Abstract
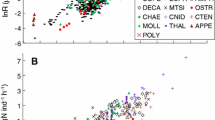
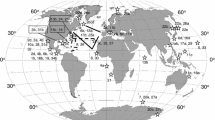
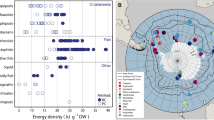
Respiration and ammonia excretion rates of 19–24 euphausiids from the epipelagic through bathypelagic zones of the world’s oceans were compiled. Body mass (expressed in terms of dry mass, carbon or nitrogen), habitat temperature and sampling depth were designated as parameters in multiple regression analysis. Results suggested that the three parameters were highly significant, contributing 71–89 % of the variance in respiration rates and 69–81 % of the variance in ammonia excretion rates. Atomic O:N ratios derived from simultaneous measurements of respiration and ammonia excretion rates ranged from 11 to 90 (median: 27), and no appreciable effects of the three parameters on O:N ratios were detected. If global-bathymetric models for the metabolism and chemical composition of copepods and chaetognaths are compared with those of euphausiids, it becomes evident that euphausiids are unique in that they maintain high metabolic rates and accumulate moderate amounts of energy reserves (lipids).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Båmstedt U (1986) Chemical composition and energy content. In: Corner EDS, O’Hara SCM (eds) The biological chemistry of marine copepods. Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 1–58
Brinton E (1967) Vertical migration and avoidance capability of euphausiids in the California Current. Limnol Oceanogr 12:451–483
Brown JH, Gillooly JF, Allen AP, Savage VM, West GB (2004) Toward a metabolic theory of ecology. Ecology 85:1771–1789
Childress JJ (1975) The respiratory rates of midwater crustaceans as a function of depth occurrence and relation to the oxygen minimum layer off Southern California. Comp Biochem Physiol A 50:787–799
Childress JJ (1995) Are there physiological and biochemical adaptation of metabolism in deep-sea animals? Trends Ecol Evol 10:30–36
Childress JJ, Nygaard M (1973) The chemical composition of midwater fishes as a function of depth of occurrence off southern California. Deep-Sea Res 20:1093–1109
Childress JJ, Nygaard M (1974) The chemical composition and relative buoyancy of midwater crustaceans as a function of depth off Southern California. Mar Biol 27:225–238
Clarke A (1987) The adaptation of aquatic animals to low temperatures. In: Grout BWW, Morris GJ (eds) The effects of low temperatures on biological systems. Edward Arnold, London, pp 315–348
Clarke A, Johnston NM (1999) Scaling of metabolic rate with body mass and temperature in teleost fish. J Anim Ecol 68:893–905
Clarke A, Morris DJ (1983) Towards an energy budget for kirll: the physiology and biochemistry of Eupahusia superba Dana. Polar Biol 2:69–86
Conover RJ, Corner EDS (1968) Respiration and nitrogen excretion by some marine zooplankton in relation to their life cycles. J Mar Biol Ass UK 48:49–75
Cowles DL, Childress JJ, Wells ME (1991) Metabolic rates of midwater crustaceans as a function of depth of occurrence off the Hawaii Islands: food availability as a selective factor? Mar Biol 110:75–83
Davenport J, Trueman ER (1985) Oxygen uptake and buoyancy in zooplanktonic organisms from the tropical eastern Atlantic. Comp Biochem Physiol 81A:857–863
Donnelly J, Torres JJ (1988) Oxygen consumption of midwater fishes and crustaceans from the eastern Gulf of Mexico. Mar Biol 97:483–494
Gillooly JF, Brown JH, West GB, Savage VM, Charnov EL (2001) Effects of size and temperature on metabolic rate. Science 293:2248–2251
Harvey HR, Pleuthner RL, Lessard EJ, Bernhardt MJ, Shaw CT (2012) Physical and biochemical properties of the euphausiids Thysanoessa inermis, Thysanoessa raschii, and Thysanoessa longipes in the eastern Bering Sea. Deep-Sea Res II 65–70:173–183
Hidaka K, Kawaguchi K, Murakami M, Takahashi M (2001) Downward transport of organic carbon by diel migratory micronekton in the western equatorial Pacific: its quantitative importance. Deep-Sea Res I 48:1923–1939
