Abstract
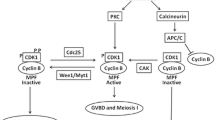
Marine invertebrates are a major source of bioactive natural products, many of which are produced by associated microbes. These compounds protect the invertebrate host against predators, competitors, or pathogens by affecting the cellular processes of the host’s adversary, but knowledge about the interaction of the host itself with these symbiont-produced natural products is limited. For example, larvae of the marine bryozoan, Bugula neritina, are defended from predation by the bryostatins, polyketides synthesized by its uncultured endosymbiont, “Candidatus Endobugula sertula.” Bryostatins are potent modulators of the eukaryotic signaling protein, protein kinase C (PKC) that is involved in many cellular processes. In this study, we investigated how host reproduction responds to the absence of the symbiont and symbiont-produced bryostatins in colonies after antibiotic curing and in colonies with naturally reduced symbiont titers. The fecundity of the symbiont-reduced B. neritina colonies was significantly decreased, suggesting that host reproduction is dependent on the symbiont, and/or the bryostatins they produce. To assess the role of PKC in this response, Western blot analysis of protein extracts from symbiotic and symbiont-reduced B. neritina colonies revealed a difference in bryostatin-activated conventional PKCs, but none for bryostatin-independent PKCs. Similar results were observed for PKCs in symbiotic and naturally occurring symbiont-reduced colonies, as well as in the model invertebrate, Caenorhabditis elegans, exposed to bryostatin, suggesting that the bryostatins potentially modulate PKC activity in symbiotic B. neritina and bryostatin-exposed C. elegans. Analysis of the B. neritina transcriptome led to the identification of five PKC isozymes. Since PKCs have been reported to be involved in regulation of reproductive processes and oocyte maturation in various organisms, the findings of this study suggest that the symbiont-produced bryostatins are an important cue for reproduction in the host B. neritina via PKC activation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberdam E, Dekel N (1985) Activators of protein kinase C stimulate meiotic maturation of rat oocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 132:570–574. doi:10.1016/0006-291x(85)91171-4
Akita Y (2008) Protein kinase Cε: multiple roles in the function of, and signaling mediated by, the cytoskeleton. FEBS J 275:3995–4004. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06557.x
Ashen JB, Goff LJ (2000) Molecular and ecological evidence for species specificity and coevolution in a group of marine algal-bacterial symbioses. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3024–3030
Bertness MD, Garrity SD, Levings SC (1981) Predation pressure and gastropod foraging: a tropical-temperate comparison. Evolution 35:995–1007
Blunt JW, Copp BR, Keyzers RA, Munro MH, Prinsep MR (2013) Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep 30:237–323
Blunt JW, Copp BR, Keyzers RA, Munro MH, Prinsep MR (2014) Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep 31:160–258
Blunt JW, Copp BR, Keyzers RA, Munro MH, Prinsep MR (2015) Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep 32:116–211
Carle KJ, Ruppert E (1983) Comparative ultrastructure of the bryozoan funiculus: a blood vessel homologue. J Zool Syst Evol Res 21:181–193
Chaston J, Goodrich-Blair H (2010) Common trends in mutualism revealed by model associations between invertebrates and bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:41–58. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00193.x
Clamp A, Jayson GC (2002) The clinical development of the bryostatins. Anticancer Drugs 13:673–683
Colas P, Dube F (1998) Meiotic maturation in mollusc oocytes. Semin Cell Dev Biol 9:539–548. doi:10.1006/scdb.1998.0248
Cragg GM, Newman DJ (2013) Natural products: a continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1830:3670–3695. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.02.008
