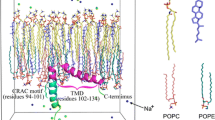
Abstract
Caveolin-1 is one of the main protein components of caveolae that acts as a mechanosensor at the cell membrane. The interactions of caveolin-1 with membranes have been shown to lead to complex effects such as curvature and the clustering of specific lipids. Here, we review the emerging concepts on the molecular interactions of caveolin-1, with a focus on insights from coarse-grain molecular dynamics simulations. Consensus structural models of caveolin-1 report a helix-turn-helix core motif with flanking domains of higher disorder that could be membrane composition dependent. Caveolin-1 appears to be mainly surface-bound and does not embed very deep in the membrane to which it is bound. The most interesting aspect of caveolin-1 membrane binding is the interplay of cholesterol clustering and membrane curvature. Although cholesterol has been reported to cluster in the vicinity of caveolin-1 by several approaches, simulations show that the clustering is maximal in membrane leaflet opposing the surface-bound caveolin-1. The intrinsic negative curvature of cholesterol appears to stabilize the negative curvature in the opposing leaflet. In fact, the simulations show that blocking cholesterol clustering (through artificial position restraints) blocks membrane curvature, and vice versa. Concomitant with cholesterol clustering is sphingomyelin clustering, again in the opposing leaflet, but in a concentration-dependent manner. The differential stress due to caveolin-1 binding and the inherent asymmetry of the membrane leaflets could be the determinant for membrane curvature and needs to be further probed. The review is an important step to reconcile the molecular level details emerging from simulations with the mesoscopic details provided by state of the art experimental approaches.
Graphic Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki S, Thomas A, Decaffmeyer M, Brasseur R, Epand RM (2010) The role of proline in the membrane re-entrant helix of caveolin-1. J Biol Chem 285(43):33371–33380
Ariotti N, Rae J, Leneva N, Ferguson C, Loo D, Okano S, Hill MM, Walser P, Collins BM, Parton RG (2015) Molecular characterization of caveolin-induced membrane curvature. J Biol Chem 290(41):24875–24890
Ayton GS, Blood PD, Voth GA (2007) Membrane remodeling from N-BAR domain interactions: Insights from multi-scale simulation. Biophys J 92(10):3595–3602
Bassereau P, Jin R, Baumgart T, Deserno M, Dimova R, Frolov VA, Bashkirov PV, Grubmüller H, Jahn R, Risselada HJ, Johannes L, Kozlov MM, Lipowsky R, Pucadyil TJ, Zeno WF, Stachowiak JC, Stamou D, Breuer A, Lauritsen L, Simon C, Sykes C, Voth GA, Weikl TR (2018) The 2018 biomembrane curvature and remodeling roadmap. J Phys D Appl Phys 51(34):343001
Beltrán-Heredia E, Tsai FC, Salinas-Almaguer S, Cao FJ, Bassereau P, Monroy F (2019) Membrane curvature induces cardiolipin sorting. Comm Biol 2:1–7
Blood PD, Swenson RD, Voth GA (2008) Factors influencing local membrane curvature induction by N-BAR domains as revealed by molecular dynamics simulations. Biophys J 95(4):1866–1876
Blouin CM, Le Lay S, Eberl A, Köfeler HC, Guerrera IC, Klein C, Le Liepvre X, Lasnier F, Bourron O, Gautier JF et al (2010) Lipid droplet analysis in caveolin-deficient adipocytes: alterations in surface phospholipid composition and maturation defects [s]. J Lip Res 51:945–956
Brown DA, Rose JK (1992) Sorting of GPI-anchored proteins to glycolipid-enriched membrane subdomains during transport to the apical cell surface. Cell 68:533–544
