Abstract
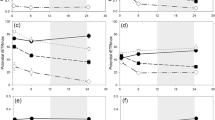
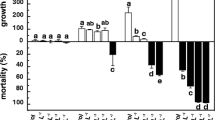
One of the major consequences of global warming is a rise in sea surface temperature which may affect the survival of marine organisms including phytoplankton. Here, we provide experimental evidence for heat-induced cell death in a symbiotic microalga. Shifting Symbiodinium microadriaticum from 27 to 32°C resulted in an increase in mortality, an increase in caspase 3-like activity, and an increase in nitric oxide (NO) production. The caspase-like activity was strongly correlated with the production of NO in thermally challenged microalgae. For this experiment, the application of Ac-DEVD-CHO, a mammalian caspase 3-specific inhibitor, partly prevented (by 65%) the increase in caspase-like activity. To verify the relationship between NO and the caspase-like activity, S. microadriaticum were subsequently incubated with 1.0 mM of the following chemical NO donors: sodium nitroprusside (SNP), S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO), S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine (SNAP) and 3,3bis(Aminoethyl)-1-hydroxy-2-oxo-1-triazene (NOC-18). The supplementation of both SNP and NOC-18 caused a significant increase in caspase-like activity compared to the control treatment. Pre-treatment of the microalgae with the inhibitor Ac-DEVD-CHO before the supplementation of the different NO donors completely prevented the increase in caspase-like activity. These results suggest that NO could play a role in the induction of cell death in heat-stressed S. microadriaticum by mediating an increase in caspase-like activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- O2 − :
-
Superoxide
- ONOO− :
-
Peroxinitrite
- PCD:
-
Programmed cell death
- ROIs:
-
Reactive oxygen intermediates
References
Affenzeller MJ, Darehshouri A, Andosch A, Lütz C, Lütz-Meindl U (2009) Salt stress-induced cell death in the unicellular green alga Micrasterias denticulata. J Exp Bot 60:939–954
Almeida B, Buttner S, Ohlmeier S, Silva A, Mesquita A, Sampaio-Marques B, Osório NS, Kollau A, Mayer B, Leão C, Laranjinha J, Rodrigues F, Madeo F, Ludovico P (2007) NO-mediated apoptosis in yeast. J Cell Sci 120:3279–3288
Berges JA, Falkowski PG (1998) Physiological stress and cell death in marine phytoplankton: induction of proteases in response to nitrogen or light limitation. Limnol Oceanogr 43:129–135
Berman-Frank I, Bidle KD, Haramaty L, Falkowski PG (2004) The demise of the marine cyanobacterium Trichodesmium spp., via an autocatalysed cell death pathway. Limnol Oceanogr 49:997–1005
Bidle KD, Bender SJ (2008) Iron starvation and culture age activate metacaspases and programmed cell death in the marine diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana. Eukaryot Cell 7:223–236
Bidle KD, Falkowski PG (2004) Cell death in planktonic, photosynthetic microorganisms. Nat Rev 2:643–655
Bidle KD, Hamaraty L, Barcelos e Ramos J, Falkowski P (2007) Viral activation and recruitment of metacaspases in the unicellular coccolithophore, Emiliania huxleyi. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:6049–6054
Bonneau L, Ge Y, Drury GE, Gallois P (2008) What happened to plant caspases? J Exp Bot 59(3):491–499. doi:10.1093/jxb/erm352
Bouchard JN, Yamasaki H (2008) Heat stress stimulates nitric oxide production in Symbiodinium microadriaticum: a possible linkage between nitric oxide and the coral bleaching phenomenon. Plant Cell Physiol 49:641–652
Bozhkov PV, Suarez MF, Filonova LH, Daniel G, Zamyatnin AA Jr, Rodriguez-Nieto S, Zhivotovsky B, Smertenko A (2005) Cysteine protease mcII-Pa executes programmed cell death during plant embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:14463–14468
Brüne B (2003) Nitric oxide: NO apoptosis or turning it ON. Cell Death Differ 10:864–869
Brussaard CPD, Marie D, Thyrhaug R, Bratbak G (2001) Flow cytometric analysis of phytoplankton viability following viral infection. Aquat Microb Ecol 26:157–166
Buma AG, Zemmerlink HJ, Sjollema K, Gieskes WWC (1996) UVB radiation modifies protein and photosynthetic pigment content, volume and ultrastructure of marine diatoms. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 142:47–54
