Abstract
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (GALDI-MS) provided new horizons and offered many functions for various applications. This review summarized AuNPs applications for analytical, biotechnology and proteomics. AuNPs efficiently absorbed the laser radiation and transferred the energy to the analyte for the desorption/ionization process. The unique features of AuNPs such as large surface area and high absorption coefficient lead not only to high resolution, low interference and low limit of detection, but also offered selective detection for certain species. AuNPs provided an excellent surface for the analysis of several species such as small molecules, biomarkers, proteins and cells (pathogenic bacteria or cancer cells). AuNPs played many roles such as surface for LDI-MS, probe and stationary phase for separation or preconcentration. AuNPs modified various surface chemistry was applied for a wide range of different wavelength. AuNPs severed as a source of Au+ ions that were suitable for analyte cationisation. Characterization of Au nanoclusters (AuNCs) by mass spectrometry, pros and cons were also highlighted.

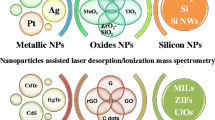
Schematic representation of the analysis by Gold Nanoparticles Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry (GALDI-MS)







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- CHCA:
-
α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid, alpha-cyano or alpha-matrix
- FA:
-
2-amino-4,5-diphenylfuran-3-carboxylic acid, furoic acid
- MA:
-
2-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)aminobenzoic acid, mefenamic acid
- AuNCs:
-
Au nanoclusters
- bio-SH:
-
Biothiols
- Cys:
-
Cysteine
- DIOS:
-
Desorption/ionization on porous silicon
- DHB:
-
2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid
- ESI-MS:
-
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
- F4-ICPMS:
-
Flow-Field-Flow Fractionation- inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
- SPR:
-
Surface plasmon resonance
- SERS:
-
Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy
- SALDI:
-
Surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization
- SA:
-
5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic acid, sinapinic acid
- TAGs:
-
Triacylglycerols
- VIS-MALDI:
-
Visible-wavelength matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization
References
Torabi SF, Lu Y. Functional DNA nanomaterials for sensing and imaging in living cells. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2014;28:88–95.
Estevez MC, Otte MA, Sepulveda B, Lechuga LM. Trends and challenges of refractometric nanoplasmonic biosensors: a review. Anal Chimica Acta. 2014;806:55–73.
Haruta M. Chance and necessity: my encounter with gold catalysts. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2014;53:52–6.
Webb JA, Bardhan R. Emerging advances in nanomedicine with engineered gold nanostructures. Nanoscale. 2014;6:2502–30.
Manikandan M, Abdelhamid HN, Talib A, Wu HF. Facile synthesis of gold nanohexagons on graphene templates in Raman spectroscopy for biosensing cancer and cancer stem cells. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;55:180–6.
Yi X, Wang F, Qin W, Yuan J, Yang X. Near-infrared fluorescent probes in cancer imaging and therapy: an emerging field. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:1347–65.
Sipova H, Homola J. Surface plasmon resonance sensing of nucleic acids: a review. Anal Chimica Acta. 2013;773:9–23.
Couture M, Zhao SS, Masson JF. Modern surface plasmon resonance for bioanalytics and biophysics. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2013;15:11190–216.
Murray-Méthot MP, Ratel M, Masson JF. Optical properties of Au, Ag, and bimetallic Au on Ag nanohole arrays. J Phys Chem C. 2010;114:8268–75.
Live LS, Murray-Méthot MP, Masson JF. Localized and propagating surface plasmons in gold particles of near-micron size. J Phys Chem C. 2009;113:40–4.
Bolduc OR, Masson JF. Advances in surface plasmon resonance sensing with nanoparticles and thin films: nanomaterials, surface chemistry, and hybrid plasmonic techniques. Anal Chem. 2011;83:8057–62.
Wei H, Xu H. Hot spots in different metal nanostructures for plasmon-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nanoscale. 2013;5:10794–805.
Valcárcel M, López-lorente AI. Gold nanoparticles in analytical chemistry. 1st ed. Netherland: Elsevier; 2014.
Fenselau C, Demirev PA. Characterization of intact microorganisms by MALDI mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2001;20:157–71.