Burley SK, Bhikadiya C, Bi C, Bittrich S, Chen L, Crichlow GV, Christie CH, Dalenberg K, Di Costanzo L, Duarte JM et al (2021) Rcsb protein data bank: powerful new tools for exploring 3d structures of biological macromolecules for basic and applied research and education in fundamental biology, biomedicine, biotechnology, bioengineering and energy sciences. Nucl Acid Res 49:D437–D451
Corradi V, Sejdiu BI, Mesa-Galloso H, Abdizadeh H, Noskov SY, Marrink SJ, Tieleman DP (2019) Emerging diversity in lipid-protein interactions. Chem Rev 119:5775–5848
Couet J, Belanger MM, Roussel E, Drolet MC (2001) Cell biology of caveolae and caveolin. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 49(3):223–235
Deserno M, Hossein A (2019) Curvature rigidity of asymmetric and differentially stressed membranes 48:S70–S70
Dietzen DJ, Hastings WR, Lublin DM (1995) Caveolin is palmitoylated on multiple cysteine residues. Palmitoylation is not necessary for localization of caveolin to caveolae. J Biol Chem 270(12):6838–6842
Epand RM, Sayer BG, Epand RF (2005) Caveolin scaffolding region and cholesterol-rich domains in membranes. J Mol Biol 345(2):339–350
Fielding CJ, Fielding PE (2000) Cholesterol and caveolae: structural and functional relationships. Biochim Biophys Acta 1529(1–3):210–222
Fra AM, Masserini M, Palestini P, Sonnino S, Simons K (1995) A photo-reactive derivative of ganglioside GM1 specifically cross-links VIP21-caveolin on the cell surface. FEBS Lett 375:11–14
Friedman R, Khalid S, Aponte-Santamaría C, Arutyunova E, Becker M, Boyd KJ, Christensen M, Coimbra JT, Daday C, van Eerden FJ et al (2018) Understanding conformational dynamics of complex lipid mixtures relevant to biology. J Membr Biol 251:609–631
Frolov VA, Shnyrova AV, Zimmerberg J (2011) Lipid polymorphisms and membrane shape. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3:a004747
Fuhrmans M, Knecht V, Marrink SJ (2009) A single bicontinuous cubic phase induced by fusion peptides. J Am Chem Soc 131(26):9166–9167
Fujimoto T (1996) GPI-anchored proteins, glycosphingolipids, and sphingomyelin are sequestered to caveolae only after crosslinking. J Histochem Cytochem 44:929–941
Golani G, Ariotti N, Parton RG, Kozlov MM (2019) Membrane curvature and tension control the formation and collapse of caveolar superstructures. Devel Cell 48:523–538
Gorfe AA, Pellarin R, Caflisch A (2004) Membrane localization and flexibility of a lipidated ras peptide studied by molecular dynamics simulations. J Am Chem Soc 126(46):15277–15286
Han B, Porta JC, Hanks JL, Peskova Y, Binshtein E, Dryden K, Claxton DP, Mchaourab HS, Karakas E, Ohi MD et al (2020) Structure and assembly of cav1 8s complexes revealed by single particle electron microscopy. Sci Adv 6:eabc6185
Han B, Copeland CA, Tiwari A, Kenworthy AK (2016) Assembly and turnover of caveolae: What do we really know? Front Cell Dev Biol 4:68
Hansen CG, Nichols BJ (2010) Exploring the caves: Cavins, caveolins and caveolae. Trends Cell Biol 20(4):177–186
Hirama T, Das R, Yang Y, Ferguson C, Won A, Yip CM, Kay JG, Grinstein S, Parton RG, Fairn GD (2017) Phosphatidylserine dictates the assembly and dynamics of caveolae in the plasma membrane. Biol Chem 292:14292–14307
Hoop CL, Sivanandam VN, Kodali R, Srnec MN, Van Der Wel PCA (2012) Structural characterization of the caveolin scaffolding domain in association with cholesterol-rich membranes. Biochemistry 51(1):90–99
Horton MR, Rädler J, Gast AP (2006) Phase behavior and the partitioning of caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptides in model lipid bilayers. J Coll Inter Sci 304:67–76
Hossein A, Deserno M (2020) Spontaneous curvature, differential stress, and bending modulus of asymmetric lipid membranes. Biophys J 118(3):624–642
Hsu PC, Samsudin F, Shearer J, Khalid S (2017) It is complicated: curvature, diffusion, and lipid sorting within the two membranes of escherichia coli. J Phys Chem Lett 8:5513–5518
