Abstract
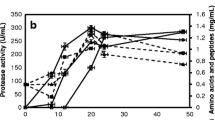
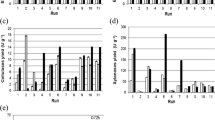
The bacterial detoxification of bitter lupine seed flours using two bacterial strains, previously shown to catabolize lupanine and to degrade other lupine alkaloids in liquid culture media containing protein, is described. The experimental starting conditions were selected to match the compositions and temperatures that might be expected in an industrial operation. A response surface methodology was used to pinpoint trends in alkaloid removal and to determine the best operating conditions for each strain. Alkaloid removal was modeled and the major constraints were identified. Based on the results obtained, it is suggested that enzymatically active bacterial lysates or purified enzyme complexes may possess a high potential for the detoxification of this material, thus constituting a new potential alternative for the processing of lupine seed material into valuable food ingredients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 29 February 2000 / Revised version: 5 May 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santana, F., Empis, J. Bacterial removal of quinolizidine alkaloids from Lupinus albus flours. Eur Food Res Technol 212, 217–224 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002170000221
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002170000221