Abstract
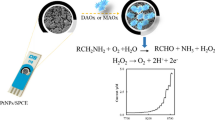
Biogenic amine biosensors, based on screen-printed carbon electrodes (SPCE) modified with Prussian blue (PB) and indium tin oxide nanoparticles (ITONP), are reported. PB/ITONP-modified SPCE was further modified with diamine oxidase (DAO) or monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzymes to construct the biosensors. The morphology of the modified electrodes was studied by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) were used to enlighten the electrochemical properties of the modified electrodes at each step of biosensor fabrication. Electrode surface composition and experimental conditions were optimized and analytical performance characteristics of the biosensors were studied. Several biogenic amines were tested and both biosensors responded to histamine, putrescine and cadaverine. DAO/ITONP/PB/SPCE biosensor exhibited the highest response to histamine 6.0 × 10−6–6.9 × 10−4 M with a sensitivity of 1.84 μA mM−1. On the other hand, the highest sensitivity was obtained for cadaverine with the MAO/ITONP/PB/SPCE biosensor. The analytical utility of the presented biosensors were illustrated by the determination of cadaverine and histamine in cheese sample.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calvo-Pérez A, Domínguez-Renedo O, Alonso-Lomillo MA, Arcos-Martínez MJ. Disposable amperometric biosensor for the determination of tyramine using plasma amino oxidase. Microchim Acta. 2013;180(3–4):253–9.
Shalaby AR. Significance of biogenic amines to food safety and human health. Food Res Int. 1996;29(7):675–90.
Henao-Escobar W, Domínguez-Renedo O, Alonso-Lomillo MA, Arcos-Martínez MJ. Simultaneous determination of cadaverine and putrescine using a disposable monoamine oxidase based biosensor. Talanta. 2013;117:405–11.
Carelli D, Centonze D, Palermo C, Quinto M, Rotunno T. An interference free amperometric biosensor for the detection of biogenic amines in food products. Biosens Bioelectron. 2007;23(5):640–7.
Romano A, Klebanowski H, La Guerche S, Beneduce L, Spano G, Murat M-L, et al. Determination of biogenic amines in wine by thin-layer chromatography/densitometry. Food Chem. 2012;135(3):1392–6.
Lapa-Guimaraes J, Pickova J. New solvent systems for thin-layer chromatographic determination of nine biogenic amines in fish and squid. J Chromatogr A. 2004;1045(1–2):223–32.
Shalaby A. Simple, rapid and valid thin layer chromatographic method for determining biogenic amines in foods. Food Chem. 1999;65(1):117–21.
Almeida C, Fernandes J, Cunha S. A novel dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC–MS) method for the determination of eighteen biogenic amines in beer. Food Control. 2012;25(1):380–8.
Innocente N, Biasutti M, Padovese M, Moret S. Determination of biogenic amines in cheese using HPLC technique and direct derivatization of acid extract. Food Chem. 2007;101(3):1285–9.
Önal A. A review: current analytical methods for the determination of biogenic amines in foods. Food Chem. 2007;103(4):1475–86.
Önal A, Tekkeli SEK, Önal C. A review of the liquid chromatographic methods for the determination of biogenic amines in foods. Food Chem. 2013;138(1):509–15.
Bóka B, Adányi N, Virág D, Sebela M, Kiss A. Spoilage detection with biogenic amine biosensors, comparison of different enzyme electrodes. Electroanalysis. 2012;24(1):181–6.
Leonardo S, Campàs M. Electrochemical enzyme sensor arrays for the detection of the biogenic amines histamine, putrescine and cadaverine using magnetic beads as immobilisation supports. Microchim Acta. 2016;183(6):1881–90.
Aigner M, Telsnig D, Kalcher K, Teubl C, Macheroux P, Wallner S, et al. Amperometric biosensor for total monoamines using a glassy carbon paste electrode modified with human monoamine oxidase B and manganese dioxide particles. Microchim Acta. 2015;182(5–6):925–31.
Boffi A, Favero G, Federico R, Macone A, Antiochia R, Tortolini C, et al. Amine oxidase-based biosensors for spermine and spermidine determination. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;407(4):1131–7.
Dalkıran B, Erden PE, Kaçar C, Kılıç E. Disposable Amperometric biosensor based on poly-L-lysine and Fe3O4 NPs-chitosan composite for the detection of Tyramine in cheese. Electroanalysis. 2019;31(7):1324–33.
Shi X, Gu W, Li B, Chen N, Zhao K, Xian Y. Enzymatic biosensors based on the use of metal oxide nanoparticles. Microchim Acta. 2014;181(1–2):1–22.
Liu B, Liu J. DNA adsorption by indium tin oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir. 2014;31(1):371–7.
Sivasakthi P, Bapu GR, Chandrasekaran M. Pulse electrodeposited nickel-indium tin oxide nanocomposite as an electrocatalyst for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Mater Sci Eng C. 2016;58:782–9.