Norris NL, Caprioli RM. Analysis of tissue specimens by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry in biological and clinical research. Chem Rev. 2013;113:2309–42.
Zenobi R, Knockenmuss R. Ion formation in MALDI mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom Rev. 1998;17:337–66.
Salum ML, Itovich LM, Erra-Balsells E. Z-sinapinic acid: the change of the stereochemistry of cinnamic acids as rational synthesis of a new matrix for carbohydrate MALDI-MS analysis. J Mass Spectrom. 2013;48:1160–9.
Beavis RC, Chaudhary T, Chait BT. α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid as a matrix for matrixassisted laser desorption mass spectrometry. Org Mass Spectrom. 1992;27:156.
Abdelhamid HN, Wu HF. Furoic and mefenamic acids as new matrices for matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization-(MALDI)-mass spectrometry. Talanta. 2013;115:442–50.
ChenS CI, Wang J, Hou HJ, Liu Q, Wang J, Xiong J, et al. 2,3,4,5-Tetrakis(3',4'-dihydroxylphenyl)thiophene: a new matrix for the selective analysis of low molecular weight amines and direct determination of creatinine in urine by MALDI-TOF MS. Anal Chem. 2012;84:10291–7.
Chen R, Chen S, Xiong C, Ding X, Chih-Che W, Chang CC, et al. N-(1-naphthyl) ethylenediaminedinitrate: a new matrix for negative ion MALDI-TOF MS analysis of small molecules. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2012;23:1454–60.
Abdelhamid HN, Khan MS, Wu HF. Design, characterization and applications of new ionic liquid matrices for multifunctional analysis of biomolecules: a novel strategy for pathogenic bacteria biosensing. Anal Chim Acta. 2014;823:51–60.
Abdelhamid HN, Gopal J, Wu HF. Synthesis and application of ionic liquid matrices (ILMs) for effective pathogenic bacteria analysis in matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI-MS). Anal Chim Acta. 2013;767:104–11.
Tanaka K, Waki H, Ido Y, Akita S, Yoshida Y, Yoshida T, et al. Protein and polymer analyses up to m/z 100 000 by laser ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1988;2:151–3.
Sunner J, Dratz E, Chen YC. Graphite surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry of peptides and proteins from liquid solutions. Anal Chem. 1995;67:4335–42.
Chiang CK, Chen WT, Chang HT. Nanoparticle-based mass spectrometry for the analysis of biomolecules. Chem Soc Rev. 2011;40:1269–81.
Abdelhamid HN. Applications of Nanomaterials and Organic Semiconductors for Bacteria & Biomolecules analysis/ biosensing using Laser Analytical Spectroscopy, National Sun-Yat Sen University, ROC. 2013.
Bergman N, Shevchenko D, Bergquist J. Approaches for the analysis of low molecular weight compounds with laser desorption/ionization techniques and mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014;406:49–61.
Wu HF, Gopal J, Abdelhamid HN, Hasan N. Quantum dot applications endowing novelty to analytical proteomics. Proteomics. 2012;12:2949–61.
Abdelhamid HN, Wu HF. Ultrasensitive, rapid, and selective detection of mercury using graphene assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014;25:861–8.
Abdelhamid HN, Wu BS, Wu HF. Graphene coated silica applied for high ionization matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry: A novel approach for environmental and biomolecule analysis. Talanta. 2014;126:27–37.
Arakawa R, Kawasaki H. Functionalized nanoparticles and nanostructured surfaces for surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Sci. 2010;12:1229–40.
Guinan T, Kirkbride P, Pigou PE, Ronci M, Kobus H, Voelcker NH. Surface-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry techniques for application in forensics. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2014;34:627–40.
Wei H, Nolkrantz K, Powell DH, Woods JH, Ko M, Kennedy RT. Electrospray sample deposition for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) and atmospheric pressure MALDI mass spectrometry with attomole detection limits. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2004;18:1193–200.
Soukup-Hein RJ, Armstrong DW, Warnke MM. Ionic liquids in analytical chemistry. Ann Rev Anal Chem. 2009;2:145–68.
Ho TD, Zhang C, Hantao LW, Anderson JL. Ionic liquids in analytical chemistry: fundamentals, advances, and perspectives. Anal Chem. 2014;86:262–85.