Janosi L, Li Z, Hancock JF, Gorfe AA (2012) Organization, dynamics, and segregation of Ras nanoclusters in membrane domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(21):8097–8102
de Jong DH, Lopez CA, Marrink SJ (2013) Molecular view on protein sorting into liquid-ordered membrane domains mediated by gangliosides and lipid anchors. Faraday Discuss 161:347–363
Jumper J, Evans R, Pritzel A, Green T, Figurnov M, Ronneberger O, Tunyasuvunakool K, Bates R, Žídek A, Potapenko A et al (2021) Highly accurate protein structure prediction with alphafold. Nature 596:583–589
Kharche SA, Sengupta D (2020) Dynamic protein interfaces and conformational landscapes of membrane protein complexes. Curr Op Struct Biol 61:191–197
Kim JH, Peng D, Schlebach JP, Hadziselimovic A, Sanders CR (2014) Modest effects of lipid modifications on the structure of caveolin-3. Biochemistry 53(27):4320–4322
Krishna A, Sengupta D (2019) Interplay between membrane curvature and cholesterol: Role of palmitoylated caveolin-1. Biophys J 116:69–78
Krishna A, Prakash S, Sengupta D (2020) Sphingomyelin effects in caveolin-1 mediated membrane curvature. J Phys Chem B 124:5177–5185
Kruglikov I, Scherer P (2019) Caveolin-1 as a pathophysiological factor and target in psoriasis. NPJ Aging Mech Dis 5:4
Last NB, Schlamadinger DE, Miranker AD (2013) A common landscape for membrane-active peptides. Prot Sci 22:870–882
Latorraca NR, Venkatakrishnan A, Dror RO (2017) Gpcr dynamics: structures in motion. Chem Rev 117:139–155
Le Lan C, Neumann JM, Jamin N (2006) Role of the membrane interface on the conformation of the caveolin scaffolding domain: a CD and NMR study. FEBS Lett 580(22):5301–5305
Le Lan C, Gallay J, Vincent M, Neumann JM, De Foresta B, Jamin N (2010) Structural and dynamic properties of juxta-membrane segments of caveolin-1 and caveolin-2 at the membrane interface. Eur Biophys J 39(2):307–325
Lee H, Woodman SE, Engelman JA, Galbiati F, Kaufman HL, Lublin DM, Lisanti MP et al (2001) Palmitoylation of caveolin-1 at a single site (cys-156) controls its coupling to the c-src tyrosine kinase: targeting of dually acylated molecules (gpi-linked, transmembrane, or cytoplasmic) to caveolae effectively uncouples c-src and caveolin-1 (tyr-14). J Biol Chem 276:35150–35158
Lee J, Glover KJ (2012) The transmembrane domain of caveolin-1 exhibits a helix-break-helix structure. Biochim Biophys Acta 5:1158–1164
Lee SW, Reimer CL, Oh P, Campbell DB, Schnitzer JE (1998) Tumor cell growth inhibition by caveolin re-expression in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 16(11):1391–1397
Li H, Gorfe AA (2013) Aggregation of lipid-anchored full-length H-Ras in lipid bilayers: Simulations with the MARTINI force field. PLoS ONE 8(7)
Li Z, Janosi L, Gorfe AA (2012) Formation and domain partitioning of H-Ras peptide nanoclusters: effects of peptide concentration and lipid composition. J Am Chem Soc 134(41):17278–17285
Liang H, Mu H, Jean-Francois F, Lakshman B, Sarkar-Banerjee S, Zhuang Y, Zeng Y, Gao W, Zaske AM, Nissley DV, et al. (2019) Membrane curvature sensing of the lipid-anchored k-ras small gtpase. Life Sci Allian 2
Liang X, Zu Y, Cao YP, Yang C (2013) A dual-scale model for the caveolin-mediated vesiculation. Soft Matter 9(33):7981
Lin Q, London E (2015) Ordered raft domains induced by outer leaflet sphingomyelin in cholesterol-rich asymmetric vesicles. Biophys J 108:2212–2222
Lin X, Li Z, Gorfe AA (2015) Reversible effects of peptide concentration and lipid composition on H-Ras lipid anchor clustering. Biophys J 109(12):2467–2470
Lin X, Gorfe AA (2018) Protein partitioning into ordered membrane domains: insights from simulations. Biophys J 114:1936–1944
