Abstract
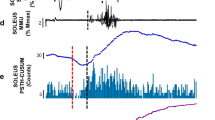
A medium-latency response (MLR) has been recorded from soleus during stance and walking, and has been attributed to stretch-evoked volleys in group II afferents. The present paper describes a MLR in soleus evoked by stimulating the deep peroneal nerve, documents its characteristics and addresses its likely origin. The MLR of soleus was recorded in healthy subjects and hemiplegic patients, following electrical stimulation of the deep peroneal nerve at the fibula at rest, during voluntary dorsiflexion, during plantar flexion, during external restraint to the ankle dorsiflexion movement, during limb cooling, during limb ischaemia and 1 h after the ingestion of tizanidine. The dorsiflexion movement of the foot was measured using an accelerometer. During cooling, ischaemia and after tizanidine, changes in the MLR were compared with changes in the soleus H reflex, Achilles tendon reflex and, during cooling, F waves of abductor hallucis. The MLR was facilitated by voluntary dorsiflexion, was suppressed during plantar flexion, disappeared when ankle movement was prevented, and was enhanced in patients with spastic hemiplegia. Cooling delayed the MLR significantly more than the Achilles tendon reflex and the abductor hallucis F wave. During ischaemia the response was significantly less affected than the Achilles tendon reflex and the soleus H reflex. Tizanidine suppressed the MLR, but not the soleus H and tendon reflexes. The latencies and the experiments using cooling, ischaemia and tizanidine implicate soleus group II afferents in the genesis of this response.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aniss AM, Gandevia SC, Burke D (1992) Reflex responses in active muscles elicited by stimulation of low-threshold afferents from the human foot. J Neurophysiol 67:1375–1384
Berger W, Dietz V, Quintern J (1984) Corrective reactions to stumbling in man: neuronal coordination of bilateral leg muscle activity during gait. J Physiol (Lond) 357:109–125
Bras H, Jankowska E, Noga B, Skoog B (1990) Comparison of effects of various types of NA and 5-HT agonists on transmission from group II muscle afferents in the cat. Eur J Neurosci 2:1029–1039
Burke D, McKeon B, Skuse NF (1981) The irrelevance of fusimotor activity to the Achilles tendon jerk of relaxed humans. Ann Neurol 10:547–550
Burke D, Gandevia SC, McKeon B (1983) The afferent volleys responsible for spinal proprioceptive reflexes in man. J Physiol (Lond) 339:535–552
Burke D, Aniss AM, Gandevia SC (1987) In-parallel and in-series behavior of human muscle spindle endings. J Neurophysiol 58:417–426
Corna S, Grasso M, Nardone A, Schieppati M (1995) Selective depression of medium-latency leg and foot muscle responses to stretch by an α2-agonist in humans. J Physiol 484:803–809
Dietz V, Quintern JB, Sillem M (1987) Stumbling reactions in man: significance of proprioceptive and pre-programmed mechanisms. J Physiol (Lond) 368:149–163
Ertekin C, Ertaş M, Efendi H, Larsson LE, Şirin H, Araç N, Toygar A, Demir Y (1995) A stable late soleus EMG response elicited by cortical stimulation during voluntary ankle dorsiflexion. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 97:75–283
Gandevia SC, Miller S, Aniss AM, Burke D (1986) Reflex influences on muscle spindle activity in relaxed human leg muscles. J Neurophysiol 56:159–170
Gibbs J, Harrison LM, Stephens JA (1995) Cutaneomuscular reflexes recorded from the lower limb in man during different tasks. J Physiol (Lond) 487:237–242
Grey MJ, Ladouceur M, Andersen JB, Nielsen JB, Sinkjær T (2001) Group II muscle afferents probably contribute to the medium latency soleus stretch reflex during walking in humans. J Physiol (Lond) 534:925–933
Grey MJ, Larsen B, Sinkjær T (2002) A task dependent change in the medium latency component of the soleus stretch reflex. Exp Brain Res 145:316–322
Hugon M (1973) Methodology of the Hoffmann reflex in man. In: Desmedt JE (ed) New developments in electromyography and clinical neurophysiology, vol 3. Karger, Basel, pp 277–293
Malmgren K, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (1988) Evidence for non-monosynaptic Ia excitation of human wrist flexor motoneurones, possibly via propriospinal neurons. J Physiol 405:747–764
Marchand-Pauvert V, Simonetta-Moreau M, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (1999) Cortical control of spinal pathways mediating group II excitation to human thigh motoneurones. J Physiol 517:301–313
