Abstract
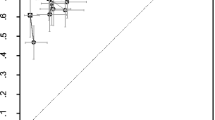
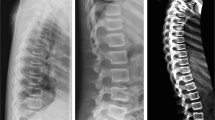
The aim of this study is to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of vertebral fractures assessment (VFA) in comparison with conventional radiography in identifying vertebral fractures in children and adolescents affected by OI. On 58 patients (33 males, 25 females; age range 1–18 years; 41 children and 17 adolescents) with osteogenesis imperfecta (OI type I, n = 44, OI type III, n = 4; OI type IV, n = 10), lateral spine images by radiographs and by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) were acquired. For vertebral fracture diagnosis, plain radiographs were used as “gold standard” and VFA and morphometric X-ray absorptiometry (MXA) were performed. The visualized vertebrae were 738 (97.9 %) by radiographs and 685 (90.9 %) by DXA of a total of 754 vertebrae from T4 to L4. VFA and MXA identified, respectively, 129 (74 %) and 116 (66 %) of the 175 vertebral fractures detected by radiographs. Radiographs identified 36 patients with vertebral fractures, VFA 35 and MXA 41 (6 false positives). On a per vertebra basis, radiographs and VFA had elevated agreement (93.9 %; k score 0.81, 95 % CI 0.76–0.86), that resulted slightly lower for MXA (90.6 %; k score 0.72, 95 % CI 0.65–0.78). VFA and MXA demonstrated high sensitivity (95.6 and 94.1 %, respectively) while specificity was 100 % for VFA and 90.6 % for MXA on a per patient basis; the agreement was excellent for VFA (98.3 %; k score 0.96, 95 % CI 0.89–1.03) and good for MXA (87.9 %; k score 0.73, 95 % CI 0.55–0.91). The diagnostic performance parameters resulted better for VFA (sensitivity 95.6 %; specificity 100 %; PPV 100 %; NPV 97.2 %), than for MXA (sensitivity 94.1 %; specificity 85.4 %; PPV 72.7 %; NPV 97.2 %). The results of our study demonstrate the reliability of VFA for diagnosis of vertebral fractures in children with OI suggesting its use as a more safe and practical alternative to conventional radiography.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rauch F, Glorieux FH (2004) Osteogenesis imperfecta. Lancet 363:1377–1385
Kok DJ, Uiterwaal CS, Van Dongen AJ, Kramer PP, Pruijs HE, Engelbert RH, Verbout AJ, Schweitzer DH, Sakkers RJ (2003) The interaction between Sillence type and BMD in osteogenesis imperfecta. Calcif Tissue Int 73:441–445
Engelbert RH, Gerver WJ, Breslau-Siderius LJ, van der Graaf Y, Pruijs HE, van Doorne JM, Beemer FA, Helders PJ (1998) Spinal complications in osteogenesis imperfecta: 47 patients 1-16 years of age. Acta Orthop Scand 69:283–286
Widmann RF, Bitan FD, Laplaza FJ, Burke SW, DiMaio MF, Schneider R (1999) Spinal deformity, pulmonary compromise, and quality of life in osteogenesis imperfecta. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 24:1673–1678
Glorieux FH, Bishop NJ, Plotkin H, Chabot G, Lanoue G, Travers R (1998) Cyclic administration of pamidronate in children with severe osteogenesis imperfecta. N Engl J Med 339:947–952
Sumnik Z, Land C, Rieger-Wettengl G, Korber F, Stabrey A, Schoenau E (2004) Effect of pamidronate treatment on vertebral deformity in children with primary osteoporosis. A pilot study using radiographic morphometry. Horm Res 61:137–142
Land C, Rauch F, Travers R, Glorieux FH (2007) Osteogenesis imperfecta type VI in childhood and adolescence: effects of cyclical intravenous pamidronate treatment. Bone 40:638–644
Gatti D, Antoniazzi F, Prizzi R, Braga V, Rossini M, Tato L, Viapiana O, Adami S (2005) Intravenous neridronate in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: a randomized controlled study. J Bone Miner Res 20:758–763
Semler O, Beccard R, Palmisano D, Demant A, Fricke O, Schoenau E, Koerber F (2011) Reshaping of vertebrae during treatment with neridronate or pamidronate in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. Horm Res Paediatr 76:321–327
Ward LM, Rauch F, Whyte MP, D’Astous J, Gates PE, Grogan D, Lester EL, McCall RE, Pressly TA, Sanders JO, Smith PA, Steiner RD, Sullivan E, Tyerman G, Smith-Wright DL, Verbruggen N, Heyden N, Lombardi A, Glorieux FH (2011) Alendronate for the treatment of pediatric osteogenesis imperfecta: a randomized placebo-controlled study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:355–364