Crawford JM, Clardy J (2011) Bacterial symbionts and natural products. Chem Commun 47:7559–7566. doi:10.1039/c1cc11574j
Davidson SK, Haygood MG (1999) Identification of sibling species of the bryozoan Bugula neritina that produce different anticancer bryostatins and harbor distinct strains of the bacterial symbiont “Candidatus Endobugula sertula”. Biol Bull 196:273–280
Davidson SK, Allen SW, Lim GE, Anderson CM, Haygood MG (2001) Evidence for the biosynthesis of bryostatins by the bacterial symbiont “Candidatus Endobugula sertula” of the bryozoan Bugula neritina. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4531–4537
De Vries DJ, Herald CL, Pettit GR, Blumberg PM (1988) Demonstration of sub-nanomolar affinity of bryostatin 1 for the phorbol ester receptor in rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 37:4069–4073
Dedeine F, Vavre F, Fleury F, Loppin B, Hochberg ME, Bouletreau M (2001) Removing symbiotic Wolbachia bacteria specifically inhibits oogenesis in a parasitic wasp. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6247–6252. doi:10.1073/pnas.101304298
Dube F, Golsteyn R, Dufresne L (1987) Protein kinase C and meiotic maturation of surf clam oocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 142:1072–1076. doi:10.1016/0006-291x(87)91524-5
Eckberg WR (1988) Intracellular signal transduction and amplification mechanisms in the regulation of oocyte maturation. Biol Bull 174:95–108. doi:10.2307/1541777
Eckberg WR, Carroll AG (1987) Evidence for involvement of protein kinase C in germinal vesicle breakdown in Chaetopterus. Dev Growth Differ 29:489–496
Eckberg WR, Szuts EZ, Carroll AG (1987) Protein kinase C activity, protein phosphorylation and germinal vesicle breakdown in Spisula oocytes. Dev Biol 124:57–64. doi:10.1016/0012-1606(87)90459-3
Eckberg WR, Johnson MR, Palazzo RE (1996) Regulation of maturation-promoting factor by protein kinase C in Chaetopterus oocytes. Invertebr Reprod Dev 30:71–79. doi:10.1080/07924259.1996.9672533
Engelstaedter J, Hurst GDD (2009) The ecology and evolution of microbes that manipulate host reproduction. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 40:127–149. doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.110308.120206
Fehlauer-Ale KH, Mackie JA, Lim-Fong GE, Ale E, Pie MR, Waeschenbach A (2014) Cryptic species in the cosmopolitan Bugula neritina complex (Bryozoa, Cheilostomata). Zool Scr 43:193–205. doi:10.1111/zsc.12042
Gerwick WH, Moore BS (2012) Lessons from the past and charting the future of marine natural products drug discovery and chemical biology. Chem Biol 19:85–98. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.12.014
Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, Adiconis X, Fan L, Raychowdhury R, Zeng Q, Chen Z, Mauceli E, Hacohen N, Gnirke A, Rhind N, di Palma F, Birren BW, Nusbaum C, Lindblad-Toh K, Friedman N, Regev A (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol 29:644–652. doi:10.1038/nbt.1883
Haygood MG, Davidson SK (1997) Small-subunit rRNA genes and in situ hybridization with oligonucleotides specific for the bacterial symbionts in the larvae of the bryozoan Bugula neritina and proposal of “Candidatus endobugula sertula”. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4612–4616
Haygood MG, Schmidt EW, Davidson SK, Faulkner DJ (1999) Microbial symbionts of marine invertebrates: opportunities for microbial biotechnology. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 1:33–43
Joyce SA, Brachmann AO, Glazer I, Lango L, Schwaer G, Clarke DJ, Bode HB (2008) Bacterial biosynthesis of a multipotent stilbene. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:1942–1945. doi:10.1002/anie.200705148
Kalive M, Faust JJ, Koeneman BA, Capco DG (2010) Involvement of the PKC family in regulation of early development. Mol Reprod Dev 77:95–104. doi:10.1002/mrd.21112
Kaltenpoth M, Roeser-Mueller K, Koehler S, Peterson A, Nechitaylo TY, Stubblefield JW, Herzner G, Seger J, Strohm E (2014) Partner choice and fidelity stabilize coevolution in a Cretaceous-age defensive symbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:6359–6364. doi:10.1073/pnas.1400457111
Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A, Stones-Havas S, Cheung M, Sturrock S, Buxton S, Cooper A, Markowitz S, Duran C, Thierer T, Ashton B, Meintjes P, Drummond A (2012) Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 28:1647–1649. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bts199
Keough MJ (1989) Variation in growth rate and reproduction of the bryozoan Bugula neritina. Biol Bull 177:277–286. doi:10.2307/1541942
Kimura K, Mizutani MY, Tomioka N, Endo Y, Shudo K, Itai A (1999) Docking study of bryostatins to protein kinase C δ Cys2 domain. Chem Pharm Bull 47:1134–1137
Kraft AS, Smith JB, Berkow RL (1986) Bryostatin, an activator of the calcium phospholipid-dependent protein kinase, blocks phorbol ester-induced differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells HL-60. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:1334–1338
Kraft A, Reeves J, Ashendel C (1988) Differing modulation of protein kinase C by bryostatin 1 and phorbol esters in JB6 mouse epidermal cells. J Biol Chem 263:8437–8442
Kwon HB, Lee WK (1991) Involvement of protein kinase c in the regulation of oocyte maturation in amphibians Rana dybowskii. J Exp Zool 257:115–123. doi:10.1002/jez.1402570115
Lackner G, Moebius N, Hertweck C (2011) Endofungal bacterium controls its host by an hrp type III secretion system. ISME J 5:252–261. doi:10.1038/ismej.2010.126
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X Version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Lew KK, Chritton S, Blumberg PM (1982) Biological responsiveness to the phorbol esters and specific binding of [3H]phorbol 12, 13-dibutyrate in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, a manipulable genetic system. Teratog Carcinog Mutagen 2:19–30
Lindquist N (1996) Palatability of invertebrate larvae to corals and sea anemones. Mar Biol 126:745–755
Lindquist N, Hay ME (1996) Palatability and chemical defense of marine invertebrate larvae. Ecol Monogr 66:431–450
Linneman J, Paulus D, Lim-Fong G, Lopanik NB (2014) Latitudinal variation of a defensive symbiosis in the Bugula neritina (Bryozoa) sibling species complex. PLoS One 9:e108783
Lopanik NB (2014) Chemical defensive symbioses in the marine environment. Funct Ecol 28:328–340. doi:10.1111/1365-2435.12160
Lopanik N, Gustafson KR, Lindquist N (2004a) Structure of bryostatin 20: a symbiont-produced chemical defense for larvae of the host bryozoan, Bugula neritina. J Nat Prod 67:1412–1414
Lopanik N, Lindquist N, Targett N (2004b) Potent cytotoxins produced by a microbial symbiont protect host larvae from predation. Oecologia 139:131–139
Mathew M, Lopanik NB (2014) Host differentially expressed genes during association with its defensive endosymbiont. Biol Bull 226:152–163
McFall-Ngai M, Hadfield MG, Bosch TCG, Carey HV, Domazet-Loso T, Douglas AE, Dubilier N, Eberl G, Fukami T, Gilbert SF, Hentschel U, King N, Kjelleberg S, Knoll AH, Kremer N, Mazmanian SK, Metcalf JL, Nealson K, Pierce NE, Rawls JF, Reid A, Ruby EG, Rumpho M, Sanders JG, Tautz D, Wernegreen JJ (2013) Animals in a bacterial world, a new imperative for the life sciences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:3229–3236. doi:10.1073/pnas.1218525110
McGovern TM, Hellberg ME (2003) Cryptic species, cryptic endosymbionts, and geographical variation in chemical defences in the bryozoan Bugula neritina. Mol Ecol 12:1207–1215
Menge BA, Lubchenco J (1981) Community organization in temperate and tropical rocky intertidal habitats: prey refuges in relation to consumer pressure gradients. Ecol Monogr 51:429–450
Miwa J, Tabuse Y, Furusawa M, Yamasaki H (1982) Tumor promoters specifically and reversibly disturb development and behavior of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 104:81–87
Miyake Y, Yasui M, Ikeda K, Kondo T, Tsukamoto S, Hori C, Okemoto N, Mashou K, Bando R, Nakamura N (2009) Molecular cloning and expression of starfish protein kinase C Isoforms. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:1550–1560
Mondadori RG, Neves JP, Goncalves PBD (2008) Protein kinase C (PKC) role in bovine oocyte maturation and early embryo development. Anim Reprod Sci 107:20–29. doi:10.1016/j.anireprosci.2007.06.015