Aydın EB, Sezgintürk MK. Indium tin oxide (ITO): a promising material in biosensing technology. TrAC Trends in Anal Chem. 2017;97:309–15.
Wang J, Wang L, Di J, Tu Y. Disposable biosensor based on immobilization of glucose oxidase at gold nanoparticles electrodeposited on indium tin oxide electrode. Sens Actuators B: Chemical. 2008;135(1):283–8.
El-Said WA, Choi J-W. Electrochemical biosensor consisted of conducting polymer layer on gold nanodots patterned indium tin oxide electrode for rapid and simultaneous determination of purine bases. Electrochim Acta. 2014;123:51–7.
Liang F, Jia M, Hu J. Pt-implanted indium tin oxide electrodes and their amperometric sensor applications for nitrite and hydrogen peroxide. Electrochim Acta. 2012;75:414–9.
Rigoni F, Drera G, Pagliara S, Goldoni A, Sangaletti L. High sensitivity, moisture selective, ammonia gas sensors based on single-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with indium tin oxide nanoparticles. Carbon. 2014;80:356–63.
Bobrowski T, Arribas EG, Ludwig R, Toscano MD, Shleev S, Schuhmann W. Rechargeable, flexible and mediator-free biosupercapacitor based on transparent ITO nanoparticle modified electrodes acting in μM glucose containing buffers. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;101:84–9.
Chen X, Wu G, Cai Z, Oyama M, Chen X. Advances in enzyme-free electrochemical sensors for hydrogen peroxide, glucose, and uric acid. Microchim Acta. 2014;181(7–8):689–705.
Erden PE, Kılıç E. A review of enzymatic uric acid biosensors based on amperometric detection. Talanta. 2013;107:312–23.
Benedet J, Lu D, Cizek K, La Belle J, Wang J. Amperometric sensing of hydrogen peroxide vapor for security screening. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009;395(2):371–6.
Özdemir DS, Kaçar C, Dalkıran B, Küçükkolbaşı S, Erden PE, Kılıç E. Effect of hexaammineruthenium chloride and/or horseradish peroxidase on the performance of hydrogen peroxide (bio) sensors: a comparative study. J Mater Sci. 2019;54(7):5381–98.
Karyakin AA, Karyakina EE. Prussian blue-basedartificial peroxidase'as a transducer for hydrogen peroxide detection. Application to biosensors. Sens Actuators B: Chemical. 1999;57(1–3):268–73.
Karyakin AA, Karyakina EE, Gorton L. Amperometric biosensor for glutamate using prussian blue-based “artificial peroxidase” as a transducer for hydrogen peroxide. Anal Chem. 2000;72(7):1720–3.
Ricci F, Amine A, Palleschi G, Moscone D. Prussian blue based screen printed biosensors with improved characteristics of long-term lifetime and pH stability. Biosens Bioelectron. 2003;18(2–3):165–74.
Garjonyte R, Yigzaw Y, Meskys R, Malinauskas A, Gorton L. Prussian blue-and lactate oxidase-based amperometric biosensor for lactic acid. Sens Actuators B: Chemical. 2001;79(1):33–8.
Li M, Li Y-T, Li D-W, Long Y-T. Recent developments and applications of screen-printed electrodes in environmental assays—a review. Anal Chim Acta. 2012;734:31–44.
Taleat Z, Khoshroo A, Mazloum-Ardakani M. Screen-printed electrodes for biosensing: a review (2008–2013). Microchim Acta. 2014;181(9–10):865–91.
Sekar NC, Shaegh SAM, Ng SH, Ge L, Tan SN. A paper-based amperometric glucose biosensor developed with Prussian blue-modified screen-printed electrodes. Sens Actuators B: Chemical. 2014;204:414–20.
Liu X, Li X, Gao X, Ge L, Sun X, Li F. A universal paper-based electrochemical sensor for zero-background assay of diverse biomarkers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(17):15381–8.
Teng Y, Zuo S, Lan M. Direct electron transfer of horseradish peroxidase on porous structure of screen-printed electrode. Biosens Bioelectron. 2009;24(5):1353–7.
Compagnone D, Isoldi G, Moscone D, Palleschi G. Amperometric detection of biogenic amines in cheese using immobilised diamine oxidase. Anal Lett. 2001;34(6):841–54.
Zotou A, Loukou Z, Soufleros E, Stratis I. Determination of biogenic amines in wines and beers by high performance liquid chromatography with pre-column dansylation and ultraviolet detection. Chromatographia. 2003;57:429–39.
Martín M, González Orive A, Lorenzo-Luis P, Hernández Creus A, González-Mora JL, Salazar P. Quinone-rich poly (dopamine) magnetic nanoparticles for biosensor applications. ChemPhysChem. 2014;15(17):3742–52.
Tsai Y-C, Chiu C-C. Amperometric biosensors based on multiwalled carbon nanotube-Nafion-tyrosinase nanobiocomposites for the determination of phenolic compounds. Sens Actuators B: Chemical. 2007;125(1):10–6.
