Abstract
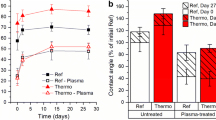
This study tests the hypothesis that thermal modification of wood influences the effectivity of air plasma treatment. Micro-veneers of European beech, Scots pine and Norway spruce were thermally modified at two different temperatures and subsequently plasma-treated for 1 and 3 s. The veneer surfaces were characterized in terms of morphology, wetting behaviour and surface chemistry. No severe changes in the veneer surfaces due to plasma treatment were observed by scanning electron microscopy. Plasma treatment increased surface free energy and wettability by water and urea–formaldehyde adhesive; it was more effective on thermally modified wood than on unmodified wood. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy revealed a similar distribution of oxygen-containing functional groups on the wood surface after plasma treatment of thermally modified and unmodified beech wood. It is suggested that enhanced wettability through plasma treatment is due to the generation of carboxyl groups within the lignin network, which contribute to the polar part of the surface free energy. The high effectiveness of plasma treatment on thermally modified wood might thus be explained by its high relative proportion of lignin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acda MN, Devera EE, Cabangon RJ, Ramos HJ (2012) Effects of plasma modification on adhesion properties of wood. Int J Adhes Adhes 32:70–75
Ahajji A, Diouf PN, Aloui F, Elbakali I, Perrin D, Merlin A, George B (2009) Influence of heat treatment on antioxidant properties and colour stability of beech and spruce wood and their extractives. Wood Sci Technol 43(1–2):69–83
Alen R, Kotilainen R, Zaman A (2002) Thermochemical behavior of Norway spruce (Picea abies) at 180–225 °C. Wood Sci Technol 36(2):163–171
Altgen D, Bellmann M, Wascher R, Viöl W, Mai C (2015a) Enhancing mechanical properties of particleboards using plasma treated wood particles. Eur J Wood Wood Prod 73(2):219–223
Altgen D, Bellmann M, Wascher R, Mai C (2015b) Enhanced urea-formaldehyde adhesive spreading on plasma treated wood particles. Eur J Wood Wood Prod 74(4):617–620
Asandulesa M, Topala I, Dumitrascu N (2010) Effect of helium DBD plasma treatment on the surface of wood samples. Holzforschung 64(2):223–227
Avramidis G, Hauswald E, Lyapin A, Militz H, Viöl W, Wolkenhauer A (2009) Plasma treatment of wood and wood-based materials to generate hydrophilic or hydrophobic surface characteristics wood. Mater Sci Eng 1–2:52–60
Avramidis G, Scholz G, Nothnick E, Militz H, Viöl W, Wolkenhauer A (2010) Improved bondability of wax-treated wood following plasma treatment. Wood Sci Technol 45(2):359–368
Avramidis G, Militz H, Avar I, Viöl W, Wolkenhauer A (2012) Improved absorption characteristics of thermally modified beech veneer produced by plasma treatment. Eur J Wood Wood Prod 70(5):545–549
Aydin I, Demirkir C (2010) Activation of spruce wood surfaces by plasma treatment after long terms of natural surface inactivation. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 30(5):697–706
Bourgois J, Bartholin MC, Guyonnet R (1989) Thermal-treatment of wood—analysis of the obtained product. Wood Sci Technol 23(4):303–310
Briggs D, Beamson G (2000) XPS database of polymers in high resolution. Surface Spectra Ltd., Manchester
Busnel F, Blanchard V, Pregent J, Stafford L, Riedl B, Blanchet P, Sarkissian A (2010) Modification of sugar maple (Acer saccharum) and black spruce (Picea mariana) wood surfaces in a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) at atmospheric pressure. J Adhes Sci Technol 24(8–10):1401–1413
Custódio J, Broughton J, Cruz H, Winfield P (2009) Activation of timber surfaces by flame and corona treatments to improve adhesion. Int J Adhes Adhes 29(2):167–172
