Abstract
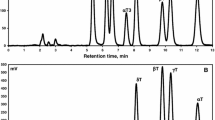
The aim of this study was to determine the tocopherol contents of wine by-products including grape seed, pomace (seed, skin and stem) and bagasse (skin and stem) by using two different extraction methods in order to evaluate the possibilities of them as natural non-polar antioxidants. Cold extraction appeared to give more tocopherol contents in seeds than hot extraction. But hot extraction was found more suitable for pomace and bagasse. α-Tocopherol was the most abundant tocopherol in the grape seed, pomace and bagasse. Although γ- and δ-tocopherols were found in the samples with low concentrations, β-tocopherol was not detected in the samples. Kalecik karası had the highest α and total tocopherol compared to the other cultivars. On the other hand, hot extracted bagasse in all cultivars gave the highest tocopherol contents. As a conclusion, wine by-products, a large scale wastes, can be evaluated both to get natural tocopherol source and to obtain economical gain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grice HC (1986) Food Chem Toxicol 24: 1127–1130
Wichi HP (1988) Food Chem Toxicol 26: 717–723
Inatani R, Nakatani N, Fuwa H (1983) Agric Biol Chem 47: 521–528
Duke JA, Beckstone-Stenberg M (1994) In: Charalambous G (ed) Spices, herbs and edible fungi. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 741–757
Nakatami M (1994) In: Charalambous G (ed) Spices, herbs and edible fungi. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 251–271
Tsimidou M, Boskou D (1994) In: Charalambous G (ed) Spices, herbs and edible fungi. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 272–283
Shadidi F (1997) Chemistry, health effects and applications. AOCS Press, Champaign, IL
Lagouri V, Boskou D (1996) Int J Food Sci Nutr 47: 439–497
Demo A, Petrakis C, Kefalas P, Boskou D (1998) Food Res Int 31: 351–354
Lagouri V, Blekas G, Tsimidou M, Kokkini S, Boskou D (1993) Z Lebensm Unters Forsch 197: 20–23
Tomeo AC, Geller M, Watkins TR, Gapor A, Bierenbaum ML (1995) Lipids 30: 1779–1183
Diplock AT (1992) INFORM 3: 1214–1217
Torres JL, Varela B, Garcia MT, Carilla J, Matito C, Centelles JJ, Cascante M, Sort X, Bobet R (2002) J Agric Food Chem 50: 7548–7555
Kotanballi N, Murty C, Singh RP, Jayaprakasha GK (2002) J Agric Food Chem 50: 5909–5914
Lavedrine F, Ravel A., Poupard A, Alary J (1997) Food Chem 58: 135–140.
Lampi AM, Kataja L, Kamal-Eldin A, Piironen V (1999) J Am Oil Chem Soc 76: 749–755
Guthrie N, Kurowska EM (2001) In: Robert EC (ed) Nutraceuticals and functional foods. Wildman CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 269–280
Gliszcynska-Swiglo A, Sikorska E (2004) J Chromatogr A 1048: 195–198
Crawley H (1993) In: Ottaway PB (ed) The technology of vitamins in food. Chapman & Hall, UK
Gregory JF (1996) In: Fennema OR (ed) Food chemistry. Marcel Dekker, New York, Hong Kong
Degreyt W (1998) Effect of physical refining on selected minor components in vegetables oils. PhD Thesis, Université des Sciences Appliqués de Gent, Belgique
Aguilera MP, Beltran G, Ortega D, Fernandez A, Jimenez A, Uceda M, (2005) Food Chem 89: 387–391
Göktürk Baydar N, Akkurt M (2001) Turk J Agric For 25: 163–168
Oomah BD, Liang J, Godfrey D, Mazza G (1998) J Agric Food Chem 46: 4017–4021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baydar, N.G., Özkan, G. Tocopherol contents of some Turkish wine by-products. Eur Food Res Technol 223, 290–293 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-005-0203-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-005-0203-y