Abstract
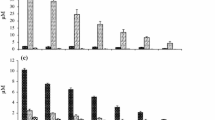
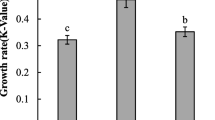
The planktonic dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea is a commonly observed bloom-forming species in estuarine and coastal waters worldwide. Large scales of A. sanguinea bloom cause the mass mortality of fish, shellfish, and sea birds. The formation of resting cysts plays as a potential vector for its wide distribution and frequent recurrence of blooms; however, the biochemical characteristics of algal cells during their life cycle remain unclear. For the first time, the variations in cellular chlorophyll a (Chl a), protein, carbohydrate, and total lipid contents during encystment of A. sanguinea cultured in different nitrate concentrations, namely 0-, 25-, 50-, 100-, 200-, and 833-μM N-added treatment, were studied in the present study. The results indicated that resting cysts were formed in all the N treatments, with the highest encystment ratio of 3.34 ± 0.57% observed in the 100-μM N-added treatment, and the lowest rate of 0.80 ± 0.03% observed in the 883-μM N-added treatment. The levels of the four biochemical components varied significantly during the encystment process. The Chl a and protein levels were significantly lower in newly formed cysts than in vegetative cells; however, continuous accumulation of carbohydrates and total lipids occurred with the algal growth, particularly of carbohydrates in the resting cysts, which was more than tenfold greater than those in the vegetative cells. Low initial N concentrations were more favorable for carbohydrate accumulation in cysts than high N concentrations. The accumulated components may play vital roles for the substance of A. sanguinea during resting stage. The results provided fundamental information for an improved understanding of the physiological response of A. sanguinea during encystment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DM, Wall D (1978) Potential importance of benthic cysts of Gonyaulax tamarensis and G. excavata in initiating toxic dinoflagellate blooms. J Phycol 14:224–234
Anderson DM, Coats D, Tyler M (1985) Encystment of the dinoflagellate Gyrodinium uncatenum: temperature and nutrient effects. J Phycol 21:200–206
Anderson DM, Taylor CD, Armbrust EV (1987) The effects of darkness and anaerobiosis on dinoflagellate cyst germination. Limnol Oceanogr 32:335–340
Badylak S, Phlips EJ, Mathews AL (2014) Akashiwo sanguinea (Dinophyceae) blooms in a sub-tropical estuary: an alga for all seasons. Plankton Benthos Res 9:147–155
Berdalet E (1992) Effects of turbulence on the marine dinoflagellate Gymnodinium nelsonii. J Phycol 28(3):267–272
Berdalet E, Latasa M, Estrada M (1994) Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus starvation on nucleic acid and protein content of Heterocapsa sp. J Plankton Res 16:303–316
Binder BJ, Anderson DM (1990) Biochemical composition and metabolic activity of Scrippsiella trochoidea (Dinophyceae) resting cysts. J Phycol 26:289–298
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911
Botes L, Smit A, Cook P (2003) The potential threat of algal blooms to the abalone (Haliotis midae) mariculture industry situated around the South African coast. Harmful Algae 2:247–259
Bravo I, Figueroa RI (2014) Towards an ecological understanding of dinoflagellate cyst functions. Microorganisms 2:11–32
Burkholder JM, Glibert PM, Skelton HM (2008) Mixotrophy, a major mode of nutrition for harmful algal species in eutrophic waters. Harmful Algae 8:77–93
Chambouvet A, Alves-de-Souza C, Cueff V, Marie D, Karpov S, Guillou L (2011) Interplay between the parasite Amoebophrya sp. (Alveolata) and the cyst formation of the red tide dinoflagellate Scrippsiella trochoidea. Protist 162:637–649
Chen T, Liu Y, Song S, Li C, Tang YZ, Yu Z (2015) The effects of major environmental factors and nutrient limitation on growth and encystment of planktonic dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea. Harmful Algae 46:62–70
D’Alessandro EB, Filho NRA (2016) Concepts and studies on lipid and pigments of microalgae: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 58:832–841
