Abstract
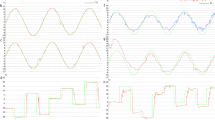
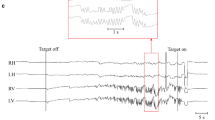
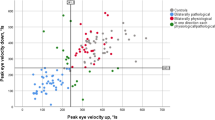
Down syndrome (DS), the most common genetically defined cause of intellectual disability, is the phenotypic consequence of a supernumerary chromosome 21. Persons with DS commonly display deficits in visuomotor integration, motor coordination, and balance. Despite the key roles of the optokinetic and vestibular systems in these submodalities of motor function, a systematic investigation of the optokinetic nystagmus (OKN) and vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) in persons with DS had lacked in the literature. Accordingly, this study generated quantitative data on oculomotor function in persons with DS under optokinetic and sinusoidal smooth pursuit stimulation. Thirty-two participants with DS (14–36 years old, equally divided by gender) and 32 chronological age- and gender-matched typically developing controls were recruited from the community. Eye movements were recorded by binocular video oculography and an LCD projector produced visual stimulation. Assessments of the gain and frequency of slow phase of OKN beats and number and mean amplitude of intruding saccades during smooth pursuit were performed. Individuals with DS displayed angular velocity-dependent reduction in OKN gain and number of produced nystagmus beats compared to controls. The gain of the smooth pursuit was not significantly different between participants with DS and control participants. However, the number and mean amplitude of intruding saccades during smooth pursuit were increased in participants with DS compared to control participants. These findings may have implications to the understanding of the neurological basis of the motor dysfunction that affects performance in many practical tasks persons with DS encounter in their everyday lives.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agiovlasitis S, McCubbin JA, Yun J, Mpitsos G, Pavol MJ (2009) Effects of Down syndrome on three-dimensional motion during walking at different speeds. Gait Posture 30:345–350
Almeida GL, Corcos DM, Hasan Z (2000) Horizontal-plane arm movements with direction reversals performed by normal individuals and individuals with down syndrome. J Neurophysiol 84:1949–1960
Aruin AS, Almeida GL, Latash ML (1996) Organization of a simple two-joint synergy in individuals with Down syndrome. Am J Ment Retard 101:256–268
Averbuch-Heller L, Dell’Osso LF, Jacobs JB, Remler BF (1999) Latent and congenital nystagmus in Down syndrome. J Neuroophthalmol 19:166–172
Baxter LL, Moran TH, Richtsmeier JT, Troncoso J, Reeves RH (2000) Discovery and genetic localization of Down syndrome cerebellar phenotypes using the Ts65Dn mouse. Hum Mol Genet 9:195–202
Bedell HE, Yap YL, Flom MC (1990) Fixational drift and nasal-temporal pursuit asymmetries in strabismic amblyopes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 31:968–976
Bense S, Janusch B, Vucurevic G, Bauermann T, Schlindwein P, Brandt T, Stoeter P, Dieterich M (2006) Brainstem and cerebellar fMRI-activation during horizontal and vertical optokinetic stimulation. Exp Brain Res 174:312–323
Bodensteiner JB, Smith SD, Schaefer GB (2003) Hypotonia, congenital hearing loss, and hypoactive labyrinths. J Child Neurol 18:171–173
Bucci MP, Kapoula Z, Yang Q, Roussat B, Bremond-Gignac D (2002) Binocular coordination of saccades in children with strabismus before and after surgery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:1040–1047
Carvalho RL, Almeida GL (2009) Assessment of postural adjustments in persons with intellectual disability during balance on the seesaw. J Intellect Disabil Res 53:389–395
Cheng M, Outerbridge JS (1975) Optokinetic nystagmus during selective retinal stimulation. Exp Brain Res 23:129–139
Chicoine B, McGuire D, Rubin S (1998) Adults with Down syndrome: specialty clinic perspectives. In: Janicki MP, Dalton AJ (eds) Dementia, aging, and intellectual disabilities: a handbook. Brunner/Mazel, New York, pp 278–293
Collewijn H, Martins AJ, Steinman RM (1983) Compensatory eye movements during active and passive eye movements; fast adaptation to changes in visual magnification. J Physiol 340:259–286
Cregg M, Woodhouse JM, Stewart RE, Pakeman VH, Bromham NR, Gunter HL, Trojanowska L, Parker M, Fraser WI (2003) Development of refractive error and strabismus in children with Down syndrome. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:1023–1030
da Cunha RP, Moreira JB (1996) Ocular findings in Down’s syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol 122:236–244
Davous P, Lamour Y, Roudier M (1989) Standardized neurologic study in senile dementia of Alzheimer’s type. Encephale 15:387–396
Dieterich M, Bucher SF, Seelos KC, Brandt T (2000) Cerebellar activation during optokinetic stimulation and saccades. Neurology 54:148–155
Gomes MM, Barela JA (2007) Postural control in down syndrome: the use of somatosensory and visual information to attenuate body sway. Mot Control 11:224–234
Hiles DA, Hoyme SH, McFarlane F (1974) Down’s syndrome and strabismus. Am Orthopt J 24:63–68
