Abstract
Purpose
Tocilizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to the interleukin-6 receptor. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of adding tocilizumab to disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) therapy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods
We performed a meta-analysis of relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs) identified in PubMed, Cochrane library, and Embase. The primary efficacy outcome was the proportion of patients with a 20% improvement in RA signs and symptoms according to American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria (ACR20 response). The primary safety outcomes were the proportion of patients reporting at least one adverse event and the proportion of patients reporting at least one serious adverse event.
Results
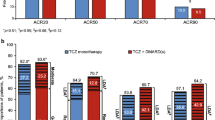
Four RCTs, involving 2701 patients, were included in our meta-analysis. The addition of tocilizumab to therapeutic regimens with DMARDs was associated both clinically and statistically with an increased number of patients achieving the ACR20 response [8 mg/kg, risk ratio (RR) 2.53, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.89–3.39; 4 mg/kg, RR 1.96, 95% CI 1.40–2.73], as well as the ACR50 and ACR70 response, and showing remission according to the Disease Activity Score based on 28 joints. However, the benefits were gained at the expense of the tendency of the patient to experience more adverse events (8 mg/kg, RR 1.12, 95% CI 1.03–1.20; 4 mg/kg, RR 1.08, 95% CI 1.00–1.17). The new finding was that the clinical benefit from the increased tocilizumab dose (from 4 to 8 mg/kg) was not correlated with a higher incidence of adverse events.
Conclusions
The superior efficacy of combined tocilizumab + DMARD therapy is associated with the tendency for the patient to have more adverse events. Consequently, the benefits and disadvantages of such combined treatments should be carefully balanced against each other in RA therapy. We suggest that 8 mg/kg every 4 weeks should be the recommended dose of tocilizumab.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott DL, Pugner K, Kaarela K, Doyle DV, Woolf A, Holmes J, Hieke K (2000) The links between joint damage and disability in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 39:122–132
Firestein GS (2003) Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 423:356–361
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Koeller M, Weisman MH, Emery P (2007) New therapies for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 370:1861–1874
Emery P, Fleischmann R, Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, Schechtman J, Szczepanski L, Kavanaugh A, Racewicz AJ, van Vollenhoven RF, Li NF, Agarwal S, Hessey EW, Shaw TM (2006) The efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate treatment: results of a phase IIB randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial. Arthritis Rheum 54:1390–1400
Jiang Y, Genant HK, Watt I, Cobby M, Bresnihan B, Aitchison R, McCabe D (2000) A multicenter, double-blind, dose-ranging, randomized, placebo-controlled study of recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: radiologic progression and correlation of Genant and Larsen scores. Arthritis Rheum 43:1001–1009
Kremer JM, Genant HK, Moreland LW, Russell AS, Emery P, Abud-Mendoza C, Szechinski J, Li T, Ge Z, Becker JC, Westhovens R (2006) Effects of abatacept in patients with methotrexate-resistant active rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 144:865–876
Lipsky PE, van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW, Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, Smolen JS, Weisman M, Emery P, Feldmann M, Harriman GR, Maini RN (2000) Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 343:1594–1602
Emery P, Salmon M (1995) Early rheumatoid arthritis: time to aim for remission? Ann Rheum Dis 54:944–947
Mierau M, Schoels M, Gonda G, Fuchs J, Aletaha D, Smolen JS (2007) Assessing remission in clinical practice. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46:975–979
Nishimoto N (2006) Interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 18:277–281
Naka T, Nishimoto N, Kishimoto T (2002) The paradigm of IL-6: from basic science to medicine. Arthritis Res 4[Suppl 3]:S233–S242
Aletaha D, Nell VP, Stamm T, Uffmann M, Pflugbeil S, Machold K, Smolen JS (2005) Acute phase reactants add little to composite disease activity indices for rheumatoid arthritis: validation of a clinical activity score. Arthritis Res Ther 7:R796–806
van Leeuwen MA, van der Heijde DM, van Rijswijk MH, Houtman PM, van Riel PL, van de Putte LB, Limburg PC (1994) Interrelationship of outcome measures and process variables in early rheumatoid arthritis. A comparison of radiologic damage, physical disability, joint counts, and acute phase reactants. J Rheumatol 21:425–429
