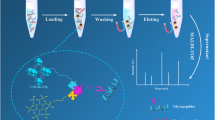
Abstract
The HILIC enrichment is a greatly compatible strategy for the extraction of glycopeptides in proteomics. Herein, a boric acid and fructose-1,6-diphosphate (FDP) dual-functionalized Zr-based metal–organic framework material UIO-PBA&FDP (UIO is the abbreviation for the University of Oslo, and PBA is the abbreviation for carboxy phenylboronic acid) was synthesized, characterized with the desirable excellent hydrophilicity and thus was explored for the enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides utilizing the HILIC interaction between the glycopeptides and the hydrophilic UIO-PBA&FDP at a high level of ACN concentration. A total of 359 N-linked glycopeptides corresponding to 104 glycoproteins were identified from only 1 μL of digested human serum by the enrichment of UIO-PBA&FDP, which showed a superiorly high coverage of the identified glycopeptides. The dual hydrophilic functionalized UIO-PBA&FDP could be an efficient HILIC material for the enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides from complex biological samples.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohtsubo K, Marth JD. Glycosylation in cellular mechanisms of health and disease. Cell. 2006;126(5):855–67.
Li JJ, Guo B, Zhang WQ, Yue S, Huang S, Gao S, et al. Recent advances in demystifying O-glycosylation in health and disease. Proteomics. 2022;22:2200156.
Reily C, Stewart TJ, Renfrow MB, Novak J. Glycosylation in health and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2019;15(6):346–66.
Selman MHJ, Hemayatkar M, Deelder AM, Wuhrer M. Cotton HILIC SPE microtips for microscale purification and enrichment of glycans and glycopeptides. Anal Chem. 2011;83(7):2492–9.
Qiu RQ, Regnier FE. Use of multidimensional lectin affinity chromatography in differential glycoproteomics. Anal Chem. 2005;77(9):2802–9.
Luo B, Chen Q, He J, Li ZY, Yu LZ, Lan F, et al. Boronic acid-functionalized magnetic metal-organic frameworks via a dual-ligand strategy for highly efficient enrichment of phosphopeptides and glycopeptides. Acs Sustain Chem Eng. 2019;7(6):6043–52.
Peng J, Zhang H, Niu H, Ra Wu. Peptidomic analyses: the progress in enrichment and identification of endogenous peptides. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2020;125:115835.
Li J, Wang J, Ling Y, Chen Z, Gao M, Zhang X, et al. Unprecedented highly efficient capture of glycopeptides by Fe3O4@Mg-MOF-74 core–shell nanoparticles. Chem Commun. 2017;53(28):4018–21.
Hong YY, Zhao H, Pu CL, Zhan QL, Sheng QY, Lan MB. Hydrophilic phytic acid-coated magnetic graphene for titanium(IV) immobilization as a novel hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-immobilized metal affinity chromatography platform for glyco- and phosphopeptide enrichment with controllable selectivity. Anal Chem. 2018;90(18):11008–15.
Shen B, Zhang W, Shi Z, Tian F, Deng Y, Sun C, et al. A novel strategy for global mapping of O-GlcNAc proteins and peptides using selective enzymatic deglycosylation, HILIC enrichment and mass spectrometry identification. Talanta. 2017;169:195–202.
Wu SJ, Li XL, Zhang FF, Jiang G, Liang XM, Yang BC. An arginine-functionalized stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography. Analyst. 2015;140(12):3921–4.
Zhou YY, Xu Y, Zhang CC, Emmer A, Zheng HQ. Amino acid-functionalized two-dimensional hollow cobalt sulfide nanoleaves for the highly selective enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides. Anal Chem. 2020;92(2):2151–8.
Wang QQ, Wu HH, Peng K, Jin HY, Shao HK, Wang YQ, et al. Hydrophilic polymeric monoliths containing choline phosphate for separation science applications. Anal Chim Acta. 2018;999:184–9.
Sun N, Xiong YT, Qing GY, Zhao YY, Li XL, Liang XM. Selective enrichment of sialylated glycopeptides with a d-allose@SiO2 matrix. Rsc Adv. 2018;8(68):38780–6.