Jaeger EA (1980) Ocular findings in Down’s syndrome. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 78:808–845
Knapp CM, Gottlob I, McLean RJ, Proudlock FA (2008) Horizontal and vertical look and stare optokinetic nystagmus symmetry in healthy adult volunteers. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49:581–588
Koo BK, Blaser S, Harwood-Nash D, Becker LE, Murphy EG (1992) Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of delayed myelination in Down syndrome: a case report and review of the literature. J Child Neurol 7:417–421
Lam MY, Hodges NJ, Virji-Babul N, Latash ML (2009) Evidence for slowing as a function of index of difficulty in young adults with Down syndrome. Am J Intellect Dev Disabil 114:411–426
Latash ML, Anson JG (2006) Synergies in health and disease: relations to adaptive changes in motor coordination. Phys Ther 86:1151–1160
Leverenz JB, Raskind MA (1998) Early amyloid deposition in the medial temporal lobe of young Down syndrome patients: a regional quantitative analysis. Exp Neurol 150:296–304
Levin S, Lipton RB, Holzman PS (1981) Pursuit eye movements in psychopathology: effects of target characteristics. Biol Psychiatry 16:255–267
Mann DM, Jones D, Prinja D, Purkiss MS (1990) The prevalence of amyloid (A4) protein deposits within the cerebral and cerebellar cortex in Down’s syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 80:318–327
Molnar GE (1978) Analysis of motor disorder in retarded infants and young children. Am J Ment Defic 83:213–222
Nadel L (2003) Down’s syndrome: a genetic disorder in biobehavioral perspective. Genes Brain Behav 2:156–166
Patterson D, Costa AC (2005) Down syndrome and genetics—a case of linked histories. Nat Rev Genet 6:137–147
Pennington BF, Moon J, Edgin J, Stedron J, Nadel L (2003) The neuropsychology of Down syndrome: evidence for hippocampal dysfunction. Child Dev 74:75–93
Post RB, Rodemer CS, Dichgans J, Leibowitz HW (1979) Dynamic orientation responses are independent of refractive error. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci (Suppl) 18:140
Pueschel SM, Louis S, McKnight P (1991) Seizure disorders in Down syndrome. Arch Neurol 48:318–320
Raz N, Torres IJ, Briggs SD, Spencer WD, Thornton AE, Loken WJ, Gunning FM, McQuain JD, Driesen NR, Acker JD (1995) Selective neuroanatomic abnormalities in Down’s syndrome and their cognitive correlates: evidence from MRI morphometry. Neurology 45:356–366
Romano C, Tine A, Fazio G, Rizzo R, Colognola RM, Sorge G, Bergonzi P, Pavone L (1990) Seizures in patients with trisomy 21. Am J Med Genet Suppl 7:298–300
Shumway-Cook A, Woollacott MH (1985) Dynamics of postural control in the child with Down syndrome. Phys Ther 65:1315–1322
Silverman W (2007) Down syndrome: cognitive phenotype. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 13:228–236
Simons B, Buttner U (1985) The influence of age on optokinetic nystagmus. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurol Sci 234:369–373
Smith BA, Kubo M, Black DP, Holt KG, Ulrich BD (2007) Effect of practice on a novel task–walking on a treadmill: preadolescents with and without Down syndrome. Phys Ther 87:766–777
Smyrnis N (2008) Metric issues in the study of eye movements in psychiatry. Brain Cogn 68:341–358
Tsiaras WG, Pueschel S, Keller C, Curran R, Giesswein S (1999) Amblyopia and visual acuity in children with Down’s syndrome. Br J Ophthalmol 83:1112–1114
Valmaggia C, Proudlock F, Gottlob I (2003) Optokinetic nystagmus in strabismus: are asymmetries related to binocularity? Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:5142–5150
van den Berg AV, Collewijn H (1988) Directional asymmetries of human optokinetic nystagmus. Exp Brain Res 70:597–604
Wagner RS, Caputo AR, Reynolds RD (1990) Nystagmus in Down’s syndrome. Ophthalmology 97:1439–1444
Welsh TN, Hoang S, Chandrasekharan S, Paulson S, Lynnes A, Ayres F (2009) Goal-directed saccades of young adults with and without Down Syndrome. Down Syndr Q 11:10–15
Wong V, Ho D (1997) Ocular abnormalities in Down syndrome: an analysis of 140 Chinese children. Pediatr Neurol 16:311–314
Zigman WB, Lott IT (2007) Alzheimer’s disease in Down syndrome: neurobiology and risk. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 13:237–246
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Coleman Institute for Cognitive Disabilities, Boulder, Colorado. The author also received salary support from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) Grants HD37424 and HD056235 and from the Linda Crnic Institute during the data analysis phase of this project. This study could not have been carried out without the enthusiastic support of the participants in the study and the Mile High Down Syndrome Association. The author is indebted to the anonymous expert reviewers of this manuscript for their constructive and insightful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, A.C.S. An assessment of optokinetic nystagmus (OKN) in persons with down syndrome. Exp Brain Res 214, 381–391 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-011-2834-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-011-2834-5