Abstract
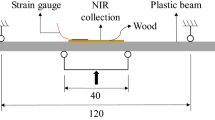
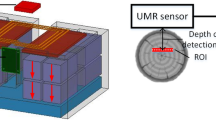
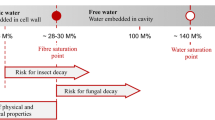
The paper describes a low-invasive experimental apparatus designed for the accurate determination of mechanical deformation and moisture content (MC) relationship on macroscopic wood samples. The device is particularly indicated for monitoring wooden handwork whose mechanical deformation is especially critical in relation to its role such as, for example, works of art or architectural works. The MC of wood is measured with a portable single-sided NMR probe and mechanical deformation by a fiber Bragg grating optical sensor. The data obtained are of high accuracy, despite the dimensions of the sample. The methodology provides an effective tool for investigating the dynamic relation between environmental relative humidity, MC, and shrinking–swelling of wood. Adsorption results collected for longitudinal deformation in silver fir (Abies alba Mill.) are presented to show the sensitivity of the optical sensor. Interesting findings include the detection of two different mechanisms of elongation and the time evolution of water mobility versus hydration and strain.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida G, Gagne S, Hernandez RE (2006) A NMR study of water distribution in hardwoods at several equilibrium moisture contents. Wood Sci Technol 41:293–307
Anferova S, Anferov V, Adams M, Blumler P, Routley N, Hailu K, Kupferschlager K, Mallett MJD, Schroeder G, Sharma S, Blumich B (2002) Construction of a NMR-MOUSE with short dead time. Concept Magn Reson 15:15–25
Borgia GC, Brown RJS, Fantazzini P (1998) Uniform-penalty inversion of multiexponential decay data. J Magn Reson 132:65–77
Bortolotti V, Camaiti M, Casieri C, De Luca F, Fantazzini P, Terenzi C (2006) Water absorption kinetics in different wettability conditions studied at pore and sample scales in porous media by NMR with portable single-sided and laboratory imaging devices. J Magn Reson 181:287–295
Camaiti M, Casieri C, De Luca F, Fantazzini P, Terenzi C (2007) The use of portable single-sided relaxometry and laboratory imaging NMR devices in stone conservation. Stud Conserv 52:39–47
Casieri C, Senni L, Romagnoli M, Santamaria U, De Luca F (2004) Determination of moisture fraction in wood by mobile NMR device. J Magn Reson 171:363–372
Casieri C, De Luca F, Fantazzini P (2005) Pore-size evaluation by single-sided nuclear magnetic resonance measurements: compensation of water self-diffusion effect on transverse relaxation. J Appl Phys 97(043901):1–10
Cignini R, Melzi R, Tedoldi F, Casieri C, De Luca F (2006) Large surface mapping by unilateral NMR scanner. Magn Reson Imaging 24:813–818
Eidmann G, Savelsberg R, Blümler P, Blümich B (1996) The NMR MOUSE, a mobile universal surface explorer. J Magn Reson 122:104–109
Fechete R, Demco DE, Blumich B (2003) Order parameters of the orientation distribution of collagen fibers in Achilles tendon by H-1 NMR of multipolar spin states. NMR Biomed 16:479–483
Ishimara Y, Arai K, Mizutani K, Oshima K, Lida I (2001) Physical and mechanical properties of wood after moisture conditioning. J Wood Sci 47:185–191
Jakiela S, Bratasz L, Kozlowski R (2008) Numerical modelling of moisture movement and related stress field in lime wood subjected to changing climate conditions. Wood Sci Technol 42:21–37
Kashyap R (1999) Fiber Bragg Gratings. Academic Press, New York
Keckes J, Burgert I, Frühmann K, Müller M, Kölln K, Hamilton M, Burghammer M, Roth SV, Stanzl-Tschegg S, Fratzl P (2003) Cell-wall recovery after irreversible deformation of wood. Nat Mater 2:810–813
Meiboom S, Gill D (1958) Modified spin-echo method for measuring nuclear relaxation times. Rev Sci Instrum 29:688–691
Rao YJ (1999) Recent progress in applications of in-fiber Bragg grating sensors. Opt Laser Eng 31:297–324
Reeb JE (1995) Wood and moisture relationships. Oregon State University Bulletin EM8600
Senni L, Casieri C, Bovino A, Gaetani MC, De Luca F (2008) A portable NMR sensor for moisture monitoring of wooden works of art, particularly of painting on wood. Wood Sci Technol 43(1–2):167–180
Skaar C (1988) Wood–water relations. Springer, Berlin
Viola I, Bubici S, Casieri C, De Luca F (2004) The Codex Major of the Collectio Altaempsiana: a non-invasive NMR study of paper. J Cult Herit 5:257–261
Wood Handbook: US Department of Agriculture (1987) Wood as an engineering material. Agriculture Handbook 72, Washington, DC
Acknowledgments
We thank Paola Fantazzini who supplied us with UPEN algorithm to get inverse Laplace transform of relaxation data. Thanks are due to Sergio Ciuchi for suggestions regarding Eq. 5. All of us are indebted to Bruker BioSpin S.r.L., Milan, Italy, for the assistance and updating of the NMR sensor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Senni, L., Caponero, M., Casieri, C. et al. Moisture content and strain relation in wood by Bragg grating sensor and unilateral NMR. Wood Sci Technol 44, 165–175 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-009-0268-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-009-0268-z