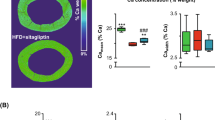
Abstract
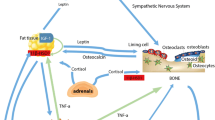
Bone metabolism may be adversely affected in metabolic diseases such as obesity and metabolic syndrome, which are characterised by weight gain, due to the expansion of adipose tissue deposits. As an important regulator of energy metabolism, adipose tissues synthesise and secrete several key regulatory adipokines that influence a range of metabolic functions. This narrative review outlines the evidence for the mechanisms by which adipose tissue dysfunction may alter bone metabolism prior to the development of frank hyperglycaemia and presents the emerging evidence for the impact of diet-induced expansion of adipose tissue on implant osseointegration. Successful osseointegration requires normal bone cell function, and the expansion of adipose tissue deposits results in dysregulated adipokine production favouring an increase in pro-inflammatory adipokines, contributing to the development of a chronic inflammatory state and insulin resistance. The increase in inflammatory cytokines promotes the growth and differentiation of osteoclasts indirectly through the modulation of osteoblastic RANKL production and directly by reducing osteoclast apoptosis and increased osteoclastic expression of RANK. Conversely, the suppression of osteoblastic regulatory genes results in reduced osteoblast numbers and function contributing to compromised bone turnover. Compromised osseointegration has been established in hyperglycaemia; however, as discussed in this review, it may not be the only driver of altered bone metabolism. The incidence of metabolic disease in the community is rising, patients may present for implant treatment with undiagnosed, underlying changes to bone cell metabolism due to adipose tissue dysmetabolism.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cordain L, Eaton SB, Sebastian A, Mann N, Lindeberg S, Watkins BA, O’Keefe JH et al (2005) Origins and evolution of the Western diet: health implications for the 21st century. Am J Clin Nutr 81(2):341–354. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn.81.2.341
Moayeri A, Mohamadpour M, Mousavi SF, Shirzadpour E, Mohamadpour S, Amraei M (2017) Fracture risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and possible risk factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther Clin Risk Manag 13:455–468. https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S131945
Pedersen AB, Mehnert F, Johnsen SP, Sorensen HT (2010) Risk of revision of a total hip replacement in patients with diabetes mellitus: a population-based follow up study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92(7):929–934. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.92b7.24461
Naujokat H, Kunzendorf B, Wiltfang J (2016) Dental implants and diabetes mellitus—a systematic review. Int J Implant Dent 2(1):5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-016-0038-2
Chrcanovic B, Albrektsson T, Wennerberg A (2014) Diabetes and oral implant failure: a systematic review. J Dent Res 93(9):859–867. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034514538820
Li X, Gong X, Jiang W (2017) Abdominal obesity and risk of hip fracture: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Osteoporos Int 28(10):2747–2757. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-017-4142-9
Ouchi N, Parker JL, Lugus JJ, Walsh K (2011) Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11(2):85–97. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2921
Diascro DD Jr, Vogel RL, Johnson TE, Witherup KM, Pitzenberger SM, Rutledge SJ, Prescott DJ et al (1998) High fatty acid content in rabbit serum is responsible for the differentiation of osteoblasts into adipocyte-like cells. J Bone Miner Res 13(1):96–106. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.1998.13.1.96
Jeon M, Kim J, Kwon S, Kim SW, Park KS, Park S-W, Kim S et al (2003) Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-inhibits the Runx2-mediated transcription of osteocalcin in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem 278:23270–23277. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M211610200
Lecka-Czernik B, Gubrij I, Moerman EJ, Kajkenova O, Lipschitz DA, Manolagas SC, Jilka RL (1999) Inhibition of Osf2/Cbfa1 expression and terminal osteoblast differentiation by PPARγ2. J Cell Biochem 74(3):357–371. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-4644(19990901)74:3%3c357::aid-jcb5%3e3.0.co;2-7
Tian L, Yu X (2015) Lipid metabolism disorders and bone dysfunction–interrelated and mutually regulated (review). Mol Med Report 12(1):783–794. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3472
World Health Organisation (2020) Health topics/Obesity Switzerland: WHO. http://www.who.int/topics/obesity/en/. Accessed April 2020
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, Gordon DJ et al (2005) Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome. Circulation 112(17):2735–2752. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.169404
Hazem A, Bissada NF, Demko C, Paes A, Lang LA (2016) Comparison of preprosthetic implant complications and failures between obese and nonobese patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 31(5):1093–1099. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.4438
