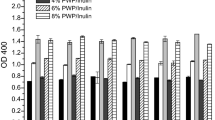
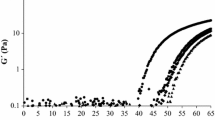
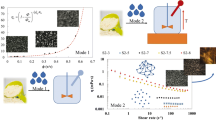
Abstract
NMR PGSTE diffusion experiments are used to characterise the gelling behaviour of carrageenan mixtures and whey protein mixtures. The structure of developing networks can be observed as a function of the composition of the mixture (concentration of hydrocolloids, sugars and salts), the measuring temperature, and the protein denaturation, depending on the denaturation temperature and duration. Besides the fundamental aspects of these preliminary studies, these data are helpful for modelling processes sufficiently precisely for industrial production, to guarantee specific properties concerning the flow-, gelling- and syneresis/storage-behaviour and the texture and sensorial behaviour of food products, and to realise a process and quality control of thermal protein denaturation and hydrocolloid gelling processes. Therefore, further quantitative correlations between macroscopic quantities and the available NMR parameters must be established to trigger industrial applications of NMR diffusion experiments.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lewis GP, Derbyshire W, Ablett S, Lillford PJ, Norton IT (1987) Carbohyd Res 160:397–410
Suggett A (1975) Polysaccharides. In: Franks F (ed) Water (Vol 4). Plenum, New York, pp 550–567
van de Velde F, Peppelman HA, Rollema HS, Tromp RH (2001) Carbohyd Res 331:271–283
Belitz HD, Grosch W, Schieberle P (2001) Lehrbuch der Lebensmittelchemie, 5th edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Kneifel W, Paquin P, Abert T, Richard J-P (1991) J Dairy Sci 74:2027–2041
Edmond E, Ogston AG (1968) Biochem J 109:569–572
Syrbe A, Bauer WJ, Klostermeyer H (1998) Int Dairy J 8:179–193
Kessler HG (1996) Lebensmittel- und bioverfahrenstechnik – molkereitechnologie, 4th edn. Verlag A. Kessler, München, Germany
Cavanagh J, Fairbrother WJ, Palmer AG, Skelton NJ (1996) Protein NMR spectroscopy, principles and practice. Academic, New York
Nölting B (1999) Protein folding kinetics. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Lagaly G, Schulz O, Zimehl R (1997) Dispersionen und emulsionen. Steinkopff, Darmstadt, Germany
Spiegel T (1999) Thermische denaturierung und aggregation von molkenproteinen in ultrafiltrationsmolkenkonzentraten. PhD Thesis, TU München, Freising-Weihenstephan, Germany
Götz J, Köhler P (2003) J Agr Food Chem (in press)
Hinrichs R, Götz J, Weisser H (2003) Food Chem 82:155–160
Ohtsuka A, Watanabe T (1996) Carbohyd Polym 30:135–140
Katz E (1996) High-performance liquid chromatography. Wiley, Chichester, UK
Abragam A (1961) Principles of nuclear magnetism. Clarendon, Oxford, UK
Farrar TC, Becker ED (1971) Pulse and Fourier transform NMR. Academic, New York
Callaghan PT (1991) Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Microscopy. Clarendon, Oxford, UK
Stejskal EO, Tanner JE (1965) J Chem Phys 41:288–232
Tanner JE, Stejskal EO (1968) J Chem Phys 49:1768–1777
Kärger J, Pfeifer H (1994) Magn Reson Imaging 12:235–239
Kimmich R (1997) NMR tomography diffusometry relaxometry. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Stejskal EO (1965) J Chem Phys 43:3597–3603
Tanner JE (1970) J Chem Phys 52:2523–2526
Colquhoun IJ, Goodfellow BJ (1994) Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. In: Wilson RH (ed) Spectroscopic techniques for food analysis. Wiley, New York
Hertz HG (1986) Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy. In: Dogonadze RR, Kálmán E, Kornyshev AA, Ulstrup J. (eds) The chemical properties of solvation, Part B: Spectroscopy of solvation. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Kärger J, Fleischer G (1994) TRAC–Trend Anal Chem 12:145–156
Holz M (1986) Nachr Chem Tech Lab 34:858–864
Latour LL, Kleinberg RL, Mitra PP, Sotak CH (1995) J Magn Reson Ser A 112:83–91
Latour LL, Mitra PP, Kleinberg RL, Sotak CH (1993) J Magn Reson Ser A 101:342–346
Velan SS, Chandrakumar N (1996) J Magn Reson 123:122–125
Mitra PP (1997) Physica A 241:122–127
Watson AT, Chang CTP (1997) Prog Nucl Mag Res Sp 31:343–386
Darken LS (1948) T Metall Soc AIME 175:184–201
Friedmann TE (1999) Flow of non-Newtonian fluids through compressible porous media in centrifugal filtration processing. PhD Thesis, ETH, Zürich, Germany
Friedmann TE, Windhab E (1998) Separ Sci Technol 33:2221–2239
Darcy H (1865) Les fontaines publiques de la ville de Diyon. Dalmont, Paris
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the financial support of the “Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Technologie (BMWi)” in the “Arbeitsgemeinschaft industrieller Forschungsvereinigungen” “Otto von Guericke” e.V. (AiF) within the project AiF-FV-Nr. 12779 N (Struktur und Wasserbindung in Mischgelen aus Milchproteinen und Hydrokolloiden – Messmethodik und Einfluss von Prozessparametern). Furthermore, we would like to thank the Bruker BioSpin GmbH, Rheinstetten, Germany for technical and scientific support, and Dr. Joop de Vries and Jesper Wichmann, Danisco Cultor, Braband, Denmark, who placed the data concerning the molecular data of the studied carrageenan types at our disposal. Finally, we would also like to acknowledge the helpful and constructive comments of the referees.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Götz, J., Zick, K., Hinrichs, R. et al. Characterisation of carrageenan and whey protein gels using NMR PGSTE diffusion experiments. Eur Food Res Technol 218, 323–332 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-003-0861-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-003-0861-6