Abstract
Objective
Increased systemic exposure of the antidepressant venlafaxine and increased risk of side effects has previously been observed in patients with defective CYP2D6 function [poor metabolisers (PMs)]. The aim of this study was to evaluate venlafaxine pharmacokinetics in carriers of one functional and one defective CYP2D6 allele [heterozygous extensive metabolisers (HEMs)].
Methods
Data was collected retrospectively from a therapeutic drug-monitoring database. All CYP-genotyped patients with steady-state serum concentration measurements of venlafaxine and metabolites were included in the study. Patients were divided in groups: *1/*1 [homozygous extensive metabolisers (EMs)], *1/*3, *4 or *5 (HEMs) and *4/*4 (PMs). Dose-adjusted serum concentrations of venlafaxine, O-desmethylvenlafaxine, N-desmethylvenlafaxine, and the metabolic ratio (O-desmethylvenlafaxine/venlafaxine) were compared between the different genotype groups.
Results
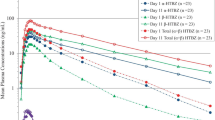
The sum of venlafaxine and O-desmethylvenlafaxine serum concentrations was not significantly different between genotype groups. Metabolic ratio was 50% lower in HEMs (n = 18) than in EMs (n = 20) (p < 0.05). Serum concentration of N-desmethylvenlafaxine was 5.5-fold higher in HEMs (p < 0.01) and 22-fold higher in PMs (p < 0.001) than in EMs.
Conclusion
The study showed a shift in the metabolic pathway resulting in substantially higher levels of N-desmethylvenlafaxine in HEMs than in EMs. The metabolic pattern of venlafaxine in HEMs was similar to previous observations in PMs and possibly represents an increased risk of venlafaxine-related side effects in HEM patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holliday SM, Benfield P (1995) Venlafaxine. A review of its pharmacology and therapeutic potential in depression. Drugs 49:280–294
Fogelman SM, Schmider J, Venkatakrishnan K, von Moltke LL, Harmatz JS, Shader RI, Greenblatt DJ (1999) O- and N-demethylation of venlafaxine in vitro by human liver microsomes and by microsomes from cDNA-transfected cells: effect of metabolic inhibitors and SSRI antidepressants. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:480–490
Otton SV, Ball SE, Cheung SW, Inaba T, Rudolph RL, Sellers EM (1996) Venlafaxine oxidation in vitro is catalysed by CYP2D6. Br J Clin Pharmacol 41:149–156
Muth EA, Haskins JT, Moyer JA, Husbands GE, Nielsen ST, Sigg EB (1986) Antidepressant biochemical profile of the novel bicyclic compound Wy-45,030, an ethyl cyclohexanol derivative. Biochem Pharmacol 35:4493–4497
Haskins JT, Moyer JA, Muth EA, Sigg EB (1985) DMI, Wy-45,030, Wy-45,881 and ciramadol inhibit locus coeruleus neuronal activity. Eur J Pharmacol 115:139–146
Lessard E, Yessine MA, Hamelin BA, O, Hara G, LeBlanc J, Turgeon J (1999) Influence of CYP2D6 activity on the disposition and cardiovascular toxicity of the antidepressant agent venlafaxine in humans. Pharmacogenetics 9:435–443
Shams ME, Arneth B, Hiemke C, Dragicevic A, Muller MJ, Kaiser R, Lackner K, Hartter S (2006) CYP2D6 polymorphism and clinical effect of the antidepressant venlafaxine. J Clin Pharm Ther 31:493–502
Fukuda T, Yamamoto I, Nishida Y, Zhou Q, Ohno M, Takada K, Azuma J (1999) Effect of the CYP2D6*10 genotype on venlafaxine pharmacokinetics in healthy adult volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 47:450–453
Bradford LD (2002) CYP2D6 allele frequency in European Caucasians, Asians, Africans and their descendants. Pharmacogenomics 3:229–243
Rudberg I, Hendset M, Uthus LH, Molden E, Refsum H (2006) Heterozygous mutation in CYP2C19 significantly increases the concentration/dose ratio of racemic citalopram and escitalopram (S-citalopram). Ther Drug Monit 28:102–105
Schaeffeler E, Schwab M, Eichelbaum M, Zanger UM (2003) CYP2D6 genotyping strategy based on gene copy number determination by TaqMan real-time PCR. Hum Mutat 22:476–485
Veefkind AH, Haffmans PM, Hoencamp E (2000) Venlafaxine serum levels and CYP2D6 genotype. Ther Drug Monit 22:202–208
Product information. Venlafaxine (Efexor). Available at www.effexorxr.com. Accessed 31 Aug 2007
Howell C, Wilson AD, Waring WS (2007) Cardiovascular toxicity due to venlafaxine poisoning in adults: a review of 235 consecutive cases. Br J Clin Pharmacol 64:192–197
Baumann P, Hiemke C, Ulrich S, Eckermann G, Gaertner I, Gerlach M, Kuss HJ, Laux G, Muller-Oerlinghausen B, Rao ML, Riederer P, Zernig G (2004) The AGNP-TDM expert group consensus guidelines: therapeutic drug monitoring in psychiatry. Pharmacopsychiatry 37:243–265
Eap CB, Lessard E, Baumann P, Brawand-Amey M, Yessine MA, O’Hara G, Turgeon J (2003) Role of CYP2D6 in the stereoselective disposition of venlafaxine in humans. Pharmacogenetics 13:39–47
Reis M, Lundmark J, Bjork H, Bengtsson F (2002) Therapeutic drug monitoring of racemic venlafaxine and its main metabolites in an everyday clinical setting. Ther Drug Monit 24:545–553
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hermann, M., Hendset, M., Fosaas, K. et al. Serum concentrations of venlafaxine and its metabolites O-desmethylvenlafaxine and N-desmethylvenlafaxine in heterozygous carriers of the CYP2D6*3, *4 or *5 allele. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 64, 483–487 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-007-0453-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-007-0453-7