Coelho PG, Pippenger B, Tovar N, Koopmans SJ, Plana NM, Graves DT, Engebretson S et al (2018) Effect of obesity or metabolic syndrome and diabetes on osseointegration of dental implants in a miniature swine model : a pilot study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 76(8):1677–1687
Yarrow JF, Toklu HZ, Balaez A, Phillips EG, Otzel DM, Chen C, Wronski TJ et al (2016) Fructose consumption does not worsen bone deficits resulting from high-fat feeding in young male rats. Bone 85:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2016.02.004
Li W, Xu P, Wang C, Ha X, Gu Y, Wang Y, Zhang J et al (2017) The effects of fat-induced obesity on bone metabolism in rats. Obes Res Clin Pract 11(4):454–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orcp.2016.12.001
Fujita Y, Maki K (2016) High-fat diet-induced obesity triggers alveolar bone loss and spontaneous periodontal disease in growing mice. BMC Obesity 3(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40608-016-0082-8
Keuroghlian A, Barroso AD, Kirikian G, Bezouglaia O, Tintut Y, Tetradis S, Moy P et al (2015) The effects of hyperlipidemia on implant osseointegration in the mouse femur. J Oral Implantol 41(2):e7–e11. https://doi.org/10.1563/aaid-joi-d-13-00105
King S, Baptiston Tanaka C, Ross D, Kruzic JJ, Levinger I, Klineberg I, Brennan-Speranza TC (2020) A diet high in fat and fructose adversely affects osseointegration of titanium implants in rats. Clin Exp Dent Res 6(1):107–116. https://doi.org/10.1002/cre2.255
Clarke B (2008) Normal bone anatomy and physiology. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3(Supplement 3):S131–S139. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.04151206
Davies JE (1998) Mechanisms of endosseous integration. Int J Prosthodont 11(5):391–401
Sims NA, Martin TJ (2014) Coupling the activities of bone formation and resorption: a multitude of signals within the basic multicellular unit. Bonekey Rep 3:481. https://doi.org/10.1038/bonekey.2013.215
Pederson L, Ruan M, Westendorf JJ, Khosla S, Oursler MJ (2008) Regulation of bone formation by osteoclasts involves Wnt/BMP signaling and the chemokine sphingosine-1-phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(52):20764–20769. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0805133106
Boyce BF, Xing L (2008) Functions of RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch Biochem Biophys 473(2):139–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2008.03.018
Bonewald LF (2011) The amazing osteocyte. J Bone Miner Res 26(2):229–238. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.320
Hay E, Bouaziz W, Funck-Brentano T, Cohen-Solal M (2016) Sclerostin and bone aging: a mini-review. Gerontology 62(6):618–623. https://doi.org/10.1159/000446278
Katcher HI, Hill AM, Lanford JLG, Yoo JS, Kris-Etherton PM (2009) Lifestyle approaches and dietary strategies to lower LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides and raise HDL-cholesterol. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 38(1):45–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2008.11.010
Frommer K, Schäffler A, Lange U, Rehart S, Steinmeyer J, Rickert M, Müller-Ladner U et al (2017) 02.03| Influence of free fatty acids on osteoblasts and osteoclasts in rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-211050.3%
Braun T, Zwerina J (2011) Positive regulators of osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3380
Ibrahim MM (2010) Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: structural and functional differences. Obes Rev 11(1):11–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2009.00623.x
Friedman JM, Halaas JL (1998) Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 395(6704):763–770. https://doi.org/10.1038/27376
Pyrzak B, Ruminska M, Popko K, Demkow U. Adiponectin as a biomarker of the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. Eur J Med Res. 2010;15 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):147–51 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-783x-15-s2-147.
Kim TY, Schafer AL (2016) Diabetes and bone marrow adiposity. Curr Osteoporos Rep 14(6):337–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-016-0336-x
Tencerova M, Figeac F, Ditzel N, Taipaleenmäki H, Nielsen TK, Kassem M (2018) High-fat diet-induced obesity promotes expansion of bone marrow adipose tissue and impairs skeletal stem cell functions in mice. J Bone Miner Res 33(6):1154–1165. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.3408
Elbaz A, Wu X, Rivas D, Gimble JM, Duque G (2010) Inhibition of fatty acid biosynthesis prevents adipocyte lipotoxicity on human osteoblasts in vitro. J Cell Mol Med 14(4):982–991. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00751.x
Coutel X, Delattre J, Marchandise P, Falgayrac G, Béhal H, Kerckhofs G, Penel G et al (2019) Mandibular bone is protected against microarchitectural alterations and bone marrow adipose conversion in ovariectomized rats. Bone 127:343–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2019.06.031
Kaneshiro S, Ebina K, Shi K, Higuchi C, Hirao M, Okamoto M, Koizumi K et al (2014) IL-6 negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation through the SHP2/MEK2 and SHP2/Akt2 pathways in vitro. J Bone Miner Metab 32(4):378–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-013-0514-1
Zhao B (2017) TNF and bone remodeling. Curr Osteoporos Rep 15(3):126–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-017-0358-z
