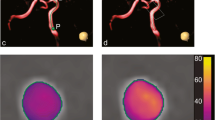
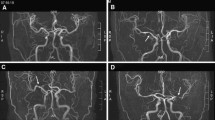
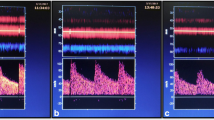
Abstract
Introduction
4D phase contrast MR imaging (4D PC MRI) has been introduced for spatiotemporal evaluation of intracranial hemodynamics in various cerebrovascular diseases. However, it still lacks validation with standards of reference. Our goal was to compare blood flow quantification derived from 4D PC MRI with transcranial ultrasound and 2D PC MRI.
Methods
Velocity measurements within large intracranial arteries [internal carotid artery (ICA), basilar artery (BA), and middle cerebral artery (MCA)] were obtained in 20 young healthy volunteers with 4D and 2D PC MRI, transcranial Doppler sonography (TCD), and transcranial color-coded duplex sonography (TCCD). Maximum velocities at peak systole (PSV) and end diastole (EDV) were compared using regression analysis and Bland–Altman plots.
Results
Correlation of 4D PC MRI measured velocities was higher in comparison with TCD (r = 0.49–0.66) than with TCCD (0.35–0.44) and 2D PC MRI (0.52–0.60). In mid-BA and ICA C7 segment, a significant correlation was found with TCD (0.68–0.81 and 0.65–0.71, respectively). No significant correlation was found in carotid siphon. On average over all volunteers, PSVs and EDVs in MCA were minimally underestimated compared with TCD/TCCD. Minimal overestimation of velocities was found compared to TCD in mid-BA and ICA C7 segment.
Conclusion
4D PC MRI appears as valid alternative for intracranial velocity measurement consistent with previous reference standards, foremost with TCD. Spatiotemporal averaging effects might contribute to vessel size-dependent mild underestimation of velocities in smaller (MCA), and overestimation in larger-sized (BA and ICA) arteries, respectively. Complete spatiotemporal flow analysis may be advantageous in anatomically complex regions (e.g. carotid siphon) relative to restrictions of ultrasound techniques.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bammer R, Hope TA, Aksoy M, Alley MT (2007) Time-resolved 3D quantitative flow MRI of the major intracranial vessels: initial experience and comparative evaluation at 1.5 T and 3.0 T in combination with parallel imaging. Magn Reson Med 57(1):127–140
Boussel L, Rayz V, Martin A, Acevedo-Bolton G, Lawton MT, Higashida R, Smith WS, Young WL, Saloner D (2009) Phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging measurements in intracranial aneurysms in vivo of flow patterns, velocity fields, and wall shear stress: comparison with computational fluid dynamics. Magn Reson Med 61(2):409–417. doi:10.1002/mrm.21861
Harloff A, Albrecht F, Spreer J, Stalder AF, Bock J, Frydrychowicz A, Schollhorn J, Hetzel A, Schumacher M, Hennig J, Markl M (2009) 3D blood flow characteristics in the carotid artery bifurcation assessed by flow-sensitive 4D MRI at 3 T. Magn Reson Med 61(1):65–74. doi:10.1002/mrm.21774
Hope MD, Purcell DD, Hope TA, von Morze C, Vigneron DB, Alley MT, Dillon WP (2009) Complete intracranial arterial and venous blood flow evaluation with 4D flow MR imaging. AJNR 30(2):362–366. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1138
Meckel S, Stalder AF, Santini F, Radu EW, Rufenacht DA, Markl M, Wetzel SG (2008) In vivo visualization and analysis of 3-D hemodynamics in cerebral aneurysms with flow-sensitized 4-D MR imaging at 3 T. Neuroradiology 50(6):473–484. doi:10.1007/s00234-008-0367-9
Wetzel S, Meckel S, Frydrychowicz A, Bonati L, Radue EW, Scheffler K, Hennig J, Markl M (2007) In vivo assessment and visualization of intracranial arterial hemodynamics with flow-sensitized 4D MR imaging at 3 T. AJNR 28(3):433–438
Yamashita S, Isoda H, Hirano M, Takeda H, Inagawa S, Takehara Y, Alley MT, Markl M, Pelc NJ, Sakahara H (2007) Visualization of hemodynamics in intracranial arteries using time-resolved three-dimensional phase-contrast MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 25(3):473–478