Dreisewerd K. The desorption process in MALDI. Chem Rev. 2003;103:395.
Abdelhamid HN, Wu HF. A method to detect metal-drug complexes and their interactions with pathogenic bacteria via graphene nanosheet assist laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry and biosensors. Anal Chimica Acta. 2012;751:94–104.
Abdelhamid HN, Wu HF. Polymer dots for quantifying the total hydrophobic pathogenic lysates in a single drop. Colloids Surf, B. 2014;115:51–60.
Abdelhamid HN, Bhaisare M, Wu HF. Ceria nanocubic-ultrasonication assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry for pathogenic bacteria analysis. Talanta. 2014;120:208–17.
Pilolli R, Ditaranto N, Monopoli A, Nacci A, Palmisano F, Sabbatini L, et al. Designing functionalized gold surfaces and nanostructures for laser desorption ionisation mass spectrometry. Vacuum. 2014;100:78–83.
Shastri L, Kailasa SK, Wu HF. Nanoparticle-single drop microextraction as multifunctional and sensitive nanoprobes: Binary matrix approach for gold nanoparticles modified with (4-mercaptophenyliminomethyl)-2-methoxyphenol for peptide and protein analysis in MALDI-TOF MS. Talanta. 2010;81:1176–82.
Cioffi N, De Palo F, Calvano CD, van der Werf ID, Palmisano F, Zambonin PG. Core–shell gold nanoparticles as Non-conventional matrix for the MALDI-ToF-MS detection of amino acids: a preliminary study. Sensor Lett. 2008;6:654–61.
Chen TH, Yu CJ, Tseng WL. Sinapinic acid-directed synthesis of gold nanoclusters and their application to quantitative matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Nanoscale. 2014;6:1347–53.
Lopez-Corte´ R, Oliveira E, Nunez C, Lodeiro C, Cadena M, Fdez-Riverola F, et al. Fast human serum profiling through chemical depletion coupled to gold-nanoparticle-assisted protein separation. Talanta. 2012;100:239–45.
Ju S, Yeo WS. Quantification of proteins on gold nanoparticles by combining MALDI-TOF MS and proteolysis. Nanotechnology. 2012;23:135701–8.
Zhang X, Zhu S, Deng C, Zhang X. An aptamer based on-plate microarray for high-throughput insulin detection by MALDI-TOF MS. Chem Commun. 2012;48:2689–91.
Lee J, Ryoo SR, Kim SK, Ahn JH, Min DH, Yeo WS. Quantitation of surface-bound proteins on biochips using MALDI-TOF MS. Anal Sci. 2011;27:1127–31.
Nayak R, Knapp DR. Matrix-free LDI mass spectrometry platform using patterned nanostructured gold thin film. Anal Chem. 2010;82:7772–8.
Sudhir PR, Wu HF, Zhou ZC. Identification of peptides using gold nanoparticle-assisted single-drop microextraction coupled with AP-MALDI mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2005;77:7380–5.
Wang Q, Jakubowski JA, Sweedler JV, Bohn PW. Quantitative submonolayer spatial mapping of Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptide organomercaptan gradients on gold with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2004;76:1–8.
Kim YE, Yi SY, LeeCS JY, Chung BH. Gold patterned biochips for on-chip immuno-MALDI-TOF MS: SPR imaging coupled multi-protein MS analysis. Analyst (Cambridge, U K). 2012;137:386–92.
Zhang X, Zhu S, Xiong Y, Deng C, Zhang X. Development of a MALDI-TOF MS strategy for the high-throughput analysis of biomarkers: on-target aptamer immobilization and laser-accelerated proteolysis. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2013;52:6055–8.
Yang B, Gu K, Sun X, Huang H, Ding Y, Wang F, et al. Simultaneous detection of attomolar pathogen DNAs by Bio-MassCode mass spectrometry. Chem Commun. 2010;46:8288–90.
Brauer HA, Lampe PD, Yasui YY, Hamajima N, Stolowitz ML. Biochips that sequentially capture and focus antigens for immunoaffinity MALDI-TOF MS: a new tool for biomarker verification. Proteomics. 2010;10:3922–7.