Chung C-C, Hwang S-PL, Chang J (2008) Nitric oxide as a signalling factor to upregulate the death-specific protein in a marine diatom, Skeletonema costatum, during blockage of electron flow in photosynthesis. Appl Env Microbiol 74:6521–6527
Clarke A, Desikan R, Hurst RD, Hancock JT, Neill SJ (2000) NO way back: nitric oxide and programmed cell death in Arabidopsis thaliana suspension cultures. Plant J 24:667–677
Coles SL, Brown BE (2003) Coral bleaching-capacity for acclimatization and adaptation. Adv Mar Biol 46:183–223
Darehshouri A, Affenzeller M, Lütz-Meindl U (2008) Cell death upon H2O2 induction in the unicellular green alga Micrasterias. Plant Biol 10:32–745
de Pinto MC, Tommasi F, De Gara L (2002) Changes in the antioxidant systems as part of the signaling pathway responsible for the programmed cell death activated by nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species in tobacco bright-yellow 2 cells. Plant Physiol 130:1–11
Delledonne M (2005) NO news is good news for plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:390–396
Delledonne M, Xia Y, Dixon RA, Lamb C (1998) Nitric oxide functions as a signal in plant disease resistance. Nature 394:585–588
Delledonne M, Zeier J, Marocco A, Lamb C (2001) Signal interactions between nitric oxide and reactive oxygen intermediates in the plant hypersensitive disease resistance response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13454–13459
Deponte M (2008) Programmed cell death in protists. Biochem Biophys Acta 1783(7):1396–1405. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.01.018
Dunn SR, Bythell JC, Le Tissier MDA, Burnett WJ, Thomason JC (2002) Programmed cell death and cell necrosis activity during hyperthermic stress-induced bleaching of the sea anemone Aiptasia sp. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 272:29–53
Dunn SR, Thomason JC, Le Tissier MDA, Bythell JC (2004) Heat stress induces different forms of cell death in sea anemones and their endosymbiotic algae depending on temperature and duration. Cell Death Differ 11:1213–1222
Dunn SR, Schnitzler CE, Weis VM (2007) Apoptosis and autophagy as mechanisms of dinoflagellate symbiont release during cnidarian bleaching: every way you lose. Proc R Soc B 274:3079–3085
Esch P, Techel D, Schimmoller N, Rensing L (1995) Heat shock effects on the circadian rhythm of protein synthesis and phosphorylation of ribosomal proteins in Gonyaulax polyedra. Chronobiol Int 12:369–381
Frada M, Probert I, Allen MJ, Wilson WH, de Vargas C (2008) The “Cheshire Cat” escape strategy of the coccolithophore Emiliania huxleyi in response to viral infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:15944–15949
Franklin DJ, Berges JA (2004) Mortality in cultures of the dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae during culture senescence and darkness. Proc Biol Sci 271:2099–2107
Franklin DJ, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Jones RJ, Berges JA (2004) Cell death and degeneration in the symbiotic dinoflagellates of the coral Stylophora pistillata during bleaching. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 272:117–130
Franklin DJ, Brussaard CPD, Berges JA (2006) What is the role and nature of programmed cell death in phytoplankton ecology? Eur J Phycol 41:1–14
Guillard RRL (1975) Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Smith WL, Chanley MH (eds) Culture of marine invertebrate animals. Plenum Press, New York, pp 26–60
Hoegh-Guldberg O (1999) Climate change and World’s coral reefs: implications for the Great Barrier Reef. Mar Freshw Res 50:839–866
Hong JK, Yun B-W, Kang J-G, Raja MU, Kwon E, Sorhagen K, Chu C, Wang Y, Loake GJ (2008) Nitric oxide function and signaling in plant disease resistance. J Exp Bot 59:147–154
Jeffrey SW, Humphrey GF (1975) New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem Physiol Pflanz 167:191–194
Jiménez C, Capasso JM, Edelstein CL, Rivard CJ, Lucia S, Breusegem S, Berl T, Segovia M (2009) Different ways to die: cell death modes of the unicellular chlorophyte Dunaliella viridis exposed to various environmental stresses are mediated by the caspase-like activity DEVDase. J Exp Bot 60(3):815–828. doi:10.1093/jxb/ern330
Kirchman DL (1999) Phytoplankton death in the sea. Nature 398:293–294
Kojima H, Urano Y, Kikuchi K, Higuchi T, Hirata Y, Nagano T (1999) Fluorescent indicators for imaging nitric oxide production. Angew Chem Int Ed 38:3209–3212
