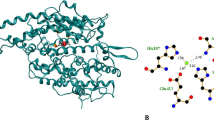
Abstract
Screening, isolation and in vitro or in vivo assays have been used for characterisation of bioactive peptides derived from food proteins. Bioinformatic computational methods as quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) and computer-predicted (in silico) proteolysis have been complementary to experimentally work. Recent developments in molecular characterisation and bioinformatics have further made it possible to “dock” small molecules (i.e. ligands) towards proteins and “score” their potential binding. Thus, methods like docking and virtual screening are becoming widely used in drug development, but to our knowledge have found limited use in food science. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory dipeptides were therefore docked towards a protein target. A significant relationship was found between results from computational docking and experimental values for inhibition (n=58, R 2=0.28, p<0.001). Docking and virtual screening were found feasible to identify promising bioactive peptide structures and could provide molecular understanding but does not replace the need for experimental verification and analysis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sousa MJ, Ardö Y, McSweeney PLH (2001) Int Dairy J 11:327–345. DOI: 10.1016/S0958-6946(01)00062-0
Gobbetti M, Stepaniak L, De Angelis M, Corsetti A, Di Cagno R (2002) Crit Rev Food Sci 42:223–239.
RoudotAlgaron F (1996) Lait 76:313–348
Silva SV, Malcata FX (2005) Int Dairy J 15:1–15. DOI: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2004.04.009
Korhonen H, Pihlanto A (2006) Int Dairy J, in press. DOI: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2005.10.012
Pripp AH, Isaksson T, Stepaniak L, Sørhaug T, Ardö Y (2005) Trends Food Sci Technol 16:484–494. DOI: 10.1016/j.tifs.2005.07.003
Dziuba J, Iwaniak A (2005) Database of protein and bioactive peptide sequences. In: Mine Y, Shahidi F (eds) Neutraceutical proteins and peptides in health and disease. Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, FL
Dziuba J, Iwaniak A, Minkiewicz P (2003) Polimery 48:50–53
Dzuiba J, Niklewicz M, Iwaniak A, Darewicz M, Minkiewicz P (2004) Acta Aliment Hung 33:227–235
Vermeirssen V, van der Bent A, Van Camp J, van Amerongen A, Verstraete W (2004) Biochimie 86:231–239. DOI 10.1016/j.biochi.2004.01.003
Pripp AH (2005) Eur Food Res Technol 211:712–716. DOI: 10.1007/s00217-005-0083-1
Berman HM, Bhat TN, Bourne PE, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Weissig H, Westbrook J (2000) Nature Struct Biol 7:957–959
Westbrook J, Feng Z, Chen L, Yang H, Bergman HM (2003) Nucleic Acid Res 31:489–491
Kitchen DB, Decornez H, Furr JR, Bajorath J (2004) Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:935–949
Sangma C, Chuakheaw D, Jongkon N, Saenbandit K, Nunrium P, Uthayopas P, Hannongbua S (2005) Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 8:417–429
Kroeger Smith MB, Hose BM, Hawkins A, Lipchock J, Farnsworth DW, Rizzo RC, Tirado-Rives J, Arnold E, Zhang W, Hughes SH, Jorgensen WL, Michejda CJ, Smith RH Jr (2003) J Med Chem 46:1940–1947. DOI: 10.1021/jm020271f
Warren GL, Andrews CW, Capelli AM, Clarke B, LaLonde J, Lambert MH, Lindvall M, Nevins N, Semus SF, Sanger S, Tedesco G, Wall ID, Woolven JM, Peishoff CE, Head MS (2005) J Med Chem ASAP article DOI: 10.1021/jm050362n
Cushman DW, Cheung HS, Sabo EF, Ondetti MA (1981) Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors: evolution of a new class of antihypertensive drugs. In: Horovitz (ed) Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. Mechanisms of action and clinical implications. Urban & Schwarzenberg, Baltimore, pp 3–25
Hellberg S, Eriksson L, Johsson J, Lindgren F, Sjöström M, Skagerberg B, Wold S, Andrews P (1989) Int J Peptide Res 37:414–424
Thomsen R, Christensen MH (2006) J Med Chem 49:3315–3321. DOI: 10.1021/jm051197e
Creighton TE (1993) Proteins: structures and molecular properties 2nd ed. WH Freeman, New York
Sturrock ED, Natesh R, van Rooyen JM, Acharya KR (2004) Cell Mol Life Sci 61:2677–2686. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-004-4239-0
Pripp AH, Isaksson T, Stepaniak L, Sørhaug T (2004) Eur Food Res Technol 219:579–583
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pripp, A.H. Docking and virtual screening of ACE inhibitory dipeptides. Eur Food Res Technol 225, 589–592 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-006-0450-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-006-0450-6