Lisanti MP, Sargiacomo M, Scherer PE (1999) Purification of caveolae-derived membrane microdomains containing lipid-anchored signaling molecules, such as GPI-anchored proteins, H-Ras, Src-family tyrosine kinases, eNOS, and G-protein alpha-, beta-, and gamma-subunits. Methods Mol Biol 116:51–60
Liu H, Yang L, Zhang Q, Mao L, Jiang H, Yang H (2016) Probing the structure and dynamics of caveolin-1 in a caveolae-mimicking asymmetric lipid bilayer model. Eur Biophys J 45(6):511–21
Lo HP, Nixon SJ, Hall TE, Cowling BS, Ferguson C, Morgan GP, Schieber NL, Fernandez-Rojo MA, Bastiani M, Floetenmeyer M et al (2015) The caveolin-cavin system plays a conserved and critical role in mechanoprotection of skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol 210:833–849
Ludwig A, Nichols BJ, Sandin S (2016) Architecture of the caveolar coat complex. J Cell Sci 129:3077–3083
Manna M, Nieminen T, Vattulainen I (2019) Understanding the role of lipids in signaling through atomistic and multiscale simulations of cell membranes. Ann Rev Biophys 48:421–439
Marrink SJ, Risselada HJ, Yefimov S, Tieleman DP, De Vries AH (2007) The MARTINI force field: coarse grained model for biomolecular simulations. J Phys Chem B 11:7812–7824
Monier S, Parton RG, Vogel F, Behlke J, Henske A, Kurzchalia TV (1995) VIP21-caveolin, a membrane protein constituent of the caveolar coat, oligomerizes in vivo and in vitro. Mol Biol Cell 6:911–927
Monticelli L, Kandasamy S, Periole X, Larson R, Tieleman D, Marrink S (2008) The MARTINI coarse grained forcefield: extension to proteins. J Comp Theor Chem 4:819–834
Murata M, Peranen J, Schreinert R, Wielandt F, Kurzchalia TV, Simons K (1995) VIP21/caveolin is a cholesterol-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci 92(22):10339–10343
Nikte SV, Sonar K, Tandale A, Joshi M, Sengupta D (2021) Loss of a water-mediated network results in reduced agonist affinity in a \(\beta\)2-adrenergic receptor clinical variant. Biochim Biophy Acta -Prot Proteom 1869:140605
Okamoto T, Schlegel A, Scherer PE, Lisanti MP (1998) Caveolins, a family of scaffolding proteins for organizing “preassembled signaling complexes” at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem 273(10):5419–5422
Örtegren U, Karlsson M, Blazic N, Blomqvist M, Nystrom FH, Gustavsson J, Fredman P, Strålfors P (2004) Lipids and glycosphingolipids in caveolae and surrounding plasma membrane of primary rat adipocytes. Eur J Biochem 271(10):2028–2036
Parat MO, Anand-Apte B, Fox PL (2003) Differential caveolin-1 polarization in endothelial cells during migration in two and three dimensions. Mol Biol Cell 14:3156–3168
Parton RG (1994) Ultrastructural localization of gangliosides; GM1 is concentrated in caveolae. J Histochem Cytochem 42:155–166
Parton RG (2018) Caveolae: structure, function, and relationship to disease. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol 34:111–136
Parton RG, Collins BM (2018) Unraveling the architecture of caveolae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:14170–14172
Parton RG, Kozlov MM, Ariotti N (2020) Caveolae and lipid sorting: shaping the cellular response to stress. J Cell Biol 219
Pawar AB, Sengupta D (2021) Role of cholesterol in transmembrane dimerization of the erbb2 growth factor receptor. J Membr Biol 254:301–310
Pezeshkian W, Chevrot G, Khandelia H (2018) The role of caveolin-1 in lipid droplets and their biogenesis. Chem Phys Lipids 211(211):93–99
Porta JC, Han B, Gulsevin A, Chung J, Peskova Y, Connolly S, Mchaourab HS, Meiler J, Karakas E, Kenworthy AK, Ohi MD (2022) Molecular architecture of the human caveolin-1 complex. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.17.480763
