Abstract
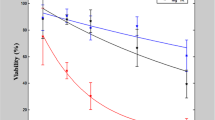
We introduced eukaryotic expression plasmid pEGFP-N1 encoding green fluorescent protein (GFP) genes into cells with different biological features through electroporation. The effects of conditions, including voltage, capacitor flow, pulse cycle, DNA dosage and buffer, on transfection efficiency were investigated based on fluorescent microscopy and posttransfection survival rate of cells by staining with trypan blue. Better electrotransfection outcomes were achieved in the following epithelial cells: Vero cells at 300 V/850 μF, PK15 cells at 300 V/500 μF, MDCK cells at 200 V/600 μF, F81 cells at 200 V/500 μF, cancer cells MB49 at 300 V/400 μF, Hela cells at 200 V/450 μF, HF-29 cells at 300 V/800 μF and B16F1 cells at 200 V/650 μF. Among fibroblast cells, better electrotransfection was achieved in BHK21 cells at 300 V/600 μF and ST cells at 200 V/750 μF. RPMI-1640 medium without antibiotics and serum demonstrated higher electrotransfection efficiency and cell survival rate than other cell culture media as electroporation buffer. Our findings further prove that electroporation transfection is an effective method for genetic transfection. Cells with different biological features require varying transfection conditions to obtain higher transfection efficiency of target genes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baron S, Poast J, Rizzo D, McFarland E, Kieff E (2000) Electroporation of antibodies, DNA, and other macromolecules into cells: a highly efficient method. J Immunol Methods 242:115–126
Baum C, Forster P, Hegewisch-Becker S, Harbers K (1994) An optimized electroporation protocol applicable to a wide range of cell lines. Biotechniques 17:1058–1062
Canatella PJ, Karr JF, Petros JA, Prausnitz MR (2001) Quantitative study of electroporation-mediated molecular uptake and cell viability. Biophys J 80:755–764
Cegovnik U, Novaković S (2004) Setting optimal parameters for in vitro electrotransfection of B16F1, SA1, LPB, SCK, L929 and CHO cells using predefined exponentially decaying electric pulses. Bioelectrochemistry 62:73–82
Gao X, Kim K-S, Liu D (2007) Nonviral gene delivery: what we know and what is next. AAPS J 9:E92–E104
Hui SW (1995) Effects of pulse length and strength on electroporation efficiency. Methods Mol Biol 55:29–40
Kawakami S, Higuchi Y, Hashida M (2008) Nonviral approaches for targeted delivery of plasmid DNA and oligonucleotide. J Pharm Sci 97:726–745
Kingston RE, Chen CA, Okayama H (2001) Calcium phosphate transfection. Current protocols in immunology. Wiley, New York
Robinson HL, Pertmer TM (2001) Nucleic acid immunizations. Current protocols in immunology. Wiley, New York
Yang W, Wang D, Cheng K, Wang M, Wang G, Hu J, Wang J (2009) Selection of electroporation condition of plasmid. Acta Medicinae Universitatis Scientiae et Technologiae Huazhong 38:858–860
Yao Y, Zhang D, Luo Y, Zhang D, Huang A, Zhou W, Ren H (2001) Influence of electroporation on the biological activities of primary rat hepatocytes. Chin J Hepatol 9:178–180
Zhang J, Zhanag X, Xie W, Shan Xiang, Lin L (2000) Survey of the highest of transformation efficiency of the competent cell. J Nanjing Normal Univ 23:72–75
Zhou Z, Zhang D, Ren H (1999) The optimal electroporation condition of recombinant plasmid. Acta Universitatis Scientiae Medicinae 24:130–132
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 31100688 and 31101838), the Foundation of Science and Technology Committee of Gansu (Grants 1102NKDA034 and 1102NKDA033) and the International Science and Technology Cooperation Program of Gansu (Grant 1104WCGA185).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Guo and R. Hao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, H., Hao, R., Wei, Y. et al. Optimization of Electrotransfection Conditions of Mammalian Cells with Different Biological Features. J Membrane Biol 245, 789–795 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-012-9480-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-012-9480-0