Lesser MP, Farrell JH (2004) Exposure to solar radiation increases damage to both host tissues and algal symbionts of corals during thermal stress. Coral Reefs 23:367–377
Madeo F, Herker E, Maldener C, Wissing S, Lächelt S, Herlan M, Fehr M, Lauber K, Sigrist SJ, Wesselborg S, Fröhlich KU (2002) A caspase-related protease regulates apoptosis in yeast. Mol Cell 9:911–917
Miller-Morey JS, Van Dolah FM (2004) Differential responses of stress proteins, antioxidant enzymes, and photosynthetic efficiency to physiological stresses in the Florida red tide dinoflagellate, Karenia brevis. Comp Biochem Physiol C 138:493–505
Murgia I, Tarantino D, Vannini C, Bracale M, Carravieri S, Soave C (2004a) Arabidopsis thaliana plants overexpressing thylakoidal ascorbate peroxidase show increased resistance to Paraquat-induced photooxidative stress and to nitric oxide-induced cell death. Plant J 38:940–953
Murgia I, Concetta de Pinto M, Delledonne M, Soave C, De Gara L (2004b) Comparative effects of various nitric oxide donors on ferritin regulation, programmed cell death, and cell redox state in plant cells. J. Plant Physiol 161:777–783
Nedelcu AM, Miles IH, Fagir AM, Karol K (2008) Adaptive eukaryote-to-eukaryote lateral gene transfer: stress-related genes of algal origin in the closest unicellular relatives of animals. J Evol Biol 21:1852–1860
Neill S, Bright J, Desikan R, Hancock J, Harrison J, Wilson I (2008) Nitric oxide evolution and perception. J Exp Bot 59:25–35
Nicholson DW (1999) Caspase structure, proteolytic substrates, and function during apoptotic cell death. Cell Death Differ 6:1028–1042
Nicholson DW, Ali A, Thornberry NA, Vaillancourt JP, Ding CK, Gallant M, Gareau Y, Griffin PR, Labelle M, Lazebnik YA, Munday NA, Raju AM, Smulson ME, Yamin T-T, Yu VL, Miller DK (1995) Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature 376:37–43
Parker MS, Mock T, Armbrust EV (2008) Genomic insights into marine microalgae. Annu Rev Genet 42:619–645
Pedroso MC, Magalhaes JR, Durzan D (2000) A nitric oxide burst precedes apoptosis in angiosperm and gymnosperm callus cells and foliar tissues. J Exp Bot 51:1027–1036
Perez S, Weis V (2006) Nitric oxide and cnidarian bleaching: an eviction notice mediates breakdown of a symbiosis. J Exp Biol 209:2804–2810
Piszczek E, Gutman W (2007) Caspase-like proteases and their role in programmed cell death in plants. Acta Physiol Plant 29:391–398
Richier S, Sabourault C, Courtiade J, Zucchini N, Allemand D (2006) Oxidative stress and apoptotic events during thermal stress in the symbiotic sea anemone, Anemonia viridis. FEBS J 273:4186–4198
Ross C, Santiago-Vázquez L, Paul V (2006) Toxin release in response to oxidative stress and programmed cell death in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat Toxicol 78:66–73
Saunders BK, Muller-Parker G (1997) The effects of temperature and light on two algal populations in the temperate sea anemone Anthopleura elegantissima (Brandt, 1835). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 211:213–224
Saviani EE, Orsi CH, Oliveira JFP, Pinto-Maglio CAF, Salgado I (2002) Participation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore in nitric oxide-induced plant cell death. FEBS Lett 510:136–140
Scheiner SM, Gurevitch J (2001) Design and analysis of ecological experiments, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, New York, p 415
Segovia M (2008) Programmed cell death in dinoflagellates. In: Pérez Martin JM (ed) Programmed cell death in protozoa. Landes Bioscience, Austin, pp 126–142
Segovia M, Berges JA (2005) Effects of inhibitors of protein synthesis and DNA replication on the induction of proteolytic activities, caspase-like activities and cell death in the unicellular chlorophyte Dunaliella tertiolecta. Eur J Phycol 40:21–30
Segovia M, Haramati L, Berges JA, Falkowski PG (2003) Cell death in the unicellular chlorophyte Dunaliella tertiolecta. A hypothesis on the evolution of apoptosis in higher plants and metazoans. Plant Physiol 132:99–105
Takahashi S, Nakamura T, Sakamizu M, van Woesik R, Yamasaki H (2004) Repair machinery of symbiotic photosynthesis as the primary target of heat stress for reef-building corals. Plant Cell Physiol 45:251–255
Thornberry NA (1999) Caspases: a decade of death research. Cell Death Differ 6:1023–1027