Prakash S, Krishna A, Sengupta D (2021) Caveolin induced membrane curvature and lipid clustering: two sides of the same coin? Faraday Disc 232:218–235
Prasanna X, Mohole M, Chattopadhyay A, Sengupta D (2020) Role of cholesterol-mediated effects in gpcr heterodimers. Chem Phys Lipid 227:104852
Risselada HJ, Marrink SJ (2009) Curvature effects on lipid packing and dynamics in liposomes revealed by coarse grained molecular dynamics simulations. Phys Chem Chem Phys 11(12):2056–2067
Risselada HJ, Kutzner C, Grubmuller H (2011) Caught in the act: visualization of SNARE-mediated fusion events in molecular detail. ChemBioChem 12(7):1049–1055
Root KT, Plucinsky SM, Glover KJ (2015) Recent progress in the topology, structure, and oligomerization of caveolin: a building block of caveolae. Curr Top Membr 75:305–336
Rothberg KG, Heuser JE, Donzell WC, Ying YS, Glenney JR, Anderson RGW (1992) Caveolin, a protein component of caveolae membrane coats. Cell 68(4):673–682
Rui H, Root KT, Lee J, Glover KJ, Im W (2014) Probing the U-shaped conformation of caveolin-1 in a bilayer. Biophys J 6(106):1371–1380
Schäfer LV, Marrink SJ (2010) Partitioning of lipids at domain boundaries in model membranes. Biophys J 99(12):L91–L93
Sengupta D (2012) Cholesterol modulates the structure, binding modes, and energetics of caveolin-membrane interactions. J Phys Chem B 116(50):14556–14564
Sengupta D, Chattopadhyay A (2012) Identification of cholesterol binding sites in the serotonin. J Phys Chem B 116(43):12991–12996
Sengupta D, Meinhold L, Langosch D, Ullmann GM, Smith JC (2005) Understanding the energetics of helical peptide orientation in membranes. Proteins 58:913–922
Sengupta D, Joshi M, Athale CA, Chattopadhyay A (2016) What can simulations tell us about gpcrs: integrating the scales. Met Cell Biol 132:429–452
Sengupta D, Prasanna X, Mohole M, Chattopadhyay A (2018) Exploring gpcr-lipid interactions by molecular dynamics simulations: excitements, challenges, and the way forward. J Phys Chem B 122(22):5727–5737
Shrestha A, Pinaud F, Haselwandter CA (2021) Mechanics of cup-shaped caveolae. Phys Rev E 104:L022401
Simón L, Campos A, Leyton L, Quest AF (2020) Caveolin-1 function at the plasma membrane and in intracellular compartments in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 39:435–453
Sinha B, Köster D, Ruez R, Gonnord P, Bastiani M, Abankwa D, Stan RV, Butler-Browne G, Vedie B, Johannes L et al (2011) Cells respond to mechanical stress by rapid disassembly of caveolae. Cell 144:402–413
Sleer LS, Brown AJ, Stanley KK (2001) Interaction of caveolin with 7-ketocholesterol. Atherosclerosis 159:49–55
Slotte JP, Ramstedt B (2007) The functional role of sphingomyelin in cell membranes. Euro J Lipid Sci Tech 109:977–981
Smart EJ, Anderson RG (2002) Alterations in membrane cholesterol that affect structure and function of caveolae. Met Enzymol 353:131–139
Smart EJ, Graf GA, Mcniven MA, Sessa WC, Engelman JA, Scherer PE, Okamoto T, Lisanti MP (1999) Caveolins, liquid-ordered domains, and signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol 19(11):7289–7304
Sodt AJ, Venable RM, Lyman E, Pastor RW (2016) Nonadditive compositional curvature energetics of lipid bilayers. Phys Rev Lett 117(13):138104
Sonnino S, Prinetti A (2009) Sphingolipids and membrane environments for caveolin. FEBS Lett 583:597–606
Sonnino S, Prioni S, Vanna C, Prinetti A (2012) Interactions between caveolin-1 and sphingolipids, and their functional relevance. Adv Exp Mol Biol 749:97–115
Srinivasan S, Zoni V, Vanni S (2021) Estimating the accuracy of the martini model towards the investigation of peripheral protein-membrane interactions. Faraday Disc 232:131–148
