Abstract
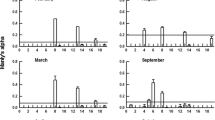
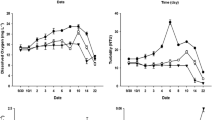
Temporal variation in abundance of the microphytobenthos on an estuarine mudflat in Hong Kong was investigated over a 13-month period. Abundance, in terms of both cell counts and chlorophyll-a (chl-a) concentration, of the diatom-dominated assemblage was higher (peak at 47 mg chl-a m−2 in January) in the cooler months than in the warmer months (minimum at 11 mg chl-a m−2 in August). Variation in surface density (range: 0.25–1.9 individuals m−2) of the herbivorous mudskipper Boleophthalmus pectinirostris was also temporally variable, with a broadly inverse pattern to that of the microphytobenthos. Comparison of the relative abundance of diatom species in the gut and on the mud surface using Strauss' linear selectivity index suggests significant size-selective feeding by B. pectinirostris. Diatoms with maximum lengths >50 μm were selectively ingested whereas smaller species were rejected. This critical diatom length is close to the average distance between branchiospines of the fish's gills, suggesting their involvement in a physical sieving process that is responsible for the size-selective feeding. Significant differences in feeding pattern exist between adult (>80 mm standard length) and juvenile fish. As a result of seasonal variations in density and selective removal of the larger diatoms, B. pectinirostris exerts a significant impact on the abundance and structure of the mudflat microphytobenthos.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Admiraal W, Peletier H (1980) Distribution of diatom species on an estuarine mud flat and experimental analysis of the selective effect of stress. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 46:157–175
Admiraal W, Peletier H, Zomer H (1982) Observations and experiments on the population dynamics of epipelic diatoms from an estuarine mudflat. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 14:471–487
Alexander RM (1967) Functional design in fishes. Hutchinson University Library, London
Al-Hussaini AH (1947) The feeding habits and the morphology of the alimentary tract of some teleosts living in the neighbourhood of the Marine Biological Station, Ghardaqa, Red Sea. Publ Mar Biol Stat Ghardaqa 5:1–61
Alongi DM, Sasekumar A (1992) Benthic communities. In: Robertson AI, Alongi DM (eds) Tropical mangrove ecosytems. American Geophysical Union, New York, pp 137–172
Berg J (1979) Discussion of methods of investigating the food of fishes, with reference to a preliminary study of the prey of Gobiusculus flavescens (Gobiidae). Mar Biol 50:263–273
Blake BF (1977) Food and feeding of the mormyrid fishes of Lake Kainji, Nigeria, with special reference to seasonal variation and interspecific differences. J Fish Biol 11:315–328
Chan KY (1989) The ecology of mudskippers (Pisces: Periophthalmidae) at the Mai Po Marshes Nature Reserve, Hong Kong. Master's thesis, University of Hong Kong
Clayton DA (1993) Mudskippers. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 31:507–577
Clayton DA, Snowden R (2000) Surface activity in the mudskipper, Periophthalmus waltoni Koumans 1941 in relation to prey activity and environmental factors. Trop Zool 13:239–249
Clayton DA, Vaughan TC (1982) Pentagonal territories of the mudskipper Boleophthalmus boddarti (Pisces: Gobiidae). Copeia 1982:232–234
Clayton DA, Vaughan TC (1986) territorial acquisition in the mudskipper Boleophthalmus boddarti (Teleostei, Gobiidae) on the mudflats of Kuwait. J Zool 209:501–519
Conde D, Bonilla S, Aubriot L, de Leon R, Pintos W (1999) Comparison of the areal amount of chlorophyll a of planktonic and attached microalgae in a shallow coastal lagoon. Hydrobiologia 408/409:285–291
Delbeek JC, Williams DD (1988) Feeding selectivity of four species of sympatric stickleback in brackish-water habitats in eastern Canada. J Fish Biol 32:41–62
Duffy EJ, Kinlan BP, Valiela I (1997) Influence of grazing and nitrogen loading on benthic microalgal biomass in estuaries of Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts. Biol Bull 193:285–286
Eaton JW, Moss B (1966) The estimation of numbers and pigment content in epipelic algal populations. Limnol Oceanogr 11:584–595
El-Ziady S, Eissa SM, Al-Naqi Z (1979) Ecological studies on the mudskipper fish Periophthalmus chrysospilos (Bleeker) in Kuwait. Bull Fac Sci Cairo Univ 47:113–137
Etim L, King RP, Udo MT (2002) Breeding, growth, mortality and yield of the mudskipper Periophthalmus barbarus (Linnaeus 1766) (Teleostei: Gobiidae) in the Imo River estuary, Nigeria. Fish Res 56:227–238
Fielding PJ, Samstra KS, Branch GM (1988) benthic diatom biomass, production and sediment chlorophyll in Langebaan Lagoon, South Africa. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 27:413–426
Geevarghese C (1983) Morphology of the alimentary tract in relation to diet among gobioid fishes. J Nat Hist 17:731–741
Germain H (1981) Flores des diatomées eaus douces et saumâtres. Société Nouvelle des Éditions Boubée, Paris
Goldfinch AC, Carman KR (2000) Chironomid grazing on benthic microalgae in a Louisiana salt marsh. Estuaries 23:536–547
Healey MC (1972) On the population ecology of the common goby in the Ythan estuary. J Nat Hist 6:133–145
Hillebrand H, Sommer U (2000) Diversity of benthic microalgae in response to colonization time and eutrophication. Aquat Bot 67:221–236
Hopkins JT (1964) A study of the diatoms of the Ouse estuary, Sussex III. The seasonal variation in the littoral epiphyte flora and the shore plankton. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 44:613–644