Du X, Peterson W, McCulloch A, Liu G (2011) An unusual bloom of the dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea off the central Oregon, USA, coast in autumn 2009. Harmful Algae 10:784–793
Ellegaard M, Ribeiro S (2018) The long-term persistence of phytoplankton resting stages in aquatic ‘seed banks’. Biol Rev 93:166–183
Eppley RW, Rogers JN, Mccarthy JJ (1969) Half-saturation constants for uptake of nitrate and ammonium by marine phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 14:912–920
Fidalgo JP, Cid A, Torres E, Sukenik A, Herrero C (1998) Effects of nitrogen source and growth phase on proximate biochemical composition, lipid classes and fatty acid profile of the marine microalga Isochrysis galbana. Aquaculture 166:105–116
Figueroa RI, Bravo I, Garcés E, Ramilo I (2006) Nuclear features and effect of nutrients on Gymnodinium catenatum (Dinophyceae) sexual stages. J Phycol 42:67–77
Guillard RRL, Ryther JH (1962) Studies of marine planktonic diatoms: I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (Cleve) Gran. Can J Microbiol 8:229–239
Hallegraeff GM (1992) Harmful algal blooms in the Australian region. Mar Pollut Bull 25:186–190
Harrison PJ, Thompson PA, Calderwood GS (1990) Effects of nutrient and light limitation on the biochemical composition of phytoplankton. J Appl Phycol 2:45–56
Heikkilä M, Pospelova V, Forest A, Stern GA, Fortier L, Macdonald RW (2016) Dinoflagellate cyst production over an annual cycle in seasonally ice-covered Hudson Bay. Mar Micropaleontol 125:1–24
Hitchcock GL (1982) A comparative study of the size-dependent organic composition of marine diatoms and dinoflagellates. J Plankton Res 4:363–377
Horner RA, Garrison DL, Plumley FG (1997) Harmful algal blooms and red tide problems on the US west coast. Limnol Oceanogr 42:1076–1088
Jessup DA, Miller MA, Ryan JP, Nevins HM, Kerkering HA, Mekebri A, Crane DB, Johnson TA, Kudela RM (2009) Mass stranding of marine birds caused by a surfactant-producing red tide. PLoS One 4:e4550
Kochert G (1978) Quantitation of the macromolecular components of microalgae. In: Hellebust JA, Craigie JS (eds) Handbook of physiological methods: physiological and biochemical methods. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 190–195
Koening ML, Flores Montes MJ, Eskinazi Leca E, Tiburcio ASXS (2014) New record of Akashiwo sanguinea (Dinophyta) in the tropical estuarine waters of Northeastern Brazil (Western Atlantic). Braz J Biol 74:191–198
Lai J, Yu Z, Song X, Cao X, Han X (2011) Responses of the growth and biochemical composition of Prorocentrum donghaiense to different nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 405:6–17
Latasa M, Berdalet E (1994) Effect of nitrogen or phosphorus starvation on pigment composition of cultured Heterocapsa sp. J Plankton Res 16:83–94
Liu Y, Chen T, Song S, Li C (2015) Effects of nitrogenous nutrition on growth and nitrogen assimilation enzymes of dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea. Harmful Algae 50:99–106
Lu S, Hodgkiss IJ (2004) Harmful algal bloom causative collected from Hong Kong waters. Hydrobiologia 512:231–238
Lundgren V, Granéli E (2011) Influence of altered light conditions and grazers on Scrippsiella trochoidea (Dinophyceae) cyst formation. Aquat Microb Ecol 63:231–243
Luo Z, Yang W, Leaw CP, Pospelova V, Bilien G, Liow GR, Lim PT, Gu H (2017) Cryptic diversity within the harmful dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea in coastal Chinese waters is related to differentiated ecological niches. Harmful Algae 66:88–96
Mansour MP, Volkman JK, Blackburn SI (2003) The effect of growth phase on the lipid class, fatty acid and sterol composition in the marine dinoflagellate, Gymnodinium sp. in batch culture. Phytochemistry 63:145–153
Matsubara T, Nagasoe S, Yamasaki Y, Shikata T, Shimasaki Y, Oshima Y, Honjo T (2007) Effects of temperature, salinity, and irradiance on the growth of the dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 342:226–230
