Abstract
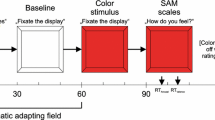
In order to study the interaction between pictures and words, we investigated the variations of their actual arousal levels through the observation of the positivity offset and negativity bias under different conditions. We used emotional pictures and emotional Chinese words to construct stimuli under four conditions: (1) only a word was presented (Word Only condition), (2) only a picture was presented (Picture Only condition), (3) a word was presented before a picture (Word Before Picture condition) and (4) a picture was presented before a word (Picture Before Word condition). The picture and word in each target pair under the conditions (3) and (4) were congruous in content and emotion. Significant negativity bias is noticed under the Picture Only and the Word Only conditions. Effects analogous to a positivity offset are observed under the other two conditions. It is suggested that the actual arousal levels of multiple stimuli, such as those presented under the conditions (3) and (4) are different from those of individual pictures and individual words, while the actual arousal levels of individual pictures do not differ significantly from those of individual words. The results indicate that content consistency can lead to a reduction in emotional attention, and also that the influence of pictures on words will differ from the opposite condition.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amrhein C, Muhlberger A, Pauli P, Wiedemann G (2004) Modulation of event-related brain potentials during affective picture processing: a complement to startle reflex and skin conductance response? Int J Psychophysiol 54:231–240
An SK, Lee SJ, Lee CH, Cho HS, Lee PG, Lee CI, Lee E, Roh KS, Namkoong K (2003) Reduced P3 amplitudes by negative facial emotional photographs in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 64:125–135
Avero P, Calvo MG (2006) Affective priming with pictures of emotional scenes: the role of perceptual similarity and category relatedness. Span J Psychol 9:10–18
Cano ME, Class QA, Polich J (2009) Affective valence, stimulus attributes, and P300: Color vs. black/white and normal vs. scrambled images. Int J Psychophysiol 71:17–24
Carretie L, Mercado F, Tapia M, Hinojosa JA (2001) Emotion, attention, and the ‘negativity bias’, studied through event-related potentials. Int J Psychophysiol 41:75–85
Carretie L, Hinojosa JA, Martin-Loeches M, Mercado F, Tapia M (2004a) Automatic attention to emotional stimuli: neural correlates. Hum Brain Mapp 22:290–299
Carretie L, Mercado F, Hinojosa JA, Martin-Loeches M, Sotillo M (2004b) Valence-related vigilance biases in anxiety studied through event-related potentials. J Affect Disord 78:119–130
Casarotto S, Bianchi AM, Ricciardi E, Gentili C, Vanello N, Guazzelli M, Pietrini P, Chiarenza GA, Cerutti S (2008) Spatiotemporal dynamics of single-letter reading: a combined ERP-FMRI study. Arch Ital Biol 146:83–105
Conroy MA, Polich J (2007) Affective valence and P300 when stimulus arousal level is controlled. Cogn Emot 21:891–901
Cuthbert B, Schupp H, Mcmanis M, Hillman C, Bradley M, Lang P (1995) Cortical slow waves—emotional perception and processing. Psychophysiology 32:S26
Cuthbert BN, Schupp HT, Bradley MM, Birbaumer N, Lang PJ (2000) Brain potentials in affective picture processing: covariation with autonomic arousal and affective report. Biol Psychol 52:95–111
Deacon D, Uhm TJ, Ritter W, Hewitt S, Dynowska A (1999) The lifetime of automatic semantic priming effects may exceed two-seconds. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 7:465–472
Delplanque S, Lavoie ME, Hot P, Silvert L, Sequeira H (2004) Modulation of cognitive processing by emotional valence studied through event-related potentials in humans. Neurosci Lett 356:1–4
Delplanque S, Silvert L, Hot P, Sequeira H (2005) Event-related P3a and P3b in response to unpredictable emotional stimuli. Biol Psychol 68:107–120
Diedrich O, Naumann E, Maier S, Becker G, Bartussek D (1997) A frontal positive slow wave in the ERP associated with emotional slides. J Psychophysiol 11:71–84
Dolcos F, Cabeza R (2002) Event-related potentials of emotional memory: encoding pleasant, unpleasant, and neutral pictures. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 2:252–263
Flaisch T, Stockburger J, Schupp HT (2008) Affective prime and target picture processing: an ERP analysis of early and late interference effects. Brain Topogr 20:183–191
Golob EJ, Starr A (2000) Age-related qualitative differences in auditory cortical responses during short-term memory. Clin Neurophysiol 111:2234–2244
Hackley SA, Woldorff M, Hillyard SA (1990) Cross-modal selective attention effects on retinal, myogenic, brainstem, and cerebral evoked potentials. Psychophysiology 27:195–208
Herbert C, Kissler J, Junghofer M, Peyk P, Rockstroh B (2006) Processing of emotional adjectives: evidence from startle EMG and ERPs. Psychophysiology 43:197–206
Hermans D, De Houwer J, Eelen P (2001) A time course analysis of the affective priming effect. Cogn Emot 15:143–165
Hermans D, Spruyt A, De Houwer J, Eelen P (2003) Affective priming with subliminally presented pictures. Can J Exp Psychol 57:97–114