Mihara M, Kasutani K, Okazaki M, Nakamura A, Kawai S, Sugimoto M, Matsumoto Y, Ohsugi Y (2005) Tocilizumab inhibits signal transduction mediated by both mIL-6R and sIL-6R, but not by the receptors of other members of IL-6 cytokine family. Int Immunopharmacol 5:1731–1740
Emery P, Keystone E, Tony HP, Cantagrel A, van Vollenhoven R, Sanchez A, Alecock E, Lee J, Kremer J (2008) IL-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor biologicals: results from a 24-week multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 67:1516–1523
Genovese MC, McKay JD, Nasonov EL, Mysler EF, da Silva NA, Alecock E, Woodworth T, Gomez-Reino JJ (2008) Interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab reduces disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: the tocilizumab in combination with traditional disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy study. Arthritis Rheum 58:2968–2980
Maini RN, Taylor PC, Szechinski J, Pavelka K, Bröll J, Balint G, Emery P, Raemen F, Petersen J, Smolen J, Thomson D, Kishimoto T (2006) Double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial of the interleukin-6 receptor antagonist, tocilizumab, in European patients with rheumatoid arthritis who had an incomplete response to methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum 54:2817–2829
Smolen JS, Beaulieu A, Rubbert-Roth A, Ramos-Remus C, Rovensky J, Alecock E, Woodworth T, Alten R (2008) Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial. Lancet 371:987–997
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ (1996) Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 17:1–12
Khan KS, Daya S, Jadad A (1996) The importance of quality of primary studies in producing unbiased systematic reviews. Arch Intern Med 156:661–666
Moher D, Jadad AR, Tugwell P (1996) Assessing the quality of randomized controlled trials. Current issues and future directions. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 12:195–208
Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, Bombardier C, Furst D, Goldsmith C, Katz LM, Lightfoot R Jr, Paulus H, Strand V, Tugwell P, Weinblatt M, Williams HJ, Wolfe F, Kieszak S (1995) Preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38:727–735
Prevoo ML, van’t Hof MA, Kuper HH, van Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL (1995) Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38:44–48
Sutton AJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR, Sheldon TA, Song F (2000) Methods for meta-analysis in medical research. Wiley, Chichester
Muraguchi A, Hirano T, Tang B, Matsuda T, Horii Y, Nakajima K, Kishimoto T (1988) The essential role of B cell stimulatory factor 2 (BSF-2/IL-6) for the terminal differentiation of B cells. J Exp Med 167:332–344
Lotz M, Jirik F, Kabouridis P, Tsoukas C, Hirano T, Kishimoto T, Carson DA (1988) B cell stimulating factor 2/interleukin 6 is a costimulant for human thymocytes and T lymphocytes. J Exp Med 167:1253–1258
Gauldie J, Richards C, Harnish D, Lansdorp P, Baumann H (1987) Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:7251–7255
Ishibashi T, Kimura H, Uchida T, Kariyone S, Friese P, Burstein SA (1989) Human interleukin 6 is a direct promoter of maturation of megakaryocytes in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 8:3546–3549
Papanicolaou DA, Wilder RL, Manolagas SC, Chrousos GP (1998) The pathophysiologic roles of interleukin-6 in human disease. Ann Intern Med 128:127–137
Sinigaglia L, Nervetti A, Mela Q, Bianchi G, Del Puente A, Di Munno O, Frediani B, Cantatore F, Pellerito R, Bartolone S, La Montagna G, Adami S (2000) A multicenter cross sectional study on bone mineral density in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 7:2582–2589
Bondeson J, Sundler R (1993) Antirheumatic gold compounds and penicillamine enhance protein kinase C-mediated activation of the arachidonate-mobilizing phospholipase A2 in mouse macrophages. J Leukocyte Biol 54:329–335
Choy EH, Panayi GS (2001) Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 344:907–916
Higgins J, Thompson S, Deeks J, Altman D (2002) Statistical heterogeneity in systematic reviews of clinical trials: a critical appraisal of guidelines and practice. J Health Serv Res Policy 7:51–61
Sterne JAC, Egger M (2001) Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: guidelines on choice of axis. J Clin Epidemiol 54:1046–1055
Lau J, Ioannidis JPA, Schmid CH (1997) summing up the evidence: one answer is not always enough. Lancet 351:123–127
Thompson SG (1994) Why sources of heterogeneity in meta-analysis should be investigated. Br Med J 309:1351–1355
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
Declaration of funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mao Mao An and Zui Zou contributed equally to this article and can be considered to be co-first authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, M.M., Zou, Z., Shen, H. et al. The addition of tocilizumab to DMARD therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 66, 49–59 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-009-0754-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-009-0754-0