Hirche H-J (1984) Temperature and metabolism of plankton-I. Respiration of Antarctic zooplankton at different temperatures with a comparison of Antarctic and Nordic krill. Comp Biochem Physiol 77A:361–368
Iguchi N, Ikeda T (1995) Growth, metabolism and growth efficiency of a euphausiid crustacean Euphausia pacifica in the southern Japan Sea, as influenced by temperature. J Plankton Res 17:1757–1769
Ikeda T (1974) Nutritional ecology of marine zooplankton. Mem Fac Fish Hokkaido Univ 22:1–97
Ikeda T (1985) Metabolic rates of epipelagic marine zooplankton as a function of body mass and temperature. Mar Biol 85:1–11
Ikeda T (1988) Metabolism and chemical composition of crustaceans from the Antarctic mesopelagic zone. Deep-Sea Res 35:1991–2002
Ikeda T (2012) Metabolism and chemical composition of zooplankton from 500 to 5,000 m depth of the western subarctic Pacific Ocean. J Oceanogr
Ikeda T, Bruce B (1986) Metabolic activity and elemental composition of krill and other zooplankton from Prydz Bay, Antarctica, during early summer (November-December). Mar Biol 92:545–555
Ikeda T, Dixon P (1984) The influence of feeding on the metabolic activity of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba Dana). Polar Biol 3:1–9
Ikeda T, Kirkwood R (1989) Metabolism and elemental composition of a giant chaetognath Sagitta gazellae from the Southern Ocean. Mar Biol 100:261–267
Ikeda T, Mckinnon DA (2012) Metabolism and chemical composition of zooplankton and hyperbenthos from the Great Barrier Reef waters, North Queensland, Australia. Plankton Benthos Res 7:8–19
Ikeda T, Mitchell AW (1982) Oxygen uptake, ammonia excretion, and phosphate excretion of krill and other Antarctic zooplankton, in relation to their body size and chemical composition. Mar Biol 71:283–298
Ikeda T, Skjoldal HR (1989) Metabolism and elemental composition of zooplankton from the Barents Sea during early arctic summer. Mar Biol 100:173–183
Ikeda T, Takahashi T (2012) Synthesis towards a global-bathymetric model of metabolism and chemical composition of marine pelagic chaetognaths. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 424–425:78–88
Ikeda T, Torres JJ, Hernández-León S, Geiger SP (2000) Metabolism. In: Harris RP, Wiebe PH, Lenz J, Skjoldal HR, Huntley M (eds) ICES zooplankton methodology manual. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 455–532
Ikeda T, Kanno Y, Ozaki K, Shinada A (2001) Metabolic rates of epipelagic marine copepods as a function of body mass and temperature. Mar Biol 139:586–587
Ikeda T, Yamaguchi A, Matsuishi T (2006) Chemical composition and energy content of deep-sea calanoid copepods in the western North Pacific Ocean. Deep-Sea Res I 53:1791–1809
Ikeda T, Sano F, Yamaguchi A (2007) Respiration in marine pelagic copepods: a global-bathymetric model. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 339:215–219
Ivleva IV (1980) The dependence of crustacean respiration rate on body mass and habitat temperature. Int Revue Ges Hydrobiol 65:1–47
James MR, Wilkinson VH (1988) Biomass, carbon ingestion, and ammonia excretion by zooplankton associated with an upwelling plume in western cook strait, New Zealand. NZ J Mar Freshw Res 22:249–257
Kim HS, Yamaguchi A, Ikeda T (2010) Metabolism and elemental composition of the euphausiids Euphausia pacifica and Thysanoessa inspinata during the phytoplankton bloom season in the Oyashio region, western subarctic Pacific Ocean. Deep-Sea Res 57:1733–1741
Kruse S, Brey T, Bathmann U (2010) Role of midwater chaetognaths in Southern Ocean pelagic energy flow. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 416:105–113
Lee RF, Hagen W, Kattner G (2006) Lipid storage in marine zooplankton. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 307:273–306
Lindley JA, Robins DB, Williams R (1999) Dry weight carbon and nitrogen of some euphausiids from the North Atlantic Ocean and the Celtic Sea. J Plankton Res 21:2053–2066
Longhurst AR (1985) The structure and evolution of plankton communities. Prog Oceanogr 15:1–35
Longhurst AR, Bedo A, Harrison WG, Head EJH, Sameoto DD (1990) Vertical flux of respiratory carbon by oceanic diel migrant biota. Deep-Sea Res 37:685–694