Pandey PC, Pandey AK, Chauhan DS. Nanocomposite of Prussian blue based sensor for L-cysteine: synergetic effect of nanostructured gold and palladium on electrocatalysis. Electrochim Acta. 2012;74:23–31.
Wang B, Ji X, Zhao H, Wang N, Li X, Ni R, et al. An amperometric β-glucan biosensor based on the immobilization of bi-enzyme on Prussian blue–chitosan and gold nanoparticles–chitosan nanocomposite films. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;55:113–9.
Luo X, Killard AJ, Smyth MR. Reagentless glucose biosensor based on the direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase on carbon nanotube-modified electrodes. Electroanalysis: An International Journal Devoted to Fundamental and Practical Aspects of Electroanalysis. 2006;18(11):1131–4.
Ricci F, Palleschi G. Sensor and biosensor preparation, optimisation and applications of Prussian blue modified electrodes. Biosens Bioelectron. 2005;21(3):389–407.
Cinti S, Arduini F, Moscone D, Palleschi G, Killard A. Development of a hydrogen peroxide sensor based on screen-printed electrodes modified with inkjet-printed Prussian blue nanoparticles. Sensors. 2014;14(8):14222–34.
Keow CM, Bakar FA, Salleh AB, Heng LY, Wagiran R, Bean LS. An amperometric biosensor for the rapid assessment of histamine level in tiger prawn (Penaeus monodon) spoilage. Food Chem. 2007;105(4):1636–41.
Alonso-Lomillo MA, Domínguez-Renedo O, Matos P, Arcos-Martínez MJ. Disposable biosensors for determination of biogenic amines. Anal Chim Acta. 2010;665(1):26–31.
Pérez S, Bartrolí J, Fàbregas E. Amperometric biosensor for the determination of histamine in fish samples. Food Chem. 2013;141(4):4066–72.
Gumpu MB, Nesakumar N, Sethuraman S, Krishnan UM, Rayappan JBB. Development of electrochemical biosensor with ceria–PANI core–shell nano-interface for the detection of histamine. Sens Actuators B: Chemical. 2014;199:330–8.
Vanegas D, Patiño L, Mendez C, Oliveira D, Torres A, Gomes C, et al. Laser scribed graphene biosensor for detection of biogenic amines in food samples using locally sourced materials. Biosensors. 2018;8(2):42.
Torre R, Costa-Rama E, Lopes P, Nouws HP, Delerue-Matos C. Amperometric enzyme sensor for the rapid determination of histamine. Anal Methods. 2019;11(9):1264–9.
Piermarini S, Volpe G, Federico R, Moscone D, Palleschi G. Detection of biogenic amines in human saliva using a screen-printed biosensor. Anal Lett. 2010;43(7–8):1310–6.
Di Fusco M, Federico R, Boffi A, Macone A, Favero G, Mazzei F. Characterization and application of a diamine oxidase from Lathyrus sativus as component of an electrochemical biosensor for the determination of biogenic amines in wine and beer. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;401(2):707–16.
Shanmugam S, Thandavan K, Gandhi S, Sethuraman S, Rayappan JBB, Krishnan UM. Development and evaluation of a highly sensitive rapid response enzymatic nanointerfaced biosensor for detection of putrescine. Analyst. 2011;136(24):5234–40.
Gumpu MB, Nesakumar N, Sethuraman S, Krishnan UM, Rayappan JBB. Determination of putrescine in tiger prawn using an amperometric biosensor based on immobilization of diamine oxidase onto ceria nanospheres. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016;9(4):717–24.
Henao-Escobar W, Domínguez-Renedo O, Alonso-Lomillo MA, Arcos-Martínez MJ. A screen-printed disposable biosensor for selective determination of putrescine. Microchim Acta. 2013;180(7–8):687–93.
Niculescu M, Nistor C, Frébort I, Peč P, Mattiasson B, Csöregi E. Redox hydrogel-based amperometric bienzyme electrodes for fish freshness monitoring. Anal Chem. 2000;72(7):1591–7.
Al Layla AM, Türkarslan Ö, Kurbanoglu S, Sulaiman ST, Al-Flayeh K, Toppare L. A new amperometric biosensor for diamine: use of a conducting polymer layer. J Macromol Sci, Part A. 2013;50(9):914–22.
Ov P, Ferreira IM, Mendes E, Oliveira BM, Ferreira M. Effect of temperature on evolution of free amino acid and biogenic amine contents during storage of Azeitão cheese. Food Chem. 2001;75(3):287–91.
Funding
This work was financially supported by The Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK Project No.: 116Z159).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaçar, C., Erden, P.E., Dalkiran, B. et al. Amperometric biogenic amine biosensors based on Prussian blue, indium tin oxide nanoparticles and diamine oxidase– or monoamine oxidase–modified electrodes. Anal Bioanal Chem 412, 1933–1946 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02448-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02448-4