Xu Y, Zhang L, Lu H, Yang P. On-plate enrichment of glycopeptides by using boronic acid functionalized gold-coated Si wafer. Proteomics. 2010;10:1079–86.
Yao G, Zhang H, Deng C, Lu H, Zhang X, Yang P. Facile synthesis of 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid functionalized gold nanoparticles for selective enrichment of glycopeptides. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2009;23:3493–500.
Chen YJ, Chen SH, Chien YY, Chang YW, Liao HK, Chang CY, et al. Carbohydrate-encapsulated gold nanoparticles for rapid target-protein identification and binding-epitope mapping. ChemBioChem. 2005;6:1169–73.
Zhang X, Zhu S, Deng C, Zhang X. Highly sensitive thrombin detection by matrix assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry with aptamer functionalized core-shell Fe3O4@C@Au magnetic microspheres. Talanta. 2012;88:295–302.
Teng CH, Ho KC, Lin YS, Chen YC. Gold nanoparticles as selective and concentrating probes for samples in MALDI MS analysis. Anal Chem. 2004;76:4337–42.
Xiong Y, Deng C, Zhang X. Development of aptamer-conjugated magnetic graphene/gold nanoparticle hybrid nanocomposites for specific enrichment and rapid analysis of thrombin by MALDI-TOF MS. Talanta. 2014;129:282–9.
Li X, Tan J, Yu J, Feng J, Pan A, Zheng S, et al. Use of a porous silicon-gold plasmonic nanostructure to enhance serum peptide signals in MALDI-TOF analysis. Anal Chim Acta. 2014;849:27–35.
Larguinho M, Capelo JL, Baptista PV. Fast nucleotide identification through fingerprinting using gold nanoparticle-based surface-assisted laser desorption/ionisation. Talanta. 2013;10:417–21.
Tang HW, Lu W, Che CM, Ng KM. Gold nanoparticles and imaging mass spectrometry: double imaging of latent fingerprints. Anal Chem. 2010;82:1589–93.
Huang RC, Chiu WJ, Lai IP, Huang CC. Multivalent Aptamer/Gold Nanoparticle–Modified Graphene Oxide for Mass Spectrometry–Based Tumor Tissue Imaging. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10292.
Son J, Lee G, Cha S. Direct analysis of triacylglycerols from crude lipid mixtures by gold nanoparticle-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014;25:891–4.
Wan D, Gao M, Wang Y, Zhang P, Zhang XA. rapid and simple separation and direct detection of glutathione by gold nanoparticles and graphene-based MALDI-TOF-MS. J Sep Sci. 2013;36:629–35.
Lee J, Lee J, Oh H, Mok H, Yeo WS. Selective analysis of thiol-containing molecules using nanoengineered micro gold shells and LDI-TOF MS. Bull Korean Chem Soc. 2012;33:3076–8.
Kailasa S, Wu HF. One-pot synthesis of dopamine dithiocarbamate functionalized gold nanoparticles for quantitative analysis of small molecules and phosphopeptides in SALDI- and MALDI-MS. Analyst (Cambridge, U K). 2012;137:1629–38.
Chiang CK, Lin YW, Chen WT, Chang HT. Accurate quantitation of glutathione in cell lysates through surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry using gold nanoparticles. Nanomedicine. 2010;6:530.
Chen WT, Chiang CK, Lin YW, Chang HT. Quantification of captopril in urine through surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry using 4-mercaptobenzoic acid-capped gold nanoparticles as an internal standard. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2010;21:864.
Zhu X, Wu L, Mungra DC, Xia S, Zhu J. Au@SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles for laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry. Analyst (Cambridge, U K). 2012;137:2454–8.
Laurent N, Haddoub R, Voglmeir J, Flitsch SL. MALDI-ToF MS analysis of glycosyltransferase activities on gold surface arrays. Carbohydr Microarrays Methods Mol Biol. 2012;808:269–84.
Su CL, Tseng WL. Gold nanoparticles as assisted matrix for determining neutral small carbohydrates through laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2007;79:1626–33.
Lee J, Lee J, Chung T, Yeo WS. Nanoengineered micro gold shells for LDI-TOF analysis of small molecules. Anal Chim Acta. 2012;736:1–6.
