2016) Performance of e-ASPECTS software in comparison to that of stroke physicians on assessing CT scans of acute ischemic stroke patients. Int J Stroke 11:438–445
Jumbo Java-based biometrical software tool; University Münster; Institute for Biometry and Clinical Research: http://jumbo.uni-muenster.de/fileadmin/jumbo/applets/falla.html (accessed 02/2018).
Grunwald IQ, Ragoschke-Schumm A, Kettner M, Schwindling L, Roumia S, Helwig S, Manitz M, Walter S, Yilmaz U, Greveson E, Lesmeister M, Reith W, Fassbender K (2016) First automated stroke imaging evaluation via electronic Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score in a mobile stroke unit. Cerebrovasc Dis 42:332–338
Dzialowski I, Hill MD, Coutts SB, Demchuk AM, Kent DM, Wunderlich O, von Kummer R (2006) Extent of early ischemic changes on computed tomography (CT) before thrombolysis: prognostic value of the Alberta stroke program early CT score in ECASS II. Stroke 37:973–978
Schröder J, Thomalla G (2017) A critical review of Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score for evaluation of acute stroke imaging. Front Neurol 7:245
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guberina, N., Dietrich, U., Radbruch, A. et al. Detection of early infarction signs with machine learning-based diagnosis by means of the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT score (ASPECTS) in the clinical routine. Neuroradiology 60, 889–901 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-018-2066-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-018-2066-5