Sun NR, Wang JW, Yao JZ, Chen HM, Deng CH. Magnetite nanoparticles coated with mercaptosuccinic acid-modified mesoporous titania as a hydrophilic sorbent for glycopeptides and phosphopeptides prior to their quantitation by LC-MS/MS. Microchimica Acta. 2019;186(3):159.
Bibi A, Ju HX. Efficient enrichment of glycopeptides with sulfonic acid-functionalized mesoporous silica. Talanta. 2016;161:681–5.
Xie ZH, Yan YH, Tang KQ, Ding CF. Post-synthesis modification of covalent organic frameworks for ultrahigh enrichment of low-abundance glycopeptides from human saliva and serum. Talanta. 2022;236:122831.
Wang MY, Zhang XM, Deng CH. Facile synthesis of magnetic poly(styrene-co-4-vinylbenzene-boronic acid) microspheres for selective enrichment of glycopeptides. Proteomics. 2015;15(13):2158–65.
Guo BL, Bi S, Zhang BY, Tong YK, Chen X, Tian MM. Synthesis of nanoparticles with a combination of metal chelation and molecular imprinting for efficient and selective extraction of glycoprotein. Microchem J. 2021;167:106262.
Rao DP, Wang BC, Zhong HZ, Yan YH, Ding CF. Construction of boric acid-functionalized metal-organic frameworks for glycopeptide recognition in the serum of cervical cancer patients. Rapid Commun Mass Sp. 2022;36(13):e9314.
Saleem S, Sajid MS, Hussain D, Jabeen F, Najam-ul-Haq M, Saeed A. Boronic acid functionalized MOFs as HILIC material for N-linked glycopeptide enrichment. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020;412(7):1509–20.
Wang XL, Xiao H, Li A, Li Z, Liu SJ, Zhang QH, et al. Constructing NiCo/Fe3O4 heteroparticles within MOF-74 for efficient oxygen evolution reactions. J Am Chem Soc. 2018;140(45):15336–41.
Zhao YJ, Cui Y, Meng XR, Ding J, Hou HW. Metal organic framework composites as adsorbents: synergistic effect for water purification. Coordin Chem Rev. 2022;473:214815.
Qin YT, Li ZX, Duan YL, Guo J, Zhao MT, Tang ZY. Nanostructural engineering of metal-organic frameworks: construction strategies and catalytic applications. Matter-Us. 2022;5(10):3260–310.
Zhao M, Zhang XM, Deng CH. Facile synthesis of hydrophilic magnetic graphene@metal-organic framework for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Rsc Adv. 2015;5(45):35361–4.
Gao W, Zhang F, Zhang S, Li J-Y, Lian H-Z. Ti(IV) immobilized bisphosphate fructose-modified magnetic Zr metal organic framework (MOF) for specific enrichment of phosphopeptides. Sep Purif Technol. 2023;305:122426.
Peng JX, Hu YC, Zhang HY, Wan LH, Wang L, Liang Z, et al. High anti-interfering profiling of endogenous glycopeptides for article human plasma by the dual-hydrophilic metal-organic framework. Anal Chem. 2019;91(7):4852–9.
Gooding JJ, Pugliano L, Hibbert DB, Erokhin P. Amperometric biosensor with enzyme amplification fabricated using self-assembled monolayers of alkanethiols: the influence of the spatial distribution of the enzymes. Electrochem Commun. 2000;2(4):217–21.
Sam S, Touahir L, Salvador Andresa J, Allongue P, Chazalviel JN, Gouget-Laemmel AC, et al. Semiquantitative study of the EDC/NHS activation of acid terminal groups at modified porous silicon surfaces. Langmuir. 2010;26(2):809–14.
Cavka JH, Jakobsen S, Olsbye U, Guillou N, Lamberti C, Bordiga S, et al. A new zirconium inorganic building brick forming metal organic frameworks with exceptional stability. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130(42):13850–1.
Zhou X, Zhang H, Wang L, Lv L, Wu R. Simultaneous enrichment optimization of glycopeptides and phosphopeptides with the highly hydrophilic DZMOF-FDP. Analyst. 2023;148(7):1483–91.