Prabhakaran A, Yin J, Nysten B, Degand H, Morsomme P, Mouhib T, et al. Metal condensates for low-molecular-weight matrix-free laser desorption/ionization. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2012;315:22–30.
Huang YF, Chang HT. Analysis of adenosine triphosphate and glutathione through gold nanoparticles assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2007;79:4852–9.
Kuo TR, Wang DY, Chiu YC, Yeh YC, Chen WT, Chen CH, et al. Layer-by-layer thin film of reduced graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles as an effective sample plate in laser-induced desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chimica Acta. 2014;809:97–103.
Yang M, Fujino T. Gold nanoparticles loaded on zeolite as inorganic matrix for laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry of small molecules. Chem Phys Lett. 2014;592:160–3.
Ocsoy I, Gulbakan B, Shukoor MI, Xiong X, Chen T, Powell DH, et al. Aptamer-conjugated multifunctional nanoflowers as a platform for targeting, capture, and detection in laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. ACS Nano. 2013;7:417–27.
Amendola V, Litti L, Meneghetti M. LDI-MS assisted by chemical-free gold nanoparticles: enhanced sensitivity and reduced background in the low-mass region. Anal Chem. 2013;85:11747–54.
Pilolli R, Ditaranto N, Di Franco C, Palmisano F, Cioffi N. Thermally annealed gold nanoparticles for surface-assisted laser desorption ionisation-mass spectrometry of low molecular weight analytes. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012;404:1703–11.
Nagahori N, Nishimura SI. Direct and efficient monitoring of glycosyltransferase reactions on gold colloidal nanoparticles by using mass spectrometry. Chem Eur J. 2006;12:6478–85.
Gopal J, Abdelhamid HN, Hua PY, Wu HF. Chitosan nanomagnets for effective extraction and sensitive mass spectrometric detection of pathogenic bacterial endotoxin from human urine. J Mater Chem B. 2013;1:2463–75.
Abdelhamid HN, Wu HF. Multifunctional graphene magnetic nanosheet decorated with chitosan for highly sensitive detection of pathogenic bacteria. J Mater Chem B. 2013;1:3950–61.
Abdelhamid HN, Wu HF (2013) Probing the interactions of chitosan capped CdS quantum dots with pathogenic bacteria and their biosensing application. J. Mater.Chem.B 1: 6094-6106.
Wu BS, Abdelhamid HN, Wu HF. Synthesis and antibacterial activities of graphene decorated with stannous dioxide. RSC Adv. 2014;4:3722–31.
Bhaisare ML, Abdelhamid HN, Wu BS, Wu HF. Rapid and direct MALDI-MS identification of pathogenic bacteria from blood using ionic liquid-modified magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4@SiO2). J Mater Chem B. 2014;2:4671–83.
Gopal J, Manikandan M, Wu HF. Low cost aluminium foil platforms for rapid mass spectrometric differentiation of the fungal pathogen Aspergillus niger mycelium and spores by in situ gold nanosphere accelerated microwave digestion. RSC Adv. 2014;4:10982–9.
Chan PH, Wong SY, Lin SH, Chen YC. Lysozyme-encapsulated gold nanocluster-based affinity mass spectrometry for pathogenic bacteria. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2013;27:2143–8.
Lai HZ, Wang SG, Wu CY, Chen YC. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus by functional gold nanoparticle-based affinity surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2015;87:2114–20.
Tseng Y, Chang HY, Huang CC. A mass spectrometry-based immunosensor for bacteria using antibody-conjugated gold nanoparticles. Chem Commun. 2012;48:8712–4.
Castellana ET, Russell DH. Tailoring nanoparticle surface chemistry to enhance laser desorption ionization of peptides and proteins. Nano Lett. 2007;7:3023–5.
Castellana ET, Gamez RC, Gómez ME, Russell DH. Longitudinal surface plasmon resonance based gold nanorod biosensorsfor mass spectrometry. Langmuir. 2010;26:6066–70.
Chen LC, Mori K, Hori H, Hiraoka K. A useful binary matrix for visible-MALDI of Low molecular weight analytes. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2009;279:41–6.