Hyslop EJ (1980) Stomach contents analysis—a review of methods and their application. J Fish Biol 17:411–429
Ikebe Y, Oishi T (1997) Relationships between environmental factors and diel and annual changes of the behaviors during low tides in Periophthalmus modestus. Zool Sci 14:49–55
Kok WK, Lim CB, Lam TJ, Ip YK (1998) The mudskipper Periophthalmodon schlosseri respires more efficiently on land than in water and vice versa for Boleophthalmus boddaerti. J Exp Zool 280:86–90
Lee SY (2000) Carbon dynamics of Deep Bay, eastern Pearl River estuary, China II. Trophic analysis using stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 205:1–10
Li MS, Lee SY (1998) Carbon budget for Deep Bay, eastern Pearl River estuary, China I. A mass balance study and implications for shorebird conservation. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 172:73–87
Light BR, Beardall J (1998) Distribution and spatial variation of benthic microalgal biomass in a temperate, shallow-water marine system. Aquat Bot 61:39–54
Lorenzen CJ (1967) Determination of chlorophyll and phaeopigments: spectrophotometric equations. Limnol Oceanogr 12:343–346
Low WP, Lane DJW, Ip KY (1988) A comparative study of terrestrial adaptations of the gills in three mudskippers—Periophthalmus chrysopilos, Boleophthalmus boddaerti, and Periophthalmus schlosseri. Biol Bull 175:434–438
Macnae W (1968) Fauna and flora of mangrove swamps in the Indo-west-Pacific. Adv Mar Biol 6:185–200
Montagna PA (1984) In situ measurements of meiobenthic grazing rates on sediment bacteria and edaphic diatoms. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 18:119–130
Moore JW, Moore IA (1976) The basis of food selection in flounders, Platychthys flesus (L.) in the Severn estuary. J Fish Biol 9:139–156
Morrisey DJ (1988) Differences in effects of grazing by deposit-feeders Hydrobia ulvae (Pennant) (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia) and Corophium arenarium Crawford (Amphipoda) on sediment microalgal populations II. Quantitative effects. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 118:43–53
Newell RIE, Marshall N, Sasekumar A, Chong VC (1995) Relative importance of benthic microalgae, phytoplankton, and mangroves as sources of nutrition for penaeid prawns and other coastal invertebrates from Malaysia. Mar Biol 123:595–606
Odum WE (1970) Utilization of the direct grazing and plant detritus food chains by the striped mullet Mugil cephalus. In: Steele JH (ed) Marine food chains. Oliver and Boyd, Edinburg, pp 222–240
Oppenheim DR (1988) The distribution of epipelic diatoms along an intertidal shore in relation to principal physical gradients. Bot Mar 31:65–72
Oppenheim DR (1991) Seasonal changes in epipelic diatoms along an intertidal shore, Berrow Flats, Somerset. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 71:579–596
Pillay TVR (1952) A critique of the methods of study of food of fishes. J Zool Soc India 4:185–200
Reise K (1985) Tidal flat ecology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Round FE (1966) Persistent, vertical-migration rhythms in benthic microflora V. The effect of artificially imposed light and dark cycles. In: Fifth International Seaweed Symposium, Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 197–203
Round FE (1971) Benthic marine diatoms. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 9:83–139
Sauriau P, Kang C (2000) Stable isotope evidence of benthic microalgae-based growth and secondary production in the suspension feeder Cerastoderma edule (Mollusca, Bivalvia) in the Marennes-Olerin Bay. Hydrobiologia 440:317–329
Strauss RE (1979) Reliability estimates for Ivlev's electivity index, the forage ratio, and a proposed linear index of food selection. Trans Am Fish Soc 108:334–352
Tytler P, Vaughan T (1983) Thermal ecology of the mudskippers, Periophthalmus koelreuteri (Pallas) and Boleophthalmus doddarti (Pallas) of Kuwait Bay. J Fish Biol 23:327–337
Underwood GJC, Paterson DM (1993) Seasonal changes in diatom biomass, sediment stability and biogenic stabilization in the Severn estuary. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 73:871–887
Yang KY (1996) The feeding ecology of the mudskipper Boleopthalmus pectinirostris (Pisces: Periophthalmidae) at the Mai Po Marshes Nature Reserve, Hong Kong. Master's thesis, University of Hong Kong
Zhang QY, Zhang L (1988) On the feeding, growth and survival of larval mudskipper (Boleophthalmus pectinirostris) (in Chinese). J Fish China 12:203–211
Zhu Y, Zhang Q (1993) On the feeding habits and histological structure of the digestive tract of the mudskipper, Boleophthalmus pectinirostris, in the intertidal zone of Jiulong River estuary (in Chinese). J Oceanogr Taiwan Strait 12:225–232
Acknowledgements
We thank the staff of WWFHK at Mai Po for their logistical support, without which much of this work would not have been possible. Part of the work was funded by a Hong Kong Research Grant Council grant 294/92 M awarded to SYL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G.F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, K.Y., Lee, S.Y. & Williams, G.A. Selective feeding by the mudskipper (Boleophthalmus pectinirostris) on the microalgal assemblage of a tropical mudflat. Marine Biology 143, 245–256 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-003-1067-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-003-1067-y