Glantschnig H, Fisher JE, Wesolowski G, Rodan GA, Reszka AA (2003) M-CSF, TNFα and RANK ligand promote osteoclast survival by signaling through mTOR/S6 kinase. Cell Death Differ 10(10):1165–1177. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401285
Baumann H, Gauldie J (1994) The acute phase response. Immunol Today 15(2):74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-5699(94)90137-6
Cho I-J, Choi KH, Oh CH, Hwang YC, Jeong I-K, Ahn KJ, Chung H-Y (2016) Effects of C-reactive protein on bone cells. Life Sci 145:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2015.12.021
Jia Z-K, Li H-Y, Liang Y-L, Potempa LA, Ji S-R, Wu Y (2018) Monomeric C-reactive protein binds and neutralizes receptor activator of NF-κB ligand-induced osteoclast differentiation. Front Immunol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00234
Dursun E, Tözüm TF (2016) Peri-implant crevicular fluid analysis, enzymes and biomarkers: a systemetic review. J Oral Maxillofac Res 7(3):e9
Fonseca FJPO, Junior MM, Lourenço EJV, de Moraes TD, Figueredo CM (2014) Cytokines expression in saliva and peri-implant crevicular fluid of patients with peri-implant disease. Clin Oral Implant Res 25(2):e68–e72. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12052
Rakic M, Lekovic V, Nikolic-Jakoba N, Vojvodic D, Petkovic-Curcin A, Sanz M (2013) Bone loss biomarkers associated with peri-implantitis. A cross-sectional study. Clin Oral Implants Res 24(10):1110–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02518.x
Borst SE (2004) The role of TNF-α in insulin resistance. Endocrine 23(2):177–182. https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:23:2-3:177
Cefalu WT (2001) Insulin resistance: cellular and clinical concepts. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 226(1):13–26. https://doi.org/10.1177/153537020122600103
Wilcox G (2005) Insulin and insulin resistance. Clin Biochem Rev 26(2):19–39
American Diabetes Association (2009) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 32(Supplement 1):S62–S67. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-S062
Thrailkill KM, Charles K, Lumpkin J, Bunn RC, Kemp SF, Fowlkes JL (2005) Is insulin an anabolic agent in bone? Dissecting the diabetic bone for clues. Endocrinol Metab. 289(5):E735–E745. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00159.2005
Freude T, Braun KF, Haug A, Pscherer S, Stöckle U, Nussler AK, Ehnert S (2012) Hyperinsulinemia reduces osteoblast activity in vitro via upregulation of TGF-β. J Mol Med 90(11):1257–1266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-012-0948-2
Huang S, Kaw M, Harris MT, Ebraheim N, McInerney MF, Najjar SM, Lecka-Czernik B (2010) Decreased osteoclastogenesis and high bone mass in mice with impaired insulin clearance due to liver-specific inactivation to CEACAM1. Bone 46(4):1138–1145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2009.12.020
Fulzele K, Riddle RC, DiGirolamo DJ, Cao X, Wan C, Chen D, Faugere M-C et al (2010) Insulin receptor signaling in osteoblasts regulates postnatal bone acquisition and body composition. Cell 142(2):309–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.002
Koldsland OC, Scheie AA, Aass AM (2010) Prevalence of peri-implantitis related to severity of the disease with different degrees of bone loss. J Periodontol 81(2):231–238. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2009.090269
Derks J, Tomasi C (2015) Peri-implant health and disease. A systematic review of current epidemiology. J Clin Periodontol 42(S16):S158–S71. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12334
Albrektsson T, Chracanovic B, Jacobsson M, Wennerberg A (2017) Osseointegration of implants-A biological and clinical overview. JSM Dent Surg 2(3):1022
Albrektsson T, Jemt T, Molne J, Tengvall P, Wennerberg A (2019) On inflammation-immunological balance theory-A critical apprehension of disease concepts around implants: Mucositis and marginal bone loss may represent normal conditions and not necessarily a state of disease. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 21(1):183–189. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12711
Chrcanovic B, Kisch J, Albrektsson T, Wennerberg A (2017) Analysis of risk factors for cluster behavior of dental implant failures. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 19(4):632–642. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12485
King S, Klineberg I, Levinger I, Brennan-Speranza TC (2016) The effect of hyperglycaemia on osseointegration: a review of animal models of diabetes mellitus and titanium implant placement. Arch Osteoporos 11(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11657-016-0284-1
Srinivasan M, Meyer S, Mombelli A, Muller F (2017) Dental implants in the elderly population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res 28(8):920–930. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12898
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SK was involved in the conception, design and drafting of the manuscript. IK and TBS were involved in conception and revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Shalinie King, Iven Klineberg, and Tara C. Brennan-Speranza declares that they have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
King, S., Klineberg, I. & Brennan-Speranza, T.C. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction: Impact on Bone and Osseointegration. Calcif Tissue Int 110, 32–40 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-021-00899-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-021-00899-0