Eliasson B, Kogelschatz U (1991) Modeling and applications of silent discharge plasmas. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 19(2):309–323
Eriksson M, Notley SM, Wågberg L (2007) Cellulose thin films: degree of cellulose ordering and its influence on adhesion. Biomacromolecules 8(3):912–919
Fengel D (1966) On changes of wood and its components in temperature range up to 200 °C. Part II. The hemicelluloses in untreated and thermally treated sprucewood. Holz Roh-Werkst 24(3):98–109
Fowkes FM (1964) Attractive forces at interfaces. Ind Eng Chem 56(12):40–52
Gellerstedt F, Gatenholm P (1999) Surface properties of lignocellulosic fibers bearing carboxylic groups. Cellulose 6(2):103–121
Gérardin P, Petrič M, Petrissans M, Lambert J, Ehrhrardt JJ (2007) Evolution of wood surface free energy after heat treatment. Polym Degrad Stabil 92(4):653–657
Hakkou M, Pétrissans M, Zoulalian A, Gérardin P (2005) Investigation of wood wettability changes during heat treatment on the basis of chemical analysis. Polym Degrad Stabil 89(1):1–5
Halliwell G (1965) Catalytic decomposition of cellulose under biological conditions. Biochem J 95:35–40
Hill CAS (2006) Wood modification: chemical, thermal and other processes. Wiley, Chichester
Huang H, Wang BJ, Dong L, Zhao M (2011) Wettability of hybrid poplar veneers with cold plasma treatments in relation to drying conditions. Dry Technol 29(3):323–330
Inari GN, Petrissans M, Lambert J, Ehrhardt JJ, Gérardin P (2006) XPS characterization of wood chemical composition after heat-treatment. Surf Interf Anal 38(10):1336–1342
Jamali A, Evans P (2011) Etching of wood surfaces by glow discharge plasma. Wood Sci Technol 45(1):169–182
Kaelble DH (1970) Dispersion-polar surface tension properties of organic solids. J Adhes 2(2):66–81
Kamdem DP, Pizzi A, Triboulot MC (2000) Heat-treated timber: potentially toxic byproducts presence and extent of wood cell wall degradation. Holz Roh-Werkst 58(4):253–257
Kang GJ, Zhang YJ, Ni YG, Vanheiningen ARP (1995) Influence of lignins on the degradation of cellulose during ozone treatment. J Wood Chem Technol 15(4):413–430
Klarhöfer L, Viöl W, Maus-Friedrichs W (2010) Electron spectroscopy on plasma treated lignin and cellulose. Holzforschung 64(3):331–336
Kollmann F, Schneider A (1963) On the sorption-behaviour of heat stabilized wood. Holz Roh-Werkst 21(3):77–85
Král P, Ráhel’ J, Stupavská M, Šrajer J, Klímek P, Mishra P, Wimmer R (2015) XPS depth profile of plasma-activated surface of beech wood (Fagus sylvatica) and its impact on polyvinyl acetate tensile shear bond strength. Wood Sci Technol 49(2):319–330
Kutnar A, Kricej B, Pavlic M, Petric M (2013) Influence of treatment temperature on wettability of Norway spruce thermally modified in vacuum. J Adhes Sci Technol 27(9):963–972
Metsa-Kortelainen S, Antikainen T, Viitaniemi P (2006) The water absorption of sapwood and heartwood of Scots pine and Norway spruce heat-treated at 170 °C, 190 °C, 210 °C and 230 °C. Holz Roh-Werkst 64(3):192–197
Notley SM, Norgren M (2010) Surface energy and wettability of spin-coated thin films of lignin isolated from wood. Langmuir 26(8):5484–5490
Nuopponen M, Vuorinen T, Jämsä S, Viitaniemi P (2003) The effects of a heat treatment on the behaviour of extractives in softwood studied by FTIR spectroscopic methods. Wood Sci Technol 37(2):109–115
Nuopponen M, Vuorinen T, Jämsä S, Viitaniemi P (2005) Thermal modifications in softwood studied by FT-IR and UV resonance Raman spectroscopies. J Wood Chem Technol 24(1):13–26
Nussbaum RM (1999) Natural surface inactivation of Scots pine and Norway spruce evaluated by contact angle measurements. Holz Roh-Werkst 57(6):419–424
Odraskova M, Rahel J, Zahoranova A, Tino R, Cernak M (2008) Plasma activation of wood surface by diffuse coplanar surface barrier discharge. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 28(2):203–211