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y (1998) Caspases: enemies within. Science 281:1312–1316
Timmermans KR, Veldhuis MJW, Brussaard CPD (2007) Cell death in three marine diatom species in response to different irradiance levels, silicate or iron concentrations. Aquat Microb Ecol 46:253–261
Trapido-Rosenthal HG, Sharp KH, Galloway TS, Morrall CE (2001) Nitric oxide and cnidarian-dinoflagellate symbioses: pieces of a puzzle. Am Zool 41:247–257
Uren AG, O’Rourke K, Aravind L, Pisabarro MT, Seshagiri S, Koonin EV, Dixit VM (2000) Identification of paracaspases and metacaspases: two ancient families of caspase-like proteins, one of which plays a key role in MALT lymphoma. Mol Cell 6:961–967
Vardi A, Berman-Frank I, Rozenberg T, Hadas O, Kaplan A, Levine A (1999) Programmed cell death of the dinoflagellate Peridinium gatunense is mediated by CO2 limitation and oxidative stress. Curr Biol 9:1061–1064
Vardi A, Eisenstadt D, Murik O, Berman-Frank I, Zohary T, Levine A, Kaplan A (2007) Synchronisation of cell death in a dinoflagellate population is mediated by an excreted thiol protease. Environ Microbiol 9:360–369
Vardi A, Bidle D, Kwityn C, Hirsh DJ, Thompson SM, Callow JA, Falkowski P, Bowler C (2008) A diatom gene regulating nitric-oxide signaling and susceptibility to diatom-derived aldehydes. Curr Biol 18:895–899
Veldhuis MJW, Cucci TL, Sieracki ME (1997) Cellular DNA content of marine phytoplankton using two new fluorochromes: taxonomic and ecological implications. J Phycol 33:527–541
Veldhuis MJW, Kraay GW, Timmermans KR (2001) Cell death in phytoplankton: correlation between changes in membrane permeability, photosynthetic activity, pigmentation and growth. Eur J Phycol 36:167–177
Vercammen D, Van de Cotte B, De Jaeger G, Eeckhout D, Casteels P, Vandepoele K, Vandenberghe I, Van Beeumen J, Inzé D, Van Breusegem F (2004) Type II metacaspases Atmc4 and Atmc9 of Arabidopsis thaliana cleave substrates after arginine and lysine. J Biol Chem 44:45329–45336
Vincent W (1983) Fluorescence properties of the freshwater phytoplankton: three algal classes compared. Br Phycol J 18:5–21
Warner ME, Fitt WK, Schmidt GW (1996) The effect of elevated temperature on the photosynthetic efficiency of zooxanthellae in hospite from four different species of reef coral: a novel approach. Plant Cell Environ 19:291–299
Watanabe N, Lam E (2005) Two Arabidopsis metacaspases AtMCP1b and AtMCP2b are arginine/lysine-specific cysteine proteases and activate apoptosis-like cell death in yeast. J Biol Chem 280:14691–14699
Weis VM (2008) Cellular mechanisms of cnidarian bleaching: stress causes the collapse of symbiosis. J Exp Biol 211:3059–3066
Wilkerson FP, Muller Parker G, Muscatine L (1983) Temporal patterns of cell division in natural populations of endosymbiotic algae. Limnol Oceanogr 28:1009–1014
Wink DA, Cook JA, Pacelli R, DeGraff W, Gamson J, Liebmann J, Krishna MA, Mitchell JB (1996) The effect of various nitric oxide-donor agents on hydrogen peroxide-mediated toxicity: a direct correlation between nitric oxide formation and protection. Arch Biochem Biophys 331:241–248
Zago E, Morsa S, Dat JF, Alard P, Ferrarini A, Inzé D, Delledonne M, Van Breusegem F (2006) Nitric oxide- and hydrogen peroxide-responsive gene regulation during cell death induction in tobacco. Plant Physiol 141:404–411
Zheng-Bin Z, Chun-Ying L, Zhen-Zhen W, Lei X, Pei-Feng L (2006) Detection of nitric oxide in culture media and studies on nitric oxide formation by marine microalgae. Med Sci Monit 12:BR75–BR85
Zuppini A, Andreoli C, Baldan B (2007) Heat stress: an inducer of programmed cell death in Chlorella saccarophila. Plant Cell Physiol 48:1000–1009
Acknowledgments
This work was made possible by a JSPS postdoctoral fellowship granted to J.N.B and by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture, Japan to H.Y.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Kühl.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouchard, J.N., Yamasaki, H. Implication of nitric oxide in the heat-stress-induced cell death of the symbiotic alga Symbiodinium microadriaticum . Mar Biol 156, 2209–2220 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-009-1249-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-009-1249-3