Spencer MT, Furutani H, Oldenburg SJ, Darlington TK, Prather KA. Gold nanoparticles as a matrix for visible-wavelength single-particle matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry of small biomolecules. J Phys Chem C. 2008;112:4083–90.
Huang YF, Chang HT. Nile Red-adsorbed gold nanoparticle matrixes for determining aminothiols through surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2006;78:1485–93.
Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhou F, Kim P, Xia Y. Protein-protected Au clusters as a new class of nanoscale biosensor for label-free fluorescence detection of proteases. Small. 2012;8:3769–73.
Waki M, Sugiyama E, Kondo T, Sano K, Setou M. Nanoparticle-assisted laser desorption/ionization for metabolite imaging. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1203:159–73.
Segu ZM, Timmons RB, Kinsel GR. Increasing surface capacity for on-probe affinity capture MALDI-MS via gold particle attachment to allyl amine plasma polymers. Anal Chem. 2011;83:2500–4.
Dufresne M, Thomas A, Breault-Turcot J, Masson JF, Chaurand P. Silver-assisted laser desorption ionization for high spatial resolution imaging mass spectrometry of olefins from thin tissue sections. Anal Chem. 2013;85:3318–24.
Chen LC, Mori K, Hori H, Hiraoka K. Au-assisted visible laser MALDI. IntJ Mass Spectrom. 2009;279:41–6.
Caballero-Díaz E, Valcárcel M. Chapter 5 – toxicity of gold nanoparticles. Compr Anal Chem. 2014;66:207–54.
Abdelhamid HN, Wu HF. Proteomics analysis of the mode of antibacterial action of nanoparticles and their interactions with proteins. Trends Anal Chem. 2014;65:30–46.
Khan MS, Vishakante GD, Siddaramaiah H. Gold nanoparticles: a paradigm shift in biomedical applications. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2013;199:44–58.
McLean JA, Stumpo KA, Russell DH. Size-selected (2-10 nm) gold nanoparticles for matrix assisted laser desorption ionization of peptides. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;27:5304–5.
Novikov A, Caroff M, Della-Negra S, Lebeyec Y, Pautrat M, Schultz JA, et al. Matrix-implanted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2004;76:7288.
Duan J, Linman MJ, Chen CY, Cheng QJ. CHCA-modified Au nanoparticles for laser desorption ionization mass spectrometric analysis of peptides. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2009;20:1530–9.
Lee J, Jayathilaka LP, Gupta S, Huang JS, Lee BS. Gold ion-angiotensin peptide interaction by mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2012;23:942–51.
Collins JA, Xirouchaki C, Palmer RE, Heath JK, Jones CH. Clusters for biology: immobilization of proteins by size-selected metal clusters. Appl Surf Sci. 2004;226:197–208.
Kirk JS, Bohn PW. Surface adsorption and transfer of organomercaptans to colloidal gold and direct identification by matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:5920–6.
Gioria S, Chassaigne H, Carpi D, Parracino A, Meschini S, Barboro P, et al. A proteomic approach to investigate AuNPs effects in Balb/3T3 cells. Toxicol Lett. 2014;228:111–26.
Ha TK, Lee TG, Song NW, Moon DW, Han SY. Cation-assisted laser desorption/ionization for matrix-free surface mass spectrometry of alkanethiolate self-assembled monolayers on gold substrates and nanoparticles. Anal Chem. 2008;80:8526–31.
Trapiella-Alfonso L, Costa-Fernández JM, Encinar JR, Pereiro R, Sanz-Medel A. Chapter 8 – mass spectrometry for the characterization of gold nanoparticles. Compr Anal Chem. 2014;66:329–56.
Bustos ARM, Jorge Ruiz Encinar JR, Sanz-Medel A. Mass spectrometry for the characterisation of nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013;405:5637–43.
Fernández B, Costa JM, Pereiro R, Sanz-Medel A. Inorganic mass spectrometry as a tool for characterization at the nanoscale. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010;396:15–29.
Trapiella-Alfonso L, Costa-Fernandez JM, Encinar JR, Pereiro R, Alfredo Sanz-Medel A Chapter 8. Mass Spectrometry for the Characterization of Gold Nanoparticles, In book: Gold Nanoparticles in Analytical Chemistry, Chapter 8, Publisher: Elsevier, Editors: Miguel Valcárcel, Angela López-Lorente, pp.329-35;2001.