Mauchline J (1980) The biology of mysids and euphausiids. Adv Mar Biol 18:1–681
Mauchline J, Fisher LR (1967) The biology of euphausiids. Adv Mar Biol 7:1–454
Mayzaud P (1973) Respiration and nitrogen excretion of zooplankton. II. Studies of the metabolic characteristics of starved animals. Mar Biol 21:19–28
Mayzaud P, Conover RJ (1988) O:N atomic ratio as a tool to describe zooplankton metabolism. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 45:289–302
Morris MJ, Hopkins TL (1983) Biochemical composition of crustacean zooplankton from the eastern Gulf of Mexico. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 69:1–19
Nemoto T, Kamada K, Hara K (1972) Fecundity of a euphausiid crustacean, Nematoscelis difficilis, in the North Pacific Ocean. Mar Biol 14:41–47
Paranjape MA (1967) Molting and respiration of euphausiids. J Fish Res Bd Canada 24:1229–1239
Quetin LB, Ross RM, Uchio K (1980) Metabolic characteristics of midwater zooplankton: ammonia excretion, O:N ratios, and the effect of starvation. Mar Biol 59:201–209
Ross RM (1982) Energetics of Euphausia pacifica. I. Effects of body carbon and nitrogen and temperature on measured and predicted production. Mar Biol 68:1–13
Saborowski R, Bröhl S, Tarling GA, Buchholz F (2002) Metabolic properties of Northern krill, Meganyctiphanes norvegica, from different climatic zones. I. Respiration and excretion. Mar Biol 140:547–556
Sameoto DD (1976) Respiration rates, energy budgets, and molting frequencies of three species of euphausiids found in the Gulf of St. Lowrence. J Fish Res Bd Can 33:2568–2576
Scholander PF, Flagg W, Walters V, Irving L (1953) Climatic adaptation in arctic and tropical poikilotherms. Physiol Zool 26:67–92
Seibel BA, Drazen JC (2007) The rate of metabolism in marine animals: environmental constraints, ecological demands and energetic opportunities. Phil Trans R Soc B 362:2061–2078
Small LF, Hebard JF (1967) Respiration of a vertically migrating marine crustacean Euphausia pacifica Hansen. Limnol Oceanogr 12:272–280
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1995) Biometry. The principles and practice of statistics in biological research. Freeman, New York
Stuart V (1986) Feeding and metabolism of Euphausia lucens (Euphausiacea) in the southern Benguela current. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 30:117–125
Teal JM, Carey FG (1967) Effects of pressure and temperature on the respiration of euphausiids. Deep-Sea Res 14:725–733
Torres JJ, Childress JJ (1983) Relationship of oxygen consumption to swimming speed in Euphausia pacifica. 1. Effects of temperature and pressure. Mar Biol 74:79–86
Torres JJ, Childress JJ (1985) Respiration and chemical composition of the bathypelagic euphausiid Bentheuphausia amblyops. Mar Biol 87:267–272
Torres JJ, Aarset AV, Donnelly J, Hopkins TL, Lancraft TM, Ainley DJ (1994) Metabolism of Antarctic micronektonic Crustacea as a function of depth of occurrence and season. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 113:207–219
Ventura M (2006) Linking biochemical and elemental composition in freshwater and marine crustacean zooplankton. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 327:233–246
Vidal J, Whitledge TE (1982) Rates of metabolism of planktonic crustaceans as relation to body weight and temperature of habitat. J Plankton Res 4:77–84
Zeuthen E (1947) Body size and metabolic rate in the Animal Kingdom with special regard to the marine microfauna. CR Trav Lab Carlsberg (Sér chim) 26:17–161
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to three anonymous referees for their comments which improved the text. I thank Jose Torres for reviewing earlier drafts of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by X. Irigoyen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikeda, T. Respiration and ammonia excretion of euphausiid crustaceans: synthesis toward a global-bathymetric model. Mar Biol 160, 251–262 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-2150-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-2150-z