Abstract
Objectives: Omeprazole is metabolized mainly by CYP2C19 which has two major mutations (CYP2C19*2 in exon5 and CYP2C19*3 in exon4) associated with the poor metabolizer (PM) phenotype. The aim of this study was to examine the relationship between genetic polymorphism of CYP2C19 and metabolism of omeprazole administrated as a single dose or as repeated-doses, which were in both cases co-administered with clarithromycin.
Methods: Twelve healthy Japanese subjects were typed for CYP2C19 polymorphism. In the single-dose study, plasma levels of omeprazole and its metabolites were measured for 24 h after administration of 20 mg omeprazole and 400 mg clarithromycin to six healthy Japanese subjects. In the repeated-dose study, plasma levels of omeprazole and its metabolites were measured after repeated oral administration of 20 mg omeprazole and 400 mg clarithromycin twice daily for 6 days and then after 20 mg omeprazole and 400 mg clarithromycin once on the 7th day to the other 6 healthy Japanese subjects.
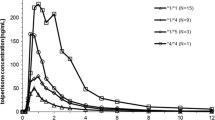
Results: In the single-dose study, the areas under the plasma concentration-versus-time curve (AUCs) of omeprazole of homozygotes for the wild-type allele (*1/*1 n = 2), heterozygotes (n = 3) for the CYP2C19*2 (*1/*2) or for the CYP2C19*3 (*1/*3) and heterozygote (n = 1) for the two defects (*2/*3) were on average 450, 1007 and 6710 ng · h−1 · ml−1, respectively. The ratios of AUCs of omeprazole/5-hydroxyomeprazole for *1/*1, *1/*2 or *1/*3 and *2/*3 were 1, 2 and 30, respectively. In the repeated-dose study, the AUCs of omeprazole for *1/*1, *1/*2 or *1/*3 and *2/*3 were 4041 (n = 2), 3149 (n = 3) and 6684 (n = 1) ng · h−1 · ml−1, respectively. The ratios of AUCs of omeprazole/5-hydroxyomeprazole for *1/*1, *1/*2 or *1/*3 and *2/*3 were 7, 11 and 30, respectively. In the repeated-dose study, the AUC of omeprazole of *1/*1 genotypes was nine-fold higher, that of *1/*2 and *1/*3 genotypes was three-fold higher, and the Cmax value of omeprazole was three-fold higher compared with subjects with the same genotype in the single-dose study. However, there were few differences in the AUC and Cmax of omeprazole between the *2/*3 genotype in the single-dose study and the homozygote for the CYP2C19*2 (*2/*2) in the repeated-dose study.
Conclusion: Subjects with *1/*1, *1/*2 and *1/*3 genotypes in the repeated-dose study had lower CYP2C19 activity than subjects of the same genotype in the single-dose study. The difference in omeprazole metabolism between subjects with different genotypes observed on day 1 seemed to disappear after 7 days of repeated-dose administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 5 June 1998 / Accepted in revised form: 27 October 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Q., Yamamoto, I., Fukuda, T. et al. CYP2C19 genotypes and omeprazole metabolism after single and repeated dosing when combined with clarithromycin. E J Clin Pharmacol 55, 43–47 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050590
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050590