Abstract
Purpose
To quantify the influence of common cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9) polymorphisms on warfarin dose requirements.
Methods
A systematic review and a meta-analysis, calculating the warfarin dose reduction associated with the five most common variant CYP2C9 genotypes.
Results
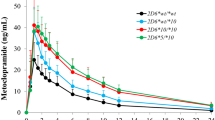
Thirty-nine studies (7,907 patients) were included in the meta-analysis. Compared to the CYP2C9*1/*1 genotype, the CYP2C9*1/*2, CYP2C9*1/*3, CYP2C9*2/*2, CYP2C9*2/*3, and CYP2C9*3/*3 required warfarin doses that were 19.6 (95% confidence interval 17.4, 21.9), 33.7 (29.4, 38.1), 36.0 (29.9, 42.0), 56.7 (49.1, 64.3), and 78.1% (72.0, 84.3) lower, respectively. The impact of CYP2C9 genotype tended to be larger in patients without interacting drugs.
Conclusions
Previous studies have rarely been powered to determine the quantitative influence of specific CYP2C9 genotypes on warfarin dose requirements. The results from our pooled analysis are likely to be the most accurate to date and the methodology could serve as a model for future pharmacogenetic meta-analyses.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wadelius M, Pirmohamed M (2007) Pharmacogenetics of warfarin: current status and future challenges. Pharmacogenomics J 7:99–111
Aithal GP, Day CP, Kesteven PJ, Daly AK (1999) Association of polymorphisms in the cytochrome P450 CYP2C9 with warfarin dose requirement and risk of bleeding complications. Lancet 353:717–719
Haining RL, Hunter AP, Veronese ME, Trager WF, Rettie AE (1996) Allelic variants of human cytochrome P450 2C9: baculovirus-mediated expression, purification, structural characterization, substrate stereoselectivity, and prochiral selectivity of the wild-type and I359L mutant forms. Arch Biochem Biophys 333:447–458
Rettie AE, Wienkers LC, Gonzalez FJ, Trager WF, Korzekwa KR (1994) Impaired (S)-warfarin metabolism catalysed by the R144C allelic variant of CYP2C9. Pharmacogenetics 4:39–42
Sullivan-Klose TH, Ghanayem BI, Bell DA, Zhang ZY, Kaminsky LS, Shenfield GM, Miners JO, Birkett DJ, Goldstein JA (1996) The role of the CYP2C9-Leu359 allelic variant in the tolbutamide polymorphism. Pharmacogenetics 6:341–349
Bax L, Yu LM, Ikeda N, Tsuruta H, Moons KG (2006) Development and validation of MIX: comprehensive free software for meta-analysis of causal research data. BMC Med Res Methodol 6:50
Anderson JL, Horne BD, Stevens SM, Grove AS, Barton S, Nicholas ZP, Kahn SF, May HT, Samuelson KM, Muhlestein JB, Carlquist JF (2007) Randomized trial of genotype-guided versus standard warfarin dosing in patients initiating oral anticoagulation. Circulation 116:2563–2570
Aquilante CL, Langaee TY, Lopez LM, Yarandi HN, Tromberg JS, Mohuczy D, Gaston KL, Waddell CD, Chirico MJ, Johnson JA (2006) Influence of coagulation factor, vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1, and cytochrome P450 2C9 gene polymorphisms on warfarin dose requirements. Clin Pharmacol Ther 79:291–302
Borgiani P, Ciccacci C, Forte V, Romano S, Federici G, Novelli G (2007) Allelic variants in the CYP2C9 and VKORC1 loci and interindividual variability in the anticoagulant dose effect of warfarin in Italians. Pharmacogenomics 8:1545–1550
Carlquist JF, Horne BD, Muhlestein JB, Lappe DL, Whiting BM, Kolek MJ, Clarke JL, James BC, Anderson JL (2006) Genotypes of the cytochrome p450 isoform, CYP2C9, and the vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 conjointly determine stable warfarin dose: a prospective study. J Thromb Thrombolysis 22:191–197