Kandiah M, Nilsen MH, Usseglio S, Jakobsen S, Olsbye U, Tilset M, et al. Synthesis and stability of tagged UiO-66 Zr-MOFs. Chem Mater. 2010;22(24):6632–40.
Cao Q, Peng Y, Yu QY, Shi Z, Jia Q. Post synthetic modification of Zr-MOF with phenylboronic acid: fluorescence sensing of sialic acid. Dyes Pigments. 2022;197:109839.
Sk M, Banesh S, Trivedi V, Biswas S. Selective and sensitive sensing of hydrogen peroxide by a boronic acid functionalized metal–organic framework and its application in live-cell imaging. Inorg Chem. 2018;57(23):14574–81.
Tan W, Chen T, Liu WR, Ye FG, Zhao SL. Design and fabrication of boric acid functionalized hierarchical porous metal-organic frameworks for specific removal of cis-diol-containing compounds from aqueous solution. Appl Surf Sci. 2021;535:147714.
Shi HL, Zhang L. Maltose-functionalized HILIC stationary phase silica gel based on self-assembled oligopeptides and its application for the separation of polar compounds. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022;414(13):3917–25.
Peng JX, Zhang HY, Li X, Liu SJ, Zhao XY, Wu J, et al. Dual-metal centered zirconium-organic framework: a metal-affinity probe for highly specific interaction with phosphopeptides. Acs Appl Mater Inter. 2016;8(51):35012–20.
Xue Y, Xie JJ, Fang P, Yao J, Yan GQ, Shen HL, et al. Study on behaviors and performances of universal N-glycopeptide enrichment methods. Analyst. 2018;143(8):1870–80.
Zhang LW, Wang Y, Pan L, Tang RZ, Asoh TA, Ou JJ, et al. Fabrication of a reusable bifunctional biomimetic Ti4+-phosphorylated cellulose monolith with a coral-like structure for enrichment of phosphorylated and glycosylated peptides. Green Chem. 2021;23(19):7674–84.
Zhang CQ, Ye ZL, Xue P, Shu QB, Zhou Y, Ji YL, et al. Evaluation of different N-glycopeptide enrichment methods for N-glycosylation sites mapping in mouse brain. J Proteome Res. 2016;15(9):2960–8.
Liu B, Wang B, Yan Y, Tang K, Ding C. Postsynthesis of zwitterionic hydrophilic composites for enhanced enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides from human serum. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2019.
Chen Y, Sheng Q, Hong Y, Lan M. Hydrophilic nanocomposite functionalized by carrageenan for the specific enrichment of glycopeptides. Anal Chem. 2019;91(6):4047–54.
Su P, Wang Z, Li X, Li M, Li G, Gong Z, et al. Fabrication of magnetic dual-hydrophilic metal organic framework for highly efficient glycopeptide enrichment. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021;413(21):5267–78.
Sheng Q, Li J, Chen Y, Liang X, Lan M. Hydrophilic graphene oxide-dopamine-cationic cellulose composites and their applications in N-glycopeptides enrichment. Talanta. 2021;226:122112.
Fu D, Liu Y, Shen A, Xiao Y, Yu L, Liang X. Preparation of glutathione-functionalized zwitterionic silica material for efficient enrichment of sialylated N-glycopeptides. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411(18):4131–40.
Gao W, Bai Y, Liu H. Glutathione-functionalized two-dimensional cobalt sulfide nanosheets for rapid and highly efficient enrichment of N-glycopeptides. Microchim Acta. 2021;188(8):274.
Liu Q, Deng CH, Sun N. Hydrophilic tripeptide-functionalized magnetic metal-organic frameworks for the highly efficient enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides. Nanoscale. 2018;10(25):12149–55.
Funding
The financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grants No.21974138) is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All experiments were performed in compliance with the Guidelines of National Health and Family Planning Commission of People’s Republic of China and were approved by the ethics committees at the Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Zhang, H., Wang, L. et al. Boronic acid and fructose-1,6-diphosphate dual-functionalized highly hydrophilic Zr-MOF for HILIC enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides. Anal Bioanal Chem 415, 4767–4777 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04770-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04770-z