Marchand-Pauvert V, Nicolas G, Burke D, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (2002) Suppression of the H reflex by disynaptic autogenetic inhibitory pathways activated by the test volley in humans. J Physiol (Lond) 542:963–976
Marchand-Pauvert V, Nicolas G, Marque P, Inglesias C, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (2005) Increase in group II excitation from ankle muscles to thigh motoneurones during human standing. J Physiol 566:257–271
Marque P, Pierrot-Deseilligny E, Simonetta-Moreau E (1996) Evidence for excitation of the human lower limb motoneurones by group II muscle afferents. Exp Brain Res 109:357–360
Marque P, Nicolas G, Simonetta-Moreau M, Pierrot-Deseilligny E, Marchand-Pauvert V (2005) Group II excitations from intrinsic foot muscles to human leg and thigh motoneurones. Exp Brain Res 161:486–501
Mazzaro N, Grey MJ, do Nascimento OF, Sinkjær T (2006) Afferent-mediated modulation of the soleus muscle activity during the stance phase of human walking. Exp Brain Res 173:713–723
Nardone A, Schieppati M (1998) Medium-latency response to muscle stretch in human lower limb: estimation of conduction velocity of group II fibres and central delay. Neurosci Lett 249:29–32
Nardone A, Schieppati M (2004) Group II spindle fibres and afferent control of stance. Clues from diabetic neuropathy. Clin Neurophysiol 115:779–789
Nardone A, Giordano A, Corrà T, Schieppati M (1990) Responses of leg muscles in humans displaced while standing. Effects of types of perturbation and of postural set. Brain 113:65–84
Nardone A, Grasso M, Giordano A, Schieppati M (1996) Different effect of height on latency of leg and foot short- and medium-latency EMG responses to perturbation of stance in humans. Neurosci Lett 206:89–92
Nielsen J, Petersen N, Fedirchuk B (1997) Evidence suggesting a transcortical pathway from cutaneous foot afferents to tibialis anterior motoneurones in man. J Physiol (Lond) 501:473–484
Pierrot-Deseilligny E, Burke D (2005) The circuitry of the human spinal cord. Its role in motor control and movement disorders. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 642
Sammut R, Thickbroom GW, Wilson SA, Mastaglia FL (1995) The origin of the soleus late response evoked by magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neuropyhsiol 97:164–168
Schieppati M, Nardone A (1995) Time course of “set”-related changes in muscle response to stance perturbation in humans. J Physiol (Lond) 487:787–796
Schieppati M, Nardone A (1997) Medium-latency stretch reflexes of foot and leg muscles analysed by cooling the lower limb in standing humans. J Physiol (Lond) 503:691–698
Schieppati M, Nardone A (1999) Group II spindle afferent fibers in humans: their possible role in the reflex control of stance. In: Binder MD (ed) Progress in brain research, vol 123. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 461–472
Schieppati M, Nardone A, Siliotto R, Grasso M (1995) Early and late stretch responses of human foot muscles induced by perturbation of stance. Exp Brain Res 105:411–422
Simonetta-Moreau M, Marque P, Marchand-Pauvert V, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (1999) The pattern of excitation of human lower limb motoneurones by probable group II muscle afferents. J Physiol (Lond) 517:287–300
Sinkjær T, Andersen JB, Nielsen JF, Hansen HJ (1999) Soleus long-latency stretch reflexes during walking in healthy and spastic humans. Clin Neurophysiol 110:951–959
Sinkjær T, Andersen JB, Ladouceur M, Christensen LOD, Nielsen JB (2000) Major role for sensory feedback in soleus EMG activity in the stance phase of walking in man. J Physiol (Lond) 523:817–827
Suga R, Tobimatsu S, Taniwaki T, Kira J-I, Kato M (2001) The soleus late response elicited magnetic stimulation reflects agonist–antagonist postural adjustment in the lower limbs. Clin Neurophysiol 112:2300–2311
Acknowledgments
Grant support from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia and partly Turkish Academy of Sciences (TUBA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
L.-E. Larsson: Deceased.
C. Ertekin: Retired.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uysal, H., Larsson, LE., Efendi, H. et al. Medium-latency reflex response of soleus elicited by peroneal nerve stimulation. Exp Brain Res 193, 275–286 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1621-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1621-4