Chern HD, Ueng TH, Fu YP, Cheng CW (2006) CYP2C9 polymorphism and warfarin sensitivity in Taiwan Chinese. Clin Chim Acta 367:108–113
Cho HJ, Sohn KH, Park HM, Lee KH, Choi B, Kim S, Kim JS, On YK, Chun MR, Kim HJ, Kim JW, Lee SY (2007) Factors affecting the interindividual variability of warfarin dose requirement in adult Korean patients. Pharmacogenomics 8:329–337
Gan GG, Phipps ME, Ku CS, Teh A, Sangkar V (2004) Genetic polymorphism of the CYP2C9 subfamily of 3 different races in warfarin maintenance dose. Int J Hematol 80:295–296
Grdic M, Coen D, Zadro R (2003) Effect of cytochrome P450 CYP2C9 genotype on warfarin sensitivity. In: 4th Croatian Congress of Medical Biochemists, 24–28 September 2003, Zadar
Higashi MK, Veenstra DL, Kondo LM, Wittkowsky AK, Srinouanprachanh SL, Farin FM, Rettie AE (2002) Association between CYP2C9 genetic variants and anticoagulation-related outcomes during warfarin therapy. JAMA 287:1690–1698
Hill CE, Duncan A, Wirth D, Nolte FS (2006) Detection and identification of cytochrome P-450 2C9 alleles *1, *2, and *3 by high-resolution melting curve analysis of PCR amplicons. Am J Clin Pathol 125:584–591
Hillman MA, Wilke RA, Caldwell MD, Berg RL, Glurich I, Burmester JK (2004) Relative impact of covariates in prescribing warfarin according to CYP2C9 genotype. Pharmacogenetics 14:539–547
Khan T, Wynne H, Wood P, Torrance A, Hankey C, Avery P, Kesteven P, Kamali F (2004) Dietary vitamin K influences intra-individual variability in anticoagulant response to warfarin. Br J Haematol 124:348–354
Kimura R, Miyashita K, Kokubo Y, Akaiwa Y, Otsubo R, Nagatsuka K, Otsuki T, Okayama A, Minematsu K, Naritomi H, Honda S, Tomoike H, Miyata T (2007) Genotypes of vitamin K epoxide reductase, gamma-glutamyl carboxylase, and cytochrome P450 2C9 as determinants of daily warfarin dose in Japanese patients. Thromb Res 120:181–186
Limdi NA, McGwin G, Goldstein JA, Beasley TM, Arnett DK, Adler BK, Baird MF, Acton RT (2008) Influence of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 1173C/T genotype on the risk of hemorrhagic complications in African-American and European-American patients on warfarin. Clin Pharmacol Ther 83:312–321
Linder MW, Looney S, Adams JE III, Johnson N, Antonino-Green D, Lacefield N, Bukaveckas BL, Valdes R Jr (2002) Warfarin dose adjustments based on CYP2C9 genetic polymorphisms. J Thromb Thrombolysis 14:227–232
Loebstein R, Yonath H, Peleg D, Almog S, Rotenberg M, Lubetsky A, Roitelman J, Harats D, Halkin H, Ezra D (2001) Interindividual variability in sensitivity to warfarin–nature or nurture? Clin Pharmacol Ther 70:159–164
Margaglione M, Colaizzo D, D’Andrea G, Brancaccio V, Ciampa A, Grandone E, Di MG (2000) Genetic modulation of oral anticoagulation with warfarin. Thromb Haemost 84:775–778
Miao L, Yang J, Huang C, Shen Z (2007) Contribution of age, body weight, and CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotype to the anticoagulant response to warfarin: proposal for a new dosing regimen in Chinese patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 63:1135–1141
Millican EA, Lenzini PA, Milligan PE, Grosso L, Eby C, Deych E, Grice G, Clohisy JC, Barrack RL, Burnett RS, Voora D, Gatchel S, Tiemeier A, Gage BF (2007) Genetic-based dosing in orthopedic patients beginning warfarin therapy. Blood 110:1511–1515