Guglielmi G, Diacinti D, van Kuijk C, Aparisi F, Krestan C, Adams JE, Link TM (2008) Vertebral morphometry: current methods and recent advances. Eur Radiol 18:1484–1496
Damilakis J, Adams JE, Guglielmi G, Link TM (2010) Radiation exposure in X-ray-based imaging techniques used in osteoporosis. Eur Radiol 20:2707–2714
Mayranpaa MK, Helenius I, Valta H, Mayranpaa MI, Toiviainen-Salo S, Makitie O (2007) Bone densitometry in the diagnosis of vertebral fractures in children: accuracy of vertebral fracture assessment. Bone 41:353–359
Buehring B, Krueger D, Checovich M, Gemar D, Vallarta-Ast N, Genant HK, Binkley N (2010) Vertebral fracture assessment: impact of instrument and reader. Osteoporos Int 21:487–494
Fuerst T, Wu C, Genant HK, von Ingersleben G, Chen Y, Johnston C, Econs MJ, Binkley N, Vokes TJ, Crans G, Mitlak BH (2009) Evaluation of vertebral fracture assessment by dual X-ray absorptiometry in a multicenter setting. Osteoporos Int 20:1199–1205
Jager PL, Jonkman S, Koolhaas W, Stiekema A, Wolffenbuttel BH, Slart RH (2011) Combined vertebral fracture assessment and bone mineral density measurement: a new standard in the diagnosis of osteoporosis in academic populations. Osteoporos Int 22:1059–1068
Diacinti D, Del Fiacco R, Pisani D, Todde F, Cattaruzza MS, Arima S, Romagnoli E, Pepe J, Cipriani C, Minisola S (2012) Diagnostic performance of vertebral fracture assessment by the lunar iDXA scanner compared to conventional radiography. Calcif Tissue Int 91:335–342
Carter DR, Bouxsein ML, Marcus R (1992) New approaches for interpreting projected bone densitometry data. J Bone Miner Res 7:137–145
Genant HK, Wu CY, van Kuijk C, Nevitt MC (1993) Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. J Bone Miner Res 8:1137–1148
Kramer MS, Feinstein AR (1981) Clinical biostatistics. LIV. The biostatistics of concordance. Clin Pharmacol Ther 29:111–123
Damiano J, Kolta S, Porcher R, Tournoux C, Dougados M, Roux C (2006) Diagnosis of vertebral fractures by vertebral fracture assessment. J Clin Densitom 9:66–71
Chapurlat RD, Duboeuf F, Marion-Audibert HO, Kalpakcioglu B, Mitlak BH, Delmas PD (2006) Effectiveness of instant vertebral assessment to detect prevalent vertebral fracture. Osteoporos Int 17:1189–1195
Ferrar L, Jiang G, Armbrecht G, Reid DM, Roux C, Gluer CC, Felsenberg D, Eastell R (2007) Is short vertebral height always an osteoporotic fracture? The Osteoporosis and Ultrasound Study (OPUS). Bone 41:5–12
Hospers IC, van der Laan JG, Zeebregts CJ, Nieboer P, Wolffenbuttel BH, Dierckx RA, Kreeftenberg HG, Jager PL, Slart RH (2009) Vertebral fracture assessment in supine position: comparison by using conventional semiquantitative radiography and visual radiography. Radiology 251:822–828
Land C, Rauch F, Munns CF, Sahebjam S, Glorieux FH (2006) Vertebral morphometry in children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta: effect of intravenous pamidronate treatment. Bone 39:901–906
Conflict of interest
Dr. Minisola reports personal fee from Abiogen Pharma, personal fee from Amgen, personal fee from Bruno Farmaceutici, personal fee from Chiesi Farmaceutici, personal fee from Eli Lilly, personal fee from ItalFarmaco SpA, personal fee from Mediolanum Farmaceutici, personal fee from Merck Sharp & Dohme, personal fee from Novartis, personal fee from Pfizer, outside the submitted work. The other authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
The parents of all the children’s and adolescent’s gave written informed consent prior to the inclusion in the study. The protocol was performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments and was approved by the “Sapienza” University of Rome Ethics Committee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diacinti, D., Pisani, D., D’Avanzo, M. et al. Reliability of Vertebral Fractures Assessment (VFA) in Children with Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Calcif Tissue Int 96, 307–312 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-015-9960-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-015-9960-1