Abstract
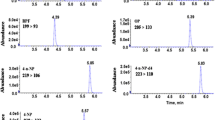
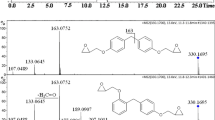
A reversed phase high performance liquid chromatographic method combined with fluorescence and mass spectrometric detection in series is presented for the separation and quantification of bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (BADGE) and novolac glycidyl ether (NOGE) derivatives in extracts from food can coatings, tuna and oil. Fifteen samples of tuna cans bought in four European countries were investigated. Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry in the positive ion mode (APCI(+)-MS) allowed to tentatively identify BADGE and NOGE related compounds originating from reactions of the glycidyl ethers with bisphenols, phenol, butanol, water and hydrochloric acid. Quantification was based on the external standard method and fluorescence detection. Mass fractions up to 3.7 μg/g were found for hydrochlorination products of bisphenol F diglycidyl ether (BFDGE + 2HCl) in tuna. Furthermore, total migration quantities of phenolic ether compounds were estimated. The highest values found were 20 μg/g in tuna and 43 μg/g in the oil phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 October 2000 / Accepted: 17 November 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berger, U., Oehme, M. & Girardin, L. Quantification of derivatives of bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (BADGE) and novolac glycidyl ether (NOGE) migrated from can coatings into tuna by HPLC/fluorescence and MS detection. Fresenius J Anal Chem 369, 115–123 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160000668
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160000668