Momary KM, Shapiro NL, Viana MA, Nutescu EA, Helgason CM, Cavallari LH (2007) Factors influencing warfarin dose requirements in African-Americans. Pharmacogenomics 8:1535–1544
Moridani M, Fu L, Selby R, Yun F, Sukovic T, Wong B, Cole DE (2006) Frequency of CYP2C9 polymorphisms affecting warfarin metabolism in a large anticoagulant clinic cohort. Clin Biochem 39:606–612
Mushiroda T, Ohnishi Y, Saito S, Takahashi A, Kikuchi Y, Saito S, Shimomura H, Wanibuchi Y, Suzuki T, Kamatani N, Nakamura Y (2006) Association of VKORC1 and CYP2C9 polymorphisms with warfarin dose requirements in Japanese patients. J Hum Genet 51:249–253
Muszkat M, Blotnik S, Elami A, Krasilnikov I, Caraco Y (2007) Warfarin metabolism and anticoagulant effect: a prospective, observational study of the impact of CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism in the presence of drug-disease and drug-drug interactions. Clin Ther 29:427–437
Pchelina SN, Sirotkina OV, Taraskina AE, Vavilova TV, Shwarzman AL, Schwartz EI (2005) The frequency of cytochrome P450 2C9 genetic variants in the Russian population and their associations with individual sensitivity to warfarin therapy. Thromb Res 115:199–203
Raggio V, Esperon P, Lorenzo M, Taub I, Cuesta A, Rodriguez A, Ortiz V, Kuster F, Lluberas R, Stoll M (2006) Variantes de los genes CYP2C9 y apolipoproteína E en la respuesta individual a la warfarina. Rev Urug Cardiol 21:104–116
Sconce EA, Khan TI, Wynne HA, Avery P, Monkhouse L, King BP, Wood P, Kesteven P, Daly AK, Kamali F (2005) The impact of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genetic polymorphism and patient characteristics upon warfarin dose requirements: proposal for a new dosing regimen. Blood 106:2329–2333
Scordo MG, Pengo V, Spina E, Dahl ML, Gusella M, Padrini R (2002) Influence of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 genetic polymorphisms on warfarin maintenance dose and metabolic clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther 72:702–710
Shikata E, Ieiri I, Ishiguro S, Aono H, Inoue K, Koide T, Ohgi S, Otsubo K (2004) Association of pharmacokinetic (CYP2C9) and pharmacodynamic (factors II, VII, IX, and X; proteins S and C; and gamma-glutamyl carboxylase) gene variants with warfarin sensitivity. Blood 103:2630–2635
Siguret V, Gouin I, Golmard JL, Geoffroy S, Andreux JP, Pautas E (2004) [Cytochrome P450 2C9 polymorphisms (CYP2C9) and warfarin maintenance dose in elderly patients]. Rev Med Interne 25:271–274
Spreafico M, Peyvandi F, Pizzotti D, Moia M, Mannucci PM (2003) Warfarin and acenocoumarol dose requirements according to CYP2C9 genotyping in North-Italian patients. J Thromb Haemost 1:2252–2253
Sychev DA, Mikheeva I, Kropacheva ES, Ignat’ev IV, Bulytova I, Ramenskaia GV, Dobrovol’skii AB, Panchenko EP, Kukes VG (2007) [The influence of CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of warfarin in patients with constant atrial fibrillation]. Klin Med (Mosk) 85:57–60
Takahashi H, Wilkinson GR, Nutescu EA, Morita T, Ritchie MD, Scordo MG, Pengo V, Barban M, Padrini R, Ieiri I, Otsubo K, Kashima T, Kimura S, Kijima S, Echizen H (2006) Different contributions of polymorphisms in VKORC1 and CYP2C9 to intra- and inter-population differences in maintenance dose of warfarin in Japanese, Caucasians and African-Americans. Pharmacogenet Genomics 16:101–110