Moosbrugger M, Schwaha T, Walzl MG, Obst M, Ostrovsky AN (2012) The placental analogue and the pattern of sexual reproduction in the cheilostome bryozoan Bicellariella ciliata (Gymnolaemata). Front Zool. doi:10.1186/1742-9994-9-29
Moran NA (2006) Symbiosis. Curr Biol 16:R866–R871
Mutter R, Wills M (2000) Chemistry and clinical biology of the bryostatins. Bioorg Med Chem 8:1841–1860
Newman DJ, Cragg GM (2007) Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod 70:461–477. doi:10.1021/np068054v
Newton AC (1995) Protein kinase C: structure, function, and regulation. J Biol Chem 270:28495–28498
Newton AC (2001) Protein kinase C: structural and spatial regulation by phosphorylation, cofactors, and macromolecular interactions. Chem Rev 101:2353–2364
Nishizuka Y (1984) The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumor promotion. Nature 308:693–698. doi:10.1038/308693a0
Pannebakker BA, Loppin B, Elemans CPH, Humblot L, Vavre F (2007) Parasitic inhibition of cell death facilitates symbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:213–215. doi:10.1073/pnas.0607845104
Partida-Martinez LP, Hertweck C (2005) Pathogenic fungus harbours endosymbiotic bacteria for toxin production. Nature 437:884–888
Partida-Martinez LP, Monajembashi S, Greulich KO, Hertweck C (2007) Endosymbiont-dependent host reproduction maintains bacterial-fungal mutualism. Curr Biol 17:773–777
Pettit GR (1996) Progress in the discovery of biosynthetic anticancer drugs. J Nat Prod 59:812–821
Pettit GR, Day JF, Hartwell JL, Wood HB (1970) Antineoplastic components of marine animals. Nature 227:962–963
Pettit GR, Herald CL, Doubek DL, Herald DL (1982) Isolation and structure of bryostatin 1. J Am Chem Soc 104:6846–6848
Piel J (2009) Metabolites from symbiotic bacteria. Nat Prod Rep 26:338–362. doi:10.1039/b703499g
Reed C (1991) Bryozoa. In: Giese ACPJ, Pearse VB (eds) Reproduction of marine invertebrates. The Boxwood Press, Pacific Grove, pp 85–245
Rose-Hellekant TA, Bavister BD (1996) Roles of protein kinase A and C in spontaneous maturation and in forskolin or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine maintained meiotic arrest of bovine oocytes. Mol Reprod Dev 44:241–249. doi:10.1002/(sici)1098-2795(199606)44:2<241:aid-mrd14>3.0.co;2-5
Ruby EG (2008) Symbiotic conversations are revealed under genetic interrogation. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:752–762. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1958
Sano T, Tabuse Y, Nishiwaki K, Miwa J (1995) The tpa-1 gene of Caenorhabditis elegans encodes two proteins similar to Ca2+-independent protein kinase Cs: evidence by complete genomic and complementary DNA sequences of the tpa-1 gene. J Mol Biol 251:477–485. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1995.0449
Schmidt EW (2008) Trading molecules and tracking targets in symbiotic interactions. Nat Chem Biol 4:466–473. doi:10.1038/nchembio.101
Schmitt I, Partida-Martinez LP, Winkler R, Voigt K, Einax E, Doelz F, Telle S, Woestemeyer J, Hertweck C (2008) Evolution of host resistance in a toxin-producing bacterial-fungal alliance. ISME J 2:632–641. doi:10.1038/ismej.2008.19
Sharp KH, Davidson SK, Haygood MG (2007) Localization of ‘Candidatus Endobugula sertula’ and the bryostatins throughout the life cycle of the bryozoan Bugula neritina. ISME J 1:693–702. doi:10.1038/ismej.2007.78
Stith BJ, Maller JL (1987) Induction of meiotic maturation in Xenopus oocytes by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate. Exp Cell Res 169:514–523. doi:10.1016/0014-4827(87)90211-4
Stouthamer R, Breeuwer JAJ, Hurst GDD (1999) Wolbachia pipientis: microbial manipulator of arthropod reproduction. Annu Rev Microbiol 53:71–102. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.53.1.71
Strauch O, Ehlers RU (1998) Food signal production of Photorhabdus luminescens inducing the recovery of entomopathogenic nematodes Heterorhabditis spp. in liquid culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50:369–374
