Abstract
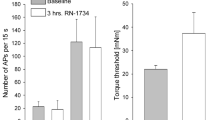
Synovial joints are complex sensory organs which provide continuous feedback regarding position sense and degree of limb movement. The transduction mechanisms which convert mechanical forces acting on the joint into an electrochemical signal which can then be transmitted to the central nervous system are not well understood. The present investigation examined the effect of the mechanogated ion channel blockers amiloride and gadolinium on knee joint mechanosensitivity. In deeply anaesthetised rats (sodium thiopental: 100–120 mg/kg, i.p.), single unit extracellular recordings were made from knee joint group III (Aδ) and group IV (C) primary afferents in response to mechanical rotation of the joint. Afferent firing rate was measured before and after topical application of either amiloride (0.1 mM, 1 mM) or gadolinium (250 μM) onto the receptive field of the sensory unit and recording was continued every 10 min up to a total of 50 min. With normal rotation of the knee, joint mechanosensitivity was significantly reduced by both amiloride (P<0.0001; n=10–21) and gadolinium (P=0.001; n=12) and this effect was sustained throughout the recording period. This investigation provides the first in vivo electrophysiological evidence that joint mechanotransduction involves the activation of amiloride and gadolinium-sensitive mechanogated ion channels. Future studies to determine the mechanogated ion channel subtypes present in joints and the modulation of their gating properties during inflammation may yield novel approaches for the control of arthritis pain.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker CL, McDougall JJ (2004) The cannabinomimetic arachidonyl-2-chloroethylamide (ACEA) acts on capsaicin-sensitive TRPV1 receptors but not cannabinoid receptors in rat joints. Br J Pharmacol 142:1361–1367
Carr MJ, Gover TD, Weinreich D, Undem BJ (2001) Inhibition of mechanical activation of guinea-pig airway afferent neurons by amiloride analogues. Brit J Pharmacol 133:1255–1262
Cho H, Shin J, Shin CY, Lee SY, Oh U (2002) Mechanosensitive ion channels in cultured sensory neurons of neonatal rats. J Neurosci 22:1238–1247
Drummond HA, Abboud FM, Welsh MJ (2000) Localization of beta and gamma subunits of ENaC in sensory nerve endings in the rat foot pad. Brain Res 884:1–12
Drummond HA, Price MP, Welsh MJ, Abboud FM (1998) A molecular component of the arterial baroreceptor mechanotransducer. Neuron 21:1435–1441
Drummond HA, Welsh MJ, Abboud FM (2001) ENaC subunits are molecular components of the arterial baroreceptor complex. Ann NY Acad Sc 940:42–47
Elinder F, Arhem P (1994) Effects of gadolinium on ion channels in the myelinated axon of Xenopus laevis: four sites of action. Biophys J 67:71–83
Ernstrom GG, Chalfie M (2002) Genetics of sensory mechanotransduction. Annu Rev Genet 36:411–453
Gauldie SD, McQueen DS, Pertwee R, Chessell IP (2001) Anandamide activates peripheral nociceptors in normal and arthritic rat knee joints. Br J Pharmacol 132:617–621
Gschossmann JM, Chaban VV, McRoberts JA, Raybould HE, Young SH, Ennes HS, Lembo T, Mayer EA (2000) Mechanical activation of dorsal root ganglion cells in vitro: comparison with capsaicin and modulation by kappa-opioids. Brain Res 856:101–110
Hajduczok G, Chapleau MW, Ferlic RJ, Mao HZ, Abboud FM (1994) Gadolinium inhibits mechanoelectrical transduction in rabbit carotid baroreceptors. Implication of stretch-activated channels. J Clin Investig 94:2392–2396
Hamill OP, McBride DW, Jr (1996) The pharmacology of mechanogated membrane ion channels. Pharmacol Rev 48:231–252
Hamill OP, McBride DW Jr (1998) Drug effects on mechano-gated channels. In: Soria B, Ceña V (eds) Ion channel pharmacology. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 271–278
Heppelmann B, Messlinger K, Neiss WF, Schmidt RF (1990) Ultrastructural three-dimensional reconstruction of group III and group IV sensory nerve endings ("free nerve endings") in the knee joint capsule of the cat: evidence for multiple receptive sites. J Comp Neurol 292:103–116
Heppelmann B, Messlinger K, Neiss WF, Schmidt RF (1995) Fine sensory innervation of the knee joint capsule by group III and group IV nerve fibers in the cat. J Comp Neurol 351:415–428
Jorgensen F, Ohmori H (1988) Amiloride blocks the mechano-electrical transduction channel of hair cells of the chick. J Physiol 403:577–588
Just S, Heppelmann B (2001) Neuropeptide Y changes the excitability of fine afferent units in the rat knee joint. Br J Pharmacol 132:703–708
Just S, Pawlak M, Heppelmann B (2000) Responses of fine primary afferent nerve fibres innervating the rat knee joint to defined torque. J Neurosci Methods 103:157–162
Lane JW, McBride DW Jr, Hamill OP (1991) Amiloride block of the mechanosensitive cation channel in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol 441:347–366
Lane JW, McBride DW Jr, Hamill OP (1992) Structure-activity relations of amiloride and its analogues in blocking the mechanosensitive channel in Xenopus oocytes. Br J Pharmacol 106:283–286
McCarter GC, Reichling DB, Levine JD (1999) Mechanical transduction by rat dorsal root ganglion neurons in vitro. Neurosci Lett 273:179–182
McDougall JJ, Hanesch U, Pawlak M, Schmidt RF (2001) Participation of NK1 receptors in nociceptin-induced modulation of rat knee joint mechanosensitivity. Exp Brain Res 137:249–253
Mutai H, Heller S (2003) Vertebrate and invertebrate TRPV-like mechanoreceptors. Cell Calcium 33:471–478
Price MP, McIlwrath SL, Xie J, Cheng C, Qiao J, Tarr DE, Sluka KA, Brennan TJ, Lewin GR, Welsh MJ (2001) The DRASIC cation channel contributes to the detection of cutaneous touch and acid stimuli in mice. Neuron 32:1071–1083
Rusch A, Kros CJ, Richardson GP (1994) Block by amiloride and its derivatives of mechano-electrical transduction in outer hair cells of mouse cochlear cultures. J Physiol 474:75–86
Suzuki M, Watanabe Y, Oyama Y, Mizuno A, Kusano E, Hirao A, Ookawara S (2003) Localization of mechanosensitive channel TRPV4 in mouse skin. Neurosci Lett 353:189–192
Yang XC, Sachs F (1989) Block of stretch-activated ion channels in Xenopus oocytes by gadolinium and calcium ions. Science 243:1068–1071
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung (98.057.1). JJMcD is funded by the Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research, the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, and the Arthritis Society of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funding: JJMcD is funded by the Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research, the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, and the Arthritis Society of Canada.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heppelmann, B., McDougall, J.J. Inhibitory effect of amiloride and gadolinium on fine afferent nerves in the rat knee: evidence of mechanogated ion channels in joints. Exp Brain Res 167, 114–118 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-0040-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-0040-z