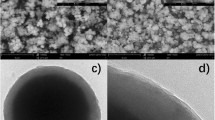
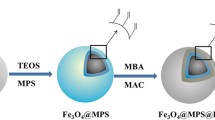
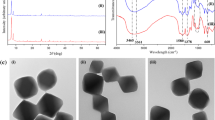
Abstract
Highly selective glycopeptide enrichment is important before mass spectrometry analysis because of the ultra-low abundance of glycopeptides in the peptide mixtures. Herein, a UiO-66-NH2-based magnetic composite was prepared and used for the hydrophilic enrichment of glycopeptides. The composite was modified with phytic acid (PA) molecules by partially replacing 2-aminoterephthalic acid ligands in UiO-66-NH2, with electrostatic interactions also promoting this modification process. Based on the hydrophilicity of both the PA molecules and the UiO-66-NH2 skeleton, the resulting material, denoted as MUiO-66-NH2/PA, showed excellent dual hydrophilicity towards glycopeptide enrichment. Compared with pure UiO-66-NH2, the specific surface area and hydrophilicity of the prepared material were increased, and MUiO-66-NH2/PA exhibited good magnetic responsiveness to facilitate a convenient enrichment procedure. HRP and IgG were used as standard proteins to evaluate the glycopeptide enrichment properties, with 21 and 34 glycopeptides enriched from their tryptic digests. Furthermore, MUiO-66-NH2/PA showed outstanding sensitivity (1 fmol/μL) and selectivity (HRP/BSA = 1:1000), and achieved remarkable glycopeptide enrichment performance for practical human serum samples. Notably, MUiO-66-NH2/PA showed perfect reusability and stability, achieving enrichment performance after five cycles similar to that of the first use. This material can be used for glycopeptide enrichment to obtain further glycosylation information, providing the possibility for cancer treatment.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rudd PM, Elliott T, Cresswell P, Wilson IA, Dwek RA. Glycosylation and the immune system. Science. 2001;291(5512):2370–6.
Pinho SS, Reis CA. Glycosylation in cancer: mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15(9):540–55.
Cao L, Diedrich JK, Ma Y, Wang N, Pauthner M, Park S, et al. Global site-specific analysis of glycoprotein N-glycan processing. Nat Protoc. 2018;13(6):1196–212.
Reily C, Stewart TJ, Renfrow MB, Novak J. Glycosylation in health and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2019;15(6):346–66.
Schjoldager KT, Narimatsu Y, Joshi HJ, Clausen H. Global view of human protein glycosylation pathways and functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio. 2020;21(12):729–49.
Shajahan A, Heiss C, Ishihara M, Azadi P. Glycomic and glycoproteomic analysis of glycoproteins—a tutorial. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017;409(19):4483–505.
Yates J, Kelleher N. Top down proteomics. Anal Chem. 2013;85(13):6151.
Xiao H, Suttapitugsakul S, Sun F, Wu R. Mass spectrometry-based chemical and enzymatic methods for global analysis of protein glycosylation. Acc Chem Res. 2018;51(8):1796–806.
Novotny MV, Alley WR. Recent trends in analytical and structural glycobiology. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013;17(5):832–40.
Ruiz-May E, Hucko S, Howe KJ, Zhang S, Sherwood RW, Thannhauser TW, et al. A comparative study of lectin affinity based plant N-glycoproteome profiling using tomato fruit as a model. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014;13(2):566–79.
Peng J, Hu Y, Zhang H, Wan L, Wang L, Liang Z, et al. High anti-interfering profiling of endogenous glycopeptides for human plasma by the dual-hydrophilic metal–organic framework. Anal Chem. 2019;91(7):4852–9.
Sajid MS, Jabeen F, Hussain D, Ashiq MN, Najam-ul-Haq M. Hydrazide-functionalized affinity on conventional support materials for glycopeptide enrichment. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017;409(12):3135–43.
Shao W, Liu J, Liang Y, Yang K, Min Y, Zhang X, et al. “Thiol-ene” grafting of silica particles with three-dimensional branched copolymer for HILIC/cation-exchange chromatographic separation and N-glycopeptide enrichment. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410(3):1019–27.
Chen Z, Huang J, Li L. Recent advances in mass spectrometry (MS)-based glycoproteomics in complex biological samples. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2019;118:880–92.
Tang F, Yu Q-W, Yuan B-F, Feng Y-Q. Hydrophilic materials in sample pretreatment. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2017;86:172–84.
Zhao X, Wang Y, Li D-S, Bu X, Feng P. Metal–organic frameworks for separation. Adv Mater. 2018;30(37):1705189.
