Abstract
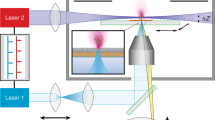
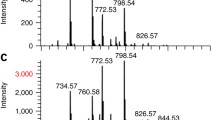
We have achieved protein imaging mass spectrometry capabilities at sub-cellular spatial resolution and at high acquisition speed by integrating a transmission geometry ion source with time of flight mass spectrometry. The transmission geometry principle allowed us to achieve a 1-μm laser spot diameter on target. A minimal raster step size of the instrument was 2.5 μm. Use of 2,5-dihydroxyacetophenone robotically sprayed on top of a tissue sample as a matrix together with additional sample preparation steps resulted in single pixel mass spectra from mouse cerebellum tissue sections having more than 20 peaks in a range 3–22 kDa. Mass spectrometry images were acquired in a standard step raster microprobe mode at 5 pixels/s and in a continuous raster mode at 40 pixels/s.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caprioli RM, Farmer TB, Gile J (1997) Molecular imaging of biological samples: localization of peptides and proteins using MALDI-TOF MS. Anal Chem 69(23):4751–4760
Fenner NC, Daly NR (1966) Laser used for mass analysis. Rev Sci Instrum 37(8):1068–1070. doi:10.1063/1.1720410
Hillenkamp F, Unsöld E, Kaufmann R, Nitsche R (1975) A high-sensitivity laser microprobe mass analyzer. Appl Phys 8(4):341–348. doi:10.1007/BF00898368
Vogt H, Heinen HJ, Meier S, Wechsung R (1981) LAMMA 500 principle and technical description of the instrument. Z Anal Chem 308(3):195–200. doi:10.1007/BF00479623
Dingle T, Griffiths BW, Ruckman JC (1981) LIMA-a laser induced ion mass analyser. Vacuum 31(10–12):571–577. doi:10.1016/0042-207X(81)90069-5
Van Vaeck L, Struyf H, Van Roy W, Adams F (1994) Organic and inorganic analysis with laser microprobe mass spectrometry. Part I: Instrumentation and methodology. Mass Spectrom Rev 13(3):189–208. doi:10.1002/mas.1280130302
Zavalin A, Todd EM, Rawhouser PD, Yang JH, Norris JL, Caprioli RM (2012) Direct imaging of single cells and tissue at sub-cellular spatial resolution using transmission geometry MALDI MS. J Mass Spectrom 47(11):1473–1481. doi:10.1002/Jms.3108
Thiery-Lavenant G, Zavalin AI, Caprioli RM (2013) Targeted multiplex imaging mass spectrometry in transmission geometry for subcellular spatial resolution. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 24(4):609–614. doi:10.1007/s13361-012-0563-z
Spraggins JM, Caprioli R (2011) High-speed MALDI-TOF imaging mass spectrometry: rapid ion image acquisition and considerations for next generation instrumentation. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 22(6):1022–1031. doi:10.1007/s13361-011-0121-0
SimulTOF 200 Combo | SimulTOF Systems. http://www.simultof.com/content/simultof-200-combo.
Ritzau S, Hayden K, Vestal M (2012) Improved MALDI-TOF performance with practical implementation of very high post-acceleration. In: 60th ASMS Conference on Mass Spectrometry and Allied Topics, Vancouver, Canada
Trim P, Djidja M-C, Atkinson S, Oakes K, Cole L, Anderson DG, Hart P, Francese S, Clench M (2010) Introduction of a 20 kHz Nd:YVO4 laser into a hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer for MALDI-MS imaging. Anal Bioanal Chem 397(8):3409–3419. doi:10.1007/s00216-010-3874-6
Zavalin A, Yang J, Caprioli R (2013) Laser beam filtration for high spatial resolution MALDI imaging mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 24(7):1153–1156. doi:10.1007/s13361-013-0638-5
Fernández-Pradas JM, Colina M, Serra P, Domı J, Morenza JL (2004) Laser-induced forward transfer of biomolecules. Thin Solid Films 453–454:27–30. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2003.11.154
Yang J, Zavalin A, Caprioli R (2014) Highly robust sample preparation with 2,5-dihydroxyacetophenone for MALDI imaging of proteins (2 -70 kDa) at high spatial resolution (5 μm). In: 62th ASMS Conference on Mass Spectrometry and Allied Topics, Baltimore, MD
Wenzel T, Sparbier K, Mieruch T, Kostrzewa M (2006) 2,5-Dihydroxyacetophenone: a matrix for highly sensitive matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometric analysis of proteins using manual and automated preparation techniques. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 20(5):785-789. doi:10.1002/rcm.2378
Anderson DM, Ablonczy Z, Koutalos Y, Spraggins J, Crouch RK, Caprioli RM, Schey KL (2014) High resolution MALDI imaging mass spectrometry of retinal tissue lipids. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 25(8):1394-1403. doi: 10.1007/s13361-014-0883-2
Prophet EB, Armed Forces Institute of Pathology et al (1992) Laboratory methods in histotechnology. American Registry of Pathology, Washington
Burnum KE, Tranguch S, Mi D, Daikoku T, Dey SK, Caprioli RM (2008) Imaging mass spectrometry reveals unique protein profiles during embryo implantation. Endocrinology 149(7):3274–3278. doi:10.1210/en.2008-0309
Crecelius AC, Cornett DS, Caprioli RM, Williams B, Dawant BM, Bodenheimer B (2005) Three-dimensional visualization of protein expression in mouse brain structures using imaging mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 16(7):1093–1099. doi:10.1016/j.jasms.2005.02.026
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank George Mills (SimulTOF Systems) and Boone Prentice and other members of the Vanderbilt Mass Spectrometry Research Center. This project was supported by grants from National Institutes of Health National Institute of General Medical Sciences NIH/NIGMS P41 GM103391-04 and NIH/NIGMS R01 GM058008-15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Mass Spectrometry Imaging with guest editors Andreas Römpp and Uwe Karst.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zavalin, A., Yang, J., Hayden, K. et al. Tissue protein imaging at 1 μm laser spot diameter for high spatial resolution and high imaging speed using transmission geometry MALDI TOF MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 407, 2337–2342 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8532-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8532-6