Owens DK, Wendt R (1969) Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J Appl Polym Sci 13(8):1741–1747
Popper R, Niemz P, Eberle G (2005) Investigations on the sorption and swelling properties of thermally treated wood. Holz Roh-Werkst 63(2):135–148
Rabel W (1971) Einige Aspekte der Benetzungstheorie und ihre Anwendung auf die Untersuchung und Veränderung der Oberflächeneigenschaften von Polymeren (Some aspects of wetting theory and its application to the study and change of surface properties of polymers) (In German). Farbe und Lack 77(10):997–1005
Sakata I, Morita M, Tsuruta N, Morita K (1993) Activation of wood surface by corona treatment to improve adhesive bonding. J Appl Polym Sci 49(7):1251–1258
Scheikl M, Dunky M (1998) Measurement of dynamic and static contact angles on wood for the determination of its surface tension and the penetration of liquids into the wood surface. Holzforschung 52(1):89–94
Scholz G, Nothnick E, Avramidis G, Krause A, Militz H, Viöl W, Wolkenhauer A (2010) Adhesion of wax impregnated solid beech wood with different glues and by plasma treatment. Eur J Wood Wood Prod 68(3):315–321
Shirley DA (1972) High-resolution X-ray photoemission spectrum of the valence bands of gold. Phys Rev B 5(12):4709–4714
Sivonen H, Maunu SL, Sundholm F, Jamsa S, Viitaniemi P (2002) Magnetic resonance studies of thermally modified wood. Holzforschung 56(6):648–654
Strom G, Carlsson G (1992) Wettability of kraft pulps—effect of surface-composition and oxygen plasma treatment. J Adhes Sci Technol 6:745–761
Wascher R, Avramidis G, Vetter U, Damm R, Peters F, Militz H, Viöl W (2014a) Plasma induced effects within the bulk material of wood veneers. Surf Coat Technol 259:62–67
Wascher R, Schulze N, Avramidis G, Militz H, Viöl W (2014b) Increasing the water uptake of wood veneers through plasma treatment at atmospheric pressure. Eur J Wood Wood Prod 72(5):685–687
Wikberg H, Maunu S (2004) Characterisation of thermally modified hard- and softwoods by 13C CPMAS NMR. Carbohydr Polym 58(4):461–466
Wolkenhauer A, Avramidis G, Cai Y, Militz H, Viöl W (2007) Investigation of wood and timber surface modification by dielectric barrier discharge at atmospheric pressure. Plasma Process Polym 4:470–474
Wolkenhauer A, Avramidis G, Militz H, Viöl W (2008) Plasma treatment of heat treated beech wood—investigation on surface free energy. Holzforschung 62(4):472–474
Wolkenhauer A, Avramidis G, Hauswald E, Militz H, Viöl W (2009) Sanding vs. plasma treatment of aged wood: a comparison with respect to surface energy. Int J Adhes Adhes 29(1):18–22
Militz H, Altgen M (2014) Processes and properties of thermally modified wood manufactured in Europe. In: Deterioration and protection of sustainable biomaterials, ACS symposium series, vol 1158
Yeh JJ, Lindau I (1985) Atomic subshell photoionization cross sections and asymmetry parameters: 1 ≤ Z ≤ 103. Atom Data Nucl Data 32(1):1–155
Yildiz S (2002) Effects of heat treatment on water repellence and anti swelling efficiency of beech wood. The International Research Group On Wood Preservation, Document No: IRG/WP 02-40223
Zaman A, Alén R, Kotilainen R (2000) Thermal behavior of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) and Silver birch (Betula pendula) at 200–230 C. Wood Fiber Sci 32(2):138–143
Zhou XY et al (2012) Glass transition of oxygen plasma treated enzymatic hydrolysis lignin. Bioresources 7(4):4776–4785
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altgen, D., Avramidis, G., Viöl, W. et al. The effect of air plasma treatment at atmospheric pressure on thermally modified wood surfaces. Wood Sci Technol 50, 1227–1241 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-016-0856-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-016-0856-7