Sudek S, Lopanik NB, Waggoner LE, Hildebrand M, Anderson C, Liu H, Patel A, Sherman DH, Haygood MG (2007) Identification of the putative bryostatin polyketide synthase gene cluster from “Candidatus Endobugula sertula”, the uncultivated microbial symbiont of the marine bryozoan Bugula neritina. J Nat Prod 70:67–74
Tabuse Y, Miwa J (1983) A gene involved in action of tumor promoters is identified and mapped in Caenorhabditis elegans. Carcinogenesis 4:783–786
Tabuse Y, Nishiwaki K, Miwa J (1989) Mutations in a protein kinase C homolog confer phorbol ester resistance on Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 243:1713–1716
Tabuse Y, Sano T, Nishiwaki K, Miwa J (1995) Molecular evidence for the direct involvement of a protein kinase C in developmental and behavioural susceptibility to tumour-promoting phorbol esters in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem J 312:69–74
Tamburri MN, Zimmer-Faust RK (1996) Suspension feeding: basic mechanisms controlling recognition and ingestion of larvae. Limnol Oceanogr 41:1188–1197
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst197
Thacker RW, Starnes S (2003) Host specificity of the symbiotic cyanobacterium Oscillatoria spongeliae in marine sponges, Dysidea spp. Mar Biol 142:643–648
Trindade-Silva AE, Lim-Fong GE, Sharp KH, Haygood MG (2010) Bryostatins: biological context and biotechnological prospects. Curr Opin Biotechnol 21:834–842. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2010.09.018
Vermeij GJ (1978) Biogeography and adaptation: patterns of marine life. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Wender PA, Cribbs CM, Koehler KF, Sharkey NA, Herald CL, Kamano Y, Pettit GR, Blumberg PM (1988) Modeling of the bryostatins to the phorbol ester pharmacophore on protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci 85:7197–7201
Wender PA, Baryza JL, Brenner SE, DeChristopher BA, Loy BA, Schrier AJ, Verma VA (2011) Design, synthesis, and evaluation of potent bryostatin analogs that modulate PKC translocation selectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:6721–6726
Werren JH, Baldo L, Clark ME (2008) Wolbachia: master manipulators of invertebrate biology. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:741–751. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1969
Woollacott R (1981) Association of bacteria with bryozoan larvae. Mar Biol 65:155–158
Woollacott RM, Zimmer RL (1975) A simplified placenta like system for the transport of extraembryonic nutrients during embryogenesis of Bugula neritina (bryozoa). J Morphol 147:355–377
Zchori-Fein E, Borad C, Harari AR (2006) Oogenesis in the date stone beetle, Coccotrypes dactyliperda, depends on symbiotic bacteria. Physiol Entomol 31:164–169. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3032.2006.00504.x
Acknowledgments
We thank Niels Lindquist (the University of North Carolina–Chapel Hill’s Institute of Marine Sciences) for allowing us generous use of both wet and dry laboratory facilities. We thank Casonya M. Johnson for guidance with the C. elegans experiments. We thank Lesley-Ann Hawthorn, Sam Chang, and the staff at the Integrated Genomics Facility, Georgia Regents University Cancer Center, for assistance in preparation and sequencing of cDNA library. We also thank Michelle Ventura and Jonathan Linneman for aid in collection of B. neritina colonies and experimental data. We would also like to thank two reviewers for their comments that significantly improved the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Georgia State University Research Foundation start-up funds and Illumina/GRU Cancer Center RNA-Seq program Grant to N.B.L.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Responible Editor: D. Gochfield.
Reviewed by L. Santiago-Vazquez and an undisclosed expert.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mathew, M., Bean, K.I., Temate-Tiagueu, Y. et al. Influence of symbiont-produced bioactive natural products on holobiont fitness in the marine bryozoan, Bugula neritina via protein kinase C (PKC). Mar Biol 163, 44 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-016-2818-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-016-2818-x