Hill H, Ott F, Weisbrod M (2005) SOA-dependent N400 and P300 semantic priming effects using pseudoword primes and a delayed lexical decision. Int J Psychophysiol 56:209–221
Holmes EA, Mathews A, Mackintosh B, Dalgleish T (2008) The causal effect of mental imagery on emotion assessed using picture-word cues. Emotion 8:395–409
Huang YX, Luo YJ (2006) Temporal course of emotional negativity bias: an ERP study. Neurosci Lett 398:91–96
Ito TA, Cacioppo JT (2000) Electrophysiological evidence of implicit and explicit categorization processes. J Exp Soc Psychol 36:660–676
Ito TA, Cacioppo JT, Lang PJ (1998a) Eliciting affect using the international affective picture system: trajectories through evaluative space. Pers Soc Psychol Bull 24:855–879
Ito TA, Larsen JT, Smith NK, Cacioppo JT (1998b) Negative information weighs more heavily on the brain: the negativity bias in evaluative categorizations. J Pers Soc Psychol 75:887–900
Kanske P, Kotz SA (2007) Concreteness in emotional words: ERP evidence from a hemifield study. Brain Res 1148:138–148
Keil A, Bradley MM, Hauk O, Rockstroh B, Elbert T, Lang PJ (2002) Large-scale neural correlates of affective picture processing. Psychophysiology 39:641–649
Key AP, Dove GO, Maguire MJ (2005) Linking brainwaves to the brain: an ERP primer. Dev Neuropsychol 27:183–215
Lang PJ, Bradley MM, Cuthbert BN (2008) International affective picture system (IAPS): affective ratings of pictures and instruction manual. Technical report A-8, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL
Liu B, Xin S, Jin Z, Gao X, Gao S, Chu R, Deng B, Huang Y (2008a) A detailed study on the modulation of emotion processing by spatial location. In: Advances in neural networks-ISNN 2008, Part I, LNCS 5263, pp 107–116
Liu B, Xin S, Jin Z, Gao X, Gao S, Chu R, Huang Y, Deng B (2008b) The effect of task relevance on electrophysiological response to emotional stimuli. In: Advances in neural networks-ISNN 2008, Part I, LNCS 5263, pp 97–106
Luck SJ, Hillyard SA (1994) Spatial filtering during visual search: evidence from human electrophysiology. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 20:1000–1014
Mini A, Palomba D, Angrilli A, Bravi S (1996) Emotional information processing and visual evoked brain potentials. Percept Mot Skills 83:143–152
Naatanen R (1990) The role of attention in auditory information processing as revealed by event-related potentials and other brain measures of cognitive function. Behav Brain Sci 13:201–288
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9:97–113
Olofsson JK, Polich J (2007) Affective visual event-related potentials: arousal, repetition, and time-on-task. Biol Psychol 75:101–108
Palomba D, Angrilli A, Mini A (1997) Visual evoked potentials, heart rate responses and memory to emotional pictorial stimuli. Int J Psychophysiol 27:55–67
Pernet C, Basan S, Doyon B, Cardebat D, Demonet JF, Celsis P (2003) Neural timing of visual implicit categorization. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 17:327–338
Radilova J (1982) The late positive component of visual evoked response sensitive to emotional factors. Act Nerv Super (Praha) Suppl 3:334–337
Rozenkrants B, Polich J (2008) Affective ERP processing in a visual oddball task: arousal, valence, and gender. Clin Neurophysiol 119:2260–2265
Schupp HT, Cuthbert BN, Bradley MM, Cacioppo JT, Ito T, Lang PJ (2000) Affective picture processing: the late positive potential is modulated by motivational relevance. Psychophysiology 37:257–261
Schupp HT, Cuthbert BN, Bradley MM, Hillman CH, Hamm AO, Lang PJ (2004a) Brain processes in emotional perception: motivated attention. Cogn Emot 18:593–611
Schupp HT, Ohman A, Junghofer M, Weike AI, Stockburger J, Hamm AO (2004b) The facilitated processing of threatening faces: an ERP analysis. Emotion 4:189–200
Smith NK, Cacioppo JT, Larsen JT, Chartrand TL (2003) May I have your attention, please: electrocortical responses to positive and negative stimuli. Neuropsychologia 41:171–183
Starr A, Barrett G (1987) Disordered auditory short-term memory in man and event-related potentials. Brain 110(Pt 4):935–959
van Schie HT, Wijers AA, Mars RB, Benjamins JS, Stowe LA (2005) Processing of visual semantic information to concrete words: temporal dynamics and neural mechanisms indicated by event-related brain potentials. Cogn Neuropsychol 22:364–386
Watson D, Clark LA, Tellegen A (1988) Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. J Pers Soc Psychol 54:1063–1070
West WC, Holcomb PJ (2000) Imaginal, semantic, and surface-level processing of concrete and abstract words: an electrophysiological investigation. J Cogn Neurosci 12:1024–1037
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 90820304). The authors would like to thank the Laboratory of Neural Engineering (Tsinghua University) for providing the Neuroscan Synamps system and the NIMH Center for the Study of Emotion and Attention (University of Florida, Gainesville) for providing the pictures of IAPS (The International Affective Picture System).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Jin, Z., Wang, Z. et al. The interaction between pictures and words: evidence from positivity offset and negativity bias. Exp Brain Res 201, 141–153 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-2018-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-2018-8