Stan RV (2005) Structure of caveolae. Biochim Biophys Acta - Mol Cell Res 1746:334–348
Thukral L, Sengupta D, Ramkumar A, Murthy D, Agrawal N, Gokhale RS (2015) The molecular mechanism underlying recruitment and insertion of lipid-anchored LC3 protein into membranes. Biophys J 109(10):2067–2078
Vanni S, Hirose H, Barelli H, Antonny B, Gautier R (2014) A sub-nanometre view of how membrane curvature and composition modulate lipid packing and protein recruitment. Nat Commun 5:4916
Varma M, Deserno M (2022) Joint effect of differential stress and compositional asymmetry on cholesterol distribution in lipid membranes. Biophys J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2021.11.925
Vogel A, Tan KT, Waldmann H, Feller SE, Brown MF, Huster D (2007) Flexibility of ras lipid modifications studied by 2H solid-state NMR and molecular dynamics simulations. Biophys J 93(8):2697–2712
Vogel A, Reuther G, Roark MB, Tan KT, Waldmann H, Feller SE, Huster D (2010) Backbone conformational flexibility of the lipid modified membrane anchor of the human N-Ras protein investigated by solid-state NMR and molecular dynamics simulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1798(2):275–285
Vykoukal J, Fahrmann JF, Gregg JR, Tang Z, Basourakos S, Irajizad E, Park S, Yang G, Creighton CJ, Fleury A et al (2020) Caveolin-1-mediated sphingolipid oncometabolism underlies a metabolic vulnerability of prostate cancer. Nat Comm 11:1–16
Walser PJ, Ariotti N, Howes M, Ferguson C, Webb R, Schwudke D, Leneva N, Cho KJ, Cooper L, Rae J et al (2012) Constitutive formation of caveolae in a bacterium. Cell 150:752–763
Wanaski SP, Ng BK, Glaser M (2003) Caveolin scaffolding region and the membrane binding region of src form lateral membrane domains. Biochemistry 42:42–56
Williams TM, Lisanti MP (2004) The caveolin proteins. Genome Biol 5(3):214
Yamada E (1955) The fine structure of the gall bladder epithelium of the mouse. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 1(5):445–458
Yang G, Xu H, Li Z, Li F (2014) Interactions of caveolin-1 scaffolding and intramembrane regions containing a CRAC motif with cholesterol in lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta 10:2588–2599
Yang G, Dong Z, Xu H, Wang C, Li H, Li Z, Li F (2015) Structural study of caveolin-1 intramembrane domain by circular dichroism and nuclear magnetic resonance. Biopolym - Pept Sci Sect 104:11–20
Zhou Y, Prakash P, Liang H, Cho KJ, Gorfe AA, Hancock JF (2017) Lipid-sorting specificity encoded in k-ras membrane anchor regulates signal output. Cell 168:239–251
Zhou Y, Ariotti N, Rae J, Liang H, Tillu V, Tee S, Bastiani M, Bademosi AT, Collins BM, Meunier FA et al (2021) Caveolin-1 and cavin1 act synergistically to generate a unique lipid environment in caveolae. J Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.202005138
Acknowledgements
SP gratefully acknowledges the Dept. Biotechnology (DBT, Govt. of India) for the BioCARe grant for funding. HM thanks CSIR for the junior research fellowship for pursuing his doctoral research. The authors thank Anjali Krishna for discussions. We thank members of our research group for critically reading the manuscript.
Funding
This study was partially funded by BioCARe grant from Dept. Biotechnology (DBT, Govt. of India) to SP and partially by the JRF fellowship (CSIR, Govt. of India) to HM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prakash, S., Malshikare, H. & Sengupta, D. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Caveolin-1 Mediated Membrane Curvature. J Membrane Biol 255, 225–236 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-022-00236-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-022-00236-y