Meisterjahn B, Neubauer E, der Kammer FV, Hennecke DT, Hofmann T. Asymmetrical flow-field-flow fractionation coupled with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for the analysis of gold nanoparticles in the presence of natural nanoparticles. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1372C:204–11.
Hamouda R, Bertorelle F, Rayane D, Antoine R, Broyer M, Dugourd P. Glutathione capped gold AuN(SG)M clusters studied by isotope-resolved mass spectrometry. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2013;335:1–6.
Zavras A, Khairallah GN, O’Hair RAJ. Bis(diphenylphosphino)methane ligated gold cluster cations: synthesis and gas-phase unimolecular reactivity. Int J Mass Spectrometry. 2013;354–355:242–8.
Johnson GE, Laskin J. Soft landing of mass-selected gold clusters: Influence of ion and ligand on charge retention and reactivity. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2014;377:205–13.
Yan B, Zhu ZJ, Miranda OR, Chompoosor A, Rotello VM, Richard Vachet RW. Laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry analysis of monolayer-protected gold nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010;396:1025–35.
Zhu ZJ, Ghosh PS, Miranda OR, Vachet RW, Rotello VM. Multiplexed screening of cellular uptake of gold nanoparticles using laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:14139–43.
Creran B, Yan B, Moyano DF, Gilbert MM, Vachet RW, Rotello VM. Laser desorption ionization mass spectrometric imaging of mass barcoded gold nanoparticles for security applications. Chem Commun. 2012;48:4543–5.
García I, Henriksen-Lacey M, Sánchez-Iglesias A, Grzelczak M, Penadés S, Liz-Marzán LM. Residual CTAB ligands as mass spectrometry labels to monitor cellular uptake of Au nanorods. J Phys Chem Lett. 2015;6:2003–8.
Dass A, Stevenson A, Dubay GR, Tracy JB, Murray RW. Nanoparticle MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry without fragmentation: Au25(SCH2CH2Ph)18 and mixed monolayer Au25(SCH2CH2Ph)(18-x)(L)(x). J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:5940–6.
della Sala F, Kay ER. Reversible control of nanoparticle functionalization and physicochemical properties by dynamic covalent exchange. Angew Chem. 2015;127:4261–5.
Kouchi H, Kawasaki H, Arakawa R. A new matrix of MALDI-TOF MS for the analysis of thiolate-protected gold clusters. Anal Methods. 2012;4:3600–3.
Beloqui A, Sanchez-Ruiz A, Martin-Lomas M, Reichardt NC. A surface-based mass spectrometry method for screening glycosidase specificity in environmental samples. Chem Commun. 2012;48:1701–3.
Tang J, Liu Y, Qi D, Yao G, Deng C, Zhang X. On-plate-selective enrichment of glycopeptides using boronic acid-modified gold nanoparticles for direct MALDI-QIT-TOF MS analysis. Proteomics. 2009;9:5046–55.
Wang MT, Liu MH, Wang CRC, Chang SY. Silver-coated gold nanoparticles as concentrating probes and matrices for surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric analysis of aminoglycosides. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2009;20:1925–32.
Hanay MS, Kelber S, Naik AK, Chi D, Hentz S, Bullard EC, et al. Single-protein nanomechanical mass spectrometry in real time. Nat Nanotechnol. 2012;7:602–8.
Pilolli R, Palmisano F, Cioffi N. Gold nanomaterials as a new tool for bioanalytical applications of laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012;402:601–23.
Daniel De Bord J, Prabhakaran A, Eller MJ, Verkhoturov SV, Delcorte A, Schweikert EA. Metal-assisted SIMS with hypervelocity gold cluster projectiles. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2013;343:28–36.
Acknowledgments
H.F.Wu is particularly grateful to the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan for her financial support. H.N. Abdelhamid thanks Assuit University and Ministry of Higher Education for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelhamid, H.N., Wu, HF. Gold nanoparticles assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry and applications: from simple molecules to intact cells. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 4485–4502 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9374-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9374-6