Markl M, Wegent F, Zech T, Bauer S, Strecker C, Schumacher M, Weiller C, Hennig J, Harloff A (2010) In vivo wall shear stress distribution in the carotid artery: effect of bifurcation geometry, internal carotid artery stenosis, and recanalization therapy. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 3(6):647–655. doi:10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.110.958504
Markl M, Chan FP, Alley MT, Wedding KL, Draney MT, Elkins CJ, Parker DW, Wicker R, Taylor CA, Herfkens RJ, Pelc NJ (2003) Time-resolved three-dimensional phase-contrast MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 17(4):499–506
Markl M, Draney MT, Hope MD, Levin JM, Chan FP, Alley MT, Pelc NJ, Herfkens RJ (2004) Time-resolved 3-dimensional velocity mapping in the thoracic aorta: visualization of 3-directional blood flow patterns in healthy volunteers and patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr 28(4):459–468
Hoppe M, Heverhagen JT, Froelich JJ, Kunisch-Hoppe M, Klose KJ, Wagner HJ (1998) Correlation of flow velocity measurements by magnetic resonance phase contrast imaging and intravascular Doppler ultrasound. Invest Radiol 33(8):427–432
Schubert T, Santini F, Stalder AF, Bock J, Meckel S, Bonati L, Markl M, Wetzel S (2011) Dampening of blood-flow pulsatility along the carotid siphon: does form follow function? Ajnr 32(6):1107–1112. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2426
Stalder AF, Russe MF, Frydrychowicz A, Bock J, Hennig J, Markl M (2008) Quantitative 2D and 3D phase contrast MRI: optimized analysis of blood flow and vessel wall parameters. Magn Reson Med 60(5):1218–1231. doi:10.1002/mrm.21778
Baumgartner RW, Mathis J, Sturzenegger M, Mattle HP (1994) A validation study on the intraobserver reproducibility of transcranial color-coded duplex sonography velocity measurements. Ultrasound Med Biol 20(3):233–237
Hoksbergen AW, Legemate DA, Ubbink DT, Jacobs MJ (1999) Success rate of transcranial color-coded duplex ultrasonography in visualizing the basal cerebral arteries in vascular patients over 60 years of age. Stroke 30(7):1450–1455
Tsuchiya T, Yasaka M, Yamaguchi T, Kimura K, Omae T (1991) Imaging of the basal cerebral arteries and measurement of blood velocity in adults by using transcranial real-time color flow Doppler sonography. Ajnr 12(3):497–502
Enzmann DR, Ross MR, Marks MP, Pelc NJ (1994) Blood flow in major cerebral arteries measured by phase-contrast cine MR. Ajnr 15(1):123–129
McCauley TR, Pena CS, Holland CK, Price TB, Gore JC (1995) Validation of volume flow measurements with cine phase-contrast MR imaging for peripheral arterial waveforms. J Magn Reson Imaging 5(6):663–668
Zananiri FV, Jackson PC, Halliwell M, Harris RA, Hayward JK, Davies ER, Wells PN (1993) A comparative study of velocity measurements in major blood vessels using magnetic resonance imaging and Doppler ultrasound. Br J Radiol 66(792):1128–1133
Bouthillier A, van Loveren HR, Keller JT (1996) Segments of the internal carotid artery: a new classification. Neurosurgery 38(3):425–432, discussion 432–423
Bock J, Kreher BW, Hennig J, Markl M (2007) Optimized pre-processing of time-resolved 2D and 3D Phase Contrast MRI data. In Proc: ISMRM 2007, May; Berlin, Germany p # 3138
Buonocore MH (1998) Visualizing blood flow patterns using streamlines, arrows, and particle paths. Magn Reson Med 40(2):210–226
Walker PG, Cranney GB, Scheidegger MB, Waseleski G, Pohost GM, Yoganathan AP (1993) Semiautomated method for noise reduction and background phase error correction in MR phase velocity data. J Magn Reson Imaging 3(3):521–530
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1(8476):307–310
Schoning M, Walter J (1992) Evaluation of the vertebrobasilar-posterior system by transcranial color duplex sonography in adults. Stroke 23(9):1280–1286
Martin PJ, Evans DH, Naylor AR (1994) Transcranial color-coded sonography of the basal cerebral circulation. Reference data from 115 volunteers. Stroke 25(2):390–396
