Abstract
Objective
To study the effect of erythromycin on metabolism of quetiapine in Chinese suffering from schizophrenia.
Methods
Nineteen patients received multiple doses of quetiapine (200 mg, twice daily) with or without co-administered erythromycin (500 mg, three times daily). Blood samples were collected at specified time intervals for determination of plasma concentrations of quetiapine and some of its metabolites.
Results
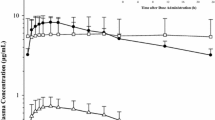
With erythromycin co-administration: for quetiapine, maximal plasma concentration (C max), area under concentration–time curve of 0–∞ h (AUC0–∞) and terminal-phase elimination half-life time (t 1/2) increased 68, 129 and 92%, respectively, and clearance (CL) and terminal elimination rate constant (K e) decreased 52% and 55%, respectively; for quetiapine sulfoxide (QTP-SF), C max, AUC0–∞ and AUC ratio decreased 64, 23, and 70%, respectively, and t 1/2 increased 211%; for 7-hydroxy-quetiapine (QTP-H), K e and AUC ratio decreased 61% and 45%, respectively, and t 1/2 increased 203%; for 7-hydroxy-N-desalkyl-quetiapine (QTP-ND), C max, AUC0–∞ and AUC ratio decreased 36, 40 and 71%, respectively.
Conclusion
Erythromycin has a noticeable effect on the metabolism of quetiapine. When quetiapine is co-administered with CYP3A inhibitors such as erythromycin, the dosing regimen should be modified according to quetiapine TDM.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
McConville BJ, Arvanitis LA, Thyrum PT, Yeh C, Wilkinson LA, Chaney RO, Foster KD, Sorter MT, Friedman LM, Brown KL, Heubi JE(2000) Pharmacokinetics, tolerability, and clinical effectiveness of quetiapine fumarate: an open-label trial in adolescents with psychotic disorders. J Clin Psychiatry 61:252–260
Arvanitis LA, Miller BG (1997) Multiple fixed doses of “Seroquel” (quetiapine) in patients with acute exacerbation of schizophrenia: a comparison with haloperidol and placebo. Biol Psychiatry 42:233–246
King DJ (1998) Drug treatment of the negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 8:33–42
Nemeroff CB, Kinkead B, Goldstein J (2002) Quetiapine: preclinical studies, pharmacokinetics, drug interactions, and dosing. J Clin Psychiatry 63(suppl 13):5–11
DeVane CL, Nemeroff CB (2001) Clinical pharmacokinetics of quetiapine: an atypical antipsychotic. Clin Pharmacokinet 40:509–522
Gefvert O, Bergstrom M, Langstrom B, Lundberg T, Lindstrom L, Yates R (1998) Time course of central nervous dopamine-D2 and 5-HT2 receptor blockade and plasma drug concentrations after discontinuation of quetiapine (Seroquel) in patients with schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 135:119–126
Dev V, Raniwalla J (2000) Quetiapine: a review of its safety in the management of schizophrenia. Drug Saf 23:295–307
Wong YW, Yeh C, Thyrum PT (2001) The effects of concomitant phenytoin administration on the steady-state pharmacokinetics of quetiapine. J Clin Psychopharmacol 21:89–93
Cooper KJ, Martin PD, Dane AL, Warwick MJ, Raza A, Schneck DW (2003) The effect of erythromycin on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 59:51–56
Psychiatry department of Chinese medical association (ed) (2001) Chinese criteria of mental disease, 3rd edn. Shandong Science & Technology Press, Jinan, pp 75–78
Li KY, Cheng ZN, Li X, Bai XL, Zhang BK, Wang F, Li HD (2004) Simultaneous determination of quetiapine and three metabolites in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography—electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Acta Pharmacol Sin 25:110–114
Acknowledgements
Thanks are due to AstraZeneca Pharmaceutical (London, UK) for providing us with pure compounds and the funds to develop this work and also to Dr. Liu Ze-Lin and Nurse Deng Meng-Xian for their clinical assistance. The experiments comply with the current laws of China in which they were performed inclusive of ethics approval.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, KY., Li, X., Cheng, ZN. et al. Effect of erythromycin on metabolism of quetiapine in Chinese suffering from schizophrenia. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 60, 791–795 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-004-0853-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-004-0853-x