Tanira MO, Al-Mukhaini MK, Al-Hinai AT, Al Balushi KA, Ahmed IS (2007) Frequency of CYP2C9 genotypes among Omani patients receiving warfarin and its correlation with warfarin dose. Community Genet 10:32–37
Taube J, Halsall D, Baglin T (2000) Influence of cytochrome P-450 CYP2C9 polymorphisms on warfarin sensitivity and risk of over-anticoagulation in patients on long-term treatment. Blood 96:1816–1819
Topic E, Stefanovic M, Samardzija M (2004) Association between the CYP2C9 polymorphism and the drug metabolism phenotype. Clin Chem Lab Med 42:72–78
Wadelius M, Sorlin K, Wallerman O, Karlsson J, Yue QY, Magnusson PK, Wadelius C, Melhus H (2004) Warfarin sensitivity related to CYP2C9, CYP3A5, ABCB1 (MDR1) and other factors. Pharmacogenomics J 4:40–48
Zhao F, Loke C, Rankin SC, Guo JY, Lee HS, Wu TS, Tan T, Liu TC, Lu WL, Lim YT, Zhang Q, Goh BC, Lee SC (2004) Novel CYP2C9 genetic variants in Asian subjects and their influence on maintenance warfarin dose. Clin Pharmacol Ther 76:210–219
Wadelius M, Chen LY, Lindh JD, Eriksson N, Ghori MJ, Bumpstead S, Holm L, McGinnis R, Rane A, Deloukas P (2008) The largest prospective warfarin-treated cohort supports genetic forecasting. Blood. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-04-149070
Li T, Chang CY, Jin DY, Lin PJ, Khvorova A, Stafford DW (2004) Identification of the gene for vitamin K epoxide reductase. Nature 427:541–544
Rieder MJ, Reiner AP, Gage BF, Nickerson DA, Eby CS, McLeod HL, Blough DK, Thummel KE, Veenstra DL, Rettie AE (2005) Effect of VKORC1 haplotypes on transcriptional regulation and warfarin dose. N Engl J Med 352:2285–2293
Rost S, Fregin A, Ivaskevicius V, Conzelmann E, Hortnagel K, Pelz HJ, Lappegard K, Seifried E, Scharrer I, Tuddenham EG, Muller CR, Strom TM, Oldenburg J (2004) Mutations in VKORC1 cause warfarin resistance and multiple coagulation factor deficiency type 2. Nature 427:537–541
Gray IC, Nobile C, Muresu R, Ford S, Spurr NK (1995) A 2.4-megabase physical map spanning the CYP2C gene cluster on chromosome 10q24. Genomics 28:328–332
Sanderson S, Emery J, Higgins J (2005) CYP2C9 gene variants, drug dose, and bleeding risk in warfarin-treated patients: a HuGEnet systematic review and meta-analysis. Genet Med 7:97–104
Acknowledgements
J.D. Lindh is supported by the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research. The project was partly supported by the Swedish Science Council (Medicine 04496), and the Swedish Drugs and Therapeutics Committee of Southwest Stockholm.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
PubMed
Warfarin as MeSH or text word was combined with each of the following search phrases:
-
MeSH
-
Cytochromes
-
Cytochrome p-450 enzyme system
-
Genotype
-
Genes
-
Genetics
-
Alleles
-
Polymorphism, genetic
-
Pharmacogenetics
-
Text words
-
Cytochrome
-
Cytochromes
-
Cytochrome-p-450
-
Cytochrome p-450
-
p-450
-
Cytochrome P450
-
Cytochrome P 450
-
cyp2c9
-
2c9
-
cyp2c
-
Genotype
-
Genotypes
-
Gene
-
Genes
-
Genetic
-
Genetics
-
Allele
-
Alleles
-
Polymorphism
-
Polymorph
-
Polymorphisms
-
Polymorphic
-
Pharmacogenetics
-
EMBASE
-
Warfarin/exp AND cytochrome p450 2c9/exp
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindh, J.D., Holm, L., Andersson, M.L. et al. Influence of CYP2C9 genotype on warfarin dose requirements—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 65, 365–375 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-008-0584-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-008-0584-5