Bartels E, Fuchs HH, Flugel KA (1995) Color Doppler imaging of basal cerebral arteries: normal reference values and clinical applications. Angiology 46(10):877–884
Shambal S, Grehl H, Zierz S, Lindner A (2003) Age dependence of Doppler parameters in the basal cerebral arteries evaluated by transcranial color-coded duplex sonography. Reference data from 290 volunteers. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr 71(5):271–277. doi:10.1055/s-2003-39064
Mattle H, Edelman RR, Wentz KU, Reis MA, Atkinson DJ, Ellert T (1991) Middle cerebral artery: determination of flow velocities with MR angiography. Radiology 181(2):527–530
Stock KW, Wetzel SG, Lyrer PA, Radu EW (2000) Quantification of blood flow in the middle cerebral artery with phase-contrast MR imaging. Eur Radiol 10(11):1795–1800
van Ooij P, Zwanenburg JJ, Visser F, Majoie CB, Vanbavel E, Hendrikse J, Nederveen AJ Quantification and visualization of flow in the circle of Willis: time-resolved three-dimensional phase contrast MRI at 7 T compared with 3 T. Magn Reson Med. doi:10.1002/mrm.24317
Markl M, Hennig J (2001) Phase contrast MRI with improved temporal resolution by view sharing: k-space related velocity mapping properties. Magn Reson Imaging 19(5):669–676
Piepgras A, Bise K, Schmiedek P (1993) Morphometry of intraluminal side-to-side differences in human basal cerebral arteries. Ultrasound Med Biol 19(3):193–195
Marks MP, Pelc NJ, Ross MR, Enzmann DR (1992) Determination of cerebral blood flow with a phase-contrast cine MR imaging technique: evaluation of normal subjects and patients with arteriovenous malformations. Radiology 182(2):467–476
Maeda H, Etani H, Handa N, Tagaya M, Oku N, Kim BH, Naka M, Kinoshita N, Nukada T, Fukunaga R et al (1990) A validation study on the reproducibility of transcranial Doppler velocimetry. Ultrasound Med Biol 16(1):9–14
Sorteberg W, Langmoen IA, Lindegaard KF, Nornes H (1990) Side-to-side differences and day-to-day variations of transcranial Doppler parameters in normal subjects. J Ultrasound Med 9(7):403–409
Krejza J, Mariak Z, Walecki J, Szydlik P, Lewko J, Ustymowicz A (1999) Transcranial color Doppler sonography of basal cerebral arteries in 182 healthy subjects: age and sex variability and normal reference values for blood flow parameters. AJR Am J Roentgenol 172(1):213–218
Chang W, Landgraf B, Johnson KM, Kecskemeti S, Wu Y, Velikina J, Rowley H, Wieben O, Mistretta C, Turski P (2011) Velocity measurements in the middle cerebral arteries of healthy volunteers using 3D radial phase-contrast HYPRFlow: comparison with transcranial Doppler sonography and 2D phase-contrast MR imaging. Ajnr 32(1):54–59. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2240
Chang W, Loecher MW, Wu Y, Niemann DB, Ciske B, Aagaard-Kienitz B, Kecskemeti S, Johnson KM, Wieben O, Mistretta C, Turski P (2012) Hemodynamic changes in patients with arteriovenous malformations assessed using high-resolution 3D radial phase-contrast magnetic resonance angiography. Ajnr. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3010
Gu T, Korosec FR, Block WF, Fain SB, Turk Q, Lum D, Zhou Y, Grist TM, Haughton V, Mistretta CA (2005) PC VIPR: a high-speed 3D phase-contrast method for flow quantification and high-resolution angiography. AJNR 26(4):743–749
Acknowledgments
We thank Gabriele Ihorst, Ph.D., Biostatistician, for valuable statistical support. This work was supported in part by a grant from the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNF 320000-113492/1).
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Stephan Meckel and Lorenz Leitner contributed equally to content of manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meckel, S., Leitner, L., Bonati, L.H. et al. Intracranial artery velocity measurement using 4D PC MRI at 3 T: comparison with transcranial ultrasound techniques and 2D PC MRI. Neuroradiology 55, 389–398 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1103-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1103-z