Abstract.
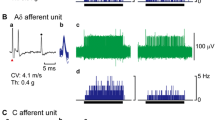
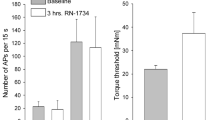
Nociceptin is known to act peripherally in the rat knee joint to modulate articular mechanosensitivity and it has been postulated that neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptors may be involved in this process. To test this hypothesis, single unit extracellular recordings were made from knee joint primary afferents in response to normal and extreme rotation of the joint. Afferent firing rate was assessed following close intraarterial injection of the NK1 antagonist RP67580 followed by administration of 20 nmol nociceptin. With both normal and hyper-rotation of the knee, nociceptin was unable to elicit its usual mechanomodulatory effect such that afferent activity was not significantly different from control (P=0.7572 and P=0.9182 for normal and hyper-rotation of the joint, respectively). These data indicate that nociceptin-induced mechanosensitivity changes in the rat knee depend upon NK1 receptor activation possibly through secondary release of substance P.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McDougall, J., Hanesch, U., Pawlak, M. et al. Participation of NK1 receptors in nociceptin-induced modulation of rat knee joint mechanosensitivity. Exp Brain Res 137, 249–253 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210000650
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210000650