Mandal S, Natarajan S, Mani P, Pankajakshan A. Post-synthetic modification of metal–organic frameworks toward applications. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31(4):2006291.
Masoomi MY, Morsali A, Dhakshinamoorthy A, Garcia H. Mixed-metal MOFs: unique opportunities in metal–organic framework (MOF) functionality and design. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2019;58(43):15188–205.
Kalaj M, Cohen SM. Postsynthetic modification: an enabling technology for the advancement of metal–organic frameworks. ACS Central Sci. 2020;6(7):1046–57.
Wang X, Na Z, Yin D, Wang C, Wu Y, Huang G, et al. Phytic acid-assisted formation of hierarchical porous CoP/C nanoboxes for enhanced lithium storage and hydrogen generation. ACS Nano. 2018;12(12):12238–46.
Zhou Y, Xu Y, Zhang C, Emmer Å, Zheng H. Amino acid-functionalized two-dimensional hollow cobalt sulfide nanoleaves for the highly selective enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides. Anal Chem. 2020;92(2):2151–8.
Hu X, Liu Q, Wu Y, Deng Z, Long J, Deng C. Magnetic metal-organic frameworks containing abundant carboxylic groups for highly effective enrichment of glycopeptides in breast cancer serum. Talanta. 2019;204:446–54.
Zhang R, Wang Z, Wang T, Su P, Yang Y. Boronic acid-decorated metal-organic frameworks modified via a mixed-ligand strategy for the selective enrichment of cis-diol containing nucleosides. Anal Chim Acta. 2020;1106:42–51.
Zhang R, Wang Z, Zhou Z, Li D, Wang T, Su P, et al. Highly effective removal of pharmaceutical compounds from aqueous solution by magnetic Zr-based MOFs composites. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2019;58(9):3876–84.
Alagesan K, Khilji SK, Kolarich D. It is all about the solvent: on the importance of the mobile phase for ZIC-HILIC glycopeptide enrichment. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017;409(2):529–38.
Xia C, Jiao F, Gao F, Wang H, Lv Y, Shen Y, et al. Two-dimensional MoS2-based zwitterionic hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography material for the specific enrichment of glycopeptides. Anal Chem. 2018;90(11):6651–9.
Ma Y, Yuan F, Zhang X, Zhou Y, Zhang X. Highly efficient enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides using a hydrophilic covalent-organic framework. Analyst. 2017;142(17):3212–8.
Zhou Z, Gao Z, Shen H, Li M, He W, Su P, et al. Metal–organic framework in situ post-encapsulating DNA–enzyme composites on a magnetic carrier with high stability and reusability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(6):7510–7.
Song J, He W, Shen H, Zhou Z, Li M, Su P, et al. Self-assembly of a magnetic DNA hydrogel as a new biomaterial for enzyme encapsulation with enhanced activity and stability. Chem Commun. 2019;55(17):2449–52.
Sarker M, Song JY, Jhung SH. Carboxylic-acid-functionalized UiO-66-NH2: a promising adsorbent for both aqueous- and non-aqueous-phase adsorptions. Chem Eng J. 2018;331:124–31.
Pu C, Zhao H, Hong Y, Zhan Q, Lan M. Facile preparation of hydrophilic mesoporous metal–organic framework via synergistic etching and surface functionalization for glycopeptides analysis. Anal Chem. 2020;92(2):1940–7.
Contreras-Ramirez A, Tao S, Day GS, Bakhmutov VI, Billinge SJL, Zhou H-C. Zirconium phosphate: the pathway from Turbostratic disorder to crystallinity. Inorg Chem. 2019;58(20):14260–74.
Ma W, Xu L, Li X, Shen S, Wu M, Bai Y, et al. Cysteine-functionalized metal–organic framework: facile synthesis and high efficient enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides in cell lysate. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(23):19562–8.
Chen Y, Sheng Q, Hong Y, Lan M. Hydrophilic nanocomposite functionalized by carrageenan for the specific enrichment of glycopeptides. Anal Chem. 2019;91(6):4047–54.
Yang S, Wang C, Yu X, Shang W, Chen DDY, Gu Z. A hydrophilic two-dimensional titanium-based metal-organic framework nanosheets for specific enrichment of glycopeptides. Anal Chim Acta. 2020;1119:60–7.
Funding
This work was supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation (2202037), National Natural Science Foundation of China (21675008), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020 M680313), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (ZY2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.68 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, P., Wang, Z., Li, X. et al. Fabrication of magnetic dual-hydrophilic metal organic framework for highly efficient glycopeptide enrichment. Anal Bioanal Chem 413, 5267–5278 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03535-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03535-w