Menden-Deuer S, Montalbano AL (2015) Bloom formation potential in the harmful dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea: clues from movement behaviors and growth characteristics. Harmful Algae 47:75–85
O’Boyle S, McDermott G (2014) Observations of a thin near surface layer in an estuarine environment: an exceptional bloom of the dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea in the Lee estuary (Lough Mahon), Co., Cork, in September 2010. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 101:244–248
Persson A, Smith BC, Cyronak T, Cooper E, Ditullio GR (2016) Differences in pigmentation between life cycle stages in Scrippsiella lachrymosa (Dinophyceae). J Phycol 52:64–74
Phlips EJ, Badylak S, Christman M, Wolny J, Brame J, Garland J, Hall L, Hart J, Landsberg J, Lasi M, Lockwood J, Paperno R, Scheidt D, Staples A, Steidinger K (2011) Scales of temporal and spatial variability in the distribution of harmful algae species in the Indian River Lagoon, Florida, USA. Harmful Algae 10:277–290
Rengefors K, Anderson DM (1998) Environmental and endogenous regulation of cyst germination in two freshwater dinoflagellates. J Phycol 34:568–577
Shumway SE (1990) A review of the effects of algal blooms on shellfish and aquaculture. J World Aquac Soc 21:65–104
Smida DB, Sahraoui I, Grami B, Mabrouk HH, Hlaili AS (2014) Population dynamics of potentially harmful algal blooms in Bizerte Lagoon, Tunisia. Afr J Aquat Sci 39:177–188
Steidinger KA, Tangen K (1996) Chapter 3: Dinoflagellates. In: Tomas CR (ed) Identifying marine diatoms and dinoflagellates. Academic, California, pp 387–584
Strickland JDH, Parsons TR (1972) A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Fish. Res. Board Can., The Alger Press Ltd, Ottawa, p 310
Susan B, Edward JP, Ashley LM, Karen K (2017) In situ observations of Akashiwo sanguinea (Dinophyceae) displaying life cycle stages during blooms in a subtropical estuary. Bot Mar 60:653–664
Tang YZ, Gobler CJ (2015) Sexual resting cyst production by the dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea: a potential mechanism contributing toward the ubiquitous distribution of a harmful alga. J Phycol 51:298–309
Uchida T (2001) The role of cell contact in the life cycle of some dinoflagellate species. J Plankton Res 23:889–891
Voltolina D (1993) The origin of recurrent blooms of Gymnodinium sanguineum Hirasaka in a shallow coastal lagoon. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 168:217–222
White AE, Watkins-Brandt KS, McKibben SM, Wood AM, Hunter M, Forster Z, Du XN, Peterson WT (2014) Large-scale bloom of Akashiwo sanguinea in the Northern California current system in 2009. Harmful Algae 37:38–46
Yang C, Li Y, Zhou Y, Zheng W, Tian Y, Zheng T (2012) Bacterial community dynamics during a bloom caused by Akashiwo sanguinea in the Xiamen Sea Area, China. Harmful Algae 20:132–141
Zhao Y, Yu Z, Song X, Cao X (2009) Biochemical compositions of two dominant bloom-forming species isolated from the Yangtze river estuary in response to different nutrient conditions. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 382:30–36
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, Grant No. 41506141), National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2017YFC1404300), the Youth Talent Support Program of the Laboratory for Marine Ecology and Environmental Science, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao, Grant No. LMEES-YTSP-2018-01-06), and the NSFC-Shandong Joint Fund for Marine Science Research Center (Grant No. U1606404).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: S. Shumway.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Reviewed by Undisclosed experts.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Chen, T., Song, S. et al. Variation in biochemical composition during encystment of the planktonic dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea in N-limited cultures. Mar Biol 166, 120 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-019-3569-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-019-3569-2