Abstract
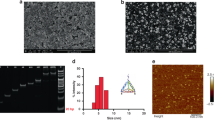
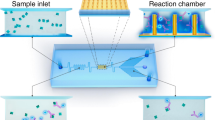
We describe an electrochemiluminescence (ECL) immunoarray incorporated into a prototype microfluidic device for highly sensitive protein detection and apply this system to accurate, sensitive measurements of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in serum. The microfluidic system employed three molded polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) channels on a conductive pyrolytic graphite chip (2.5 × 2.5 cm) inserted into a machined chamber and interfaced with a pump, switching valve, and sample injector. Each of the three PDMS channels encompasses three 3 μL analytical wells. Capture-antibody-decorated single-wall carbon nanotube forests are fabricated in the bottom of the wells. The antigen is captured by these antibodies on the well bottoms. Then, a RuBPY-silica-secondary antibody (Ab2) label is injected to bind to antigen on the array, followed by injection of sacrificial reductant tripropylamine (TPrA) to produce ECL. For detection, the chip is placed into an open-top ECL measuring cell, and the channels are in contact with electrolyte in the chamber. Potential applied at 0.95 V versus Ag/AgCl oxidizes TPrA to produce ECL by redox cycling the RuBPY species in the particles, and ECL light is measured by a charge-coupled device camera. This approach achieved ultralow detection limits of 100 fg mL−1 for PSA (9 zeptomole) and 10 fg mL−1 (1 zeptomole) for IL-6 in calf serum, a 10–25-fold improvement of a similar non-microfluidic array. PSA and IL-6 in synthetic cancer patient serum samples were detected in 1.1 h and results correlated well with single-protein enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kingsmore SF (2006) Multiplexed protein measurement: technologies and applications of protein and antibody arrays. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 5:310–320
Ferrari M (2005) Cancer nanotechnology: opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Cancer 5:161–171
Wulfkuhle JD, Liotta LA, Petricoin EF (2003) Proteomic applications for the early detection of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 3:267–275
Giljohann DA, Mirkin CA (2009) Drivers of biodiagnostic development. Nature 426:461–464
Ludwig JA, Weinstein JN (2005) Biomarkers in cancer staging, prognosis and treatment selection. Nature Rev Cancer 5:845–856
Rusling JF, Kumar CV, Patel V, Gutkind JS (2010) Measurement of biomarker proteins for point-of-care early detection and monitoring of cancer. Analyst 135:2496–2511
Zhang C, Xing D (2010) Single-molecule DNA amplification and analysis using microfluidics. Chem Rev 110:4910–4947
Gupta K, Kim D, Ellison D, Smith C, Kundu A, Tuan J, Suhc K, Levchenko A (2010) Lab-on-a-chip devices as an emerging platform for stem cell biology. Lab Chip 10:2019–2031
Gubala V, Harris LF, Ricco AJ, Tan MX, Williams DE (2012) Point of care diagnostics: status and future. Anal Chem 84:487–515
Choi S, Goryll M, Sin L, Wong PK, Chae J (2011) Microfluidic-based biosensors toward point-of-care detection of nucleic acids and proteins. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics 10:231–247
Mohammed M, Desmulliez M (2011) Lab-on-a-chip based immunosensor principles and technologies for the detection of cardiac biomarkers: a review. Lab Chip 11:569–595
Pagaduan JV, Yang W, Woolley AT (2011) Optimization of monolithic columns for microfluidic devices. Proc SPIE 8031:80311V
Ng A, Uddayasankar U, Wheeler AR (2010) Immunoassays in microfluidic systems. Anal Bioanal Chem 397:991–1007
Findlay JW, Smith WC, Lee JW, Nordblom GD, Das I, DeSilva BS, Khan MN, Bowsher RR (2000) Validation of immunoassays for bioanalysis: a pharmaceutical industry perspective. J Pharm Biomed Anal 21:1249–1273
Schmalzing D, Nashabeh W (1997) Capillary elecúophoresis based immunoassays: a critical review. Electrophoresis 18:2184–2193
Aebersold R, Mann M (2003) Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature 422:198–207
Hawkridge AM, Muddiman DC (2009) Mass spectrometry-based biomarker discovery: toward a global proteome index of individuality. Ann Rev Anal Chem 2:265–277
Hanash SM, Pitteri SJ, Faca VM (2008) Mining the plasma proteome for cancer biomarkers. Nature 452:571–579
Bange A, Halsall HB, Heinemann WR (2005) Microfluidic immunosensor systems. Biosens Bioelectron 20:2488–2503
Gervaisab L, Delamarche E (2009) Toward one-step point-of-care immunodiagnostics using capillary-driven microfluidics and PDMS substrates. Lab Chip 9:3330–3337
Garcia-Alonso J et al (2011) Micro-screening toxicity system based on living magnetic yeast and gradient chips. Anal Bioanal Chem 400:1009–1013
Fosdick SF, Crooks JA, Chang BY, Crooks RM (2010) Two-dimensional bipolar electrochemistry. J Am Chem Soc 132:9226–9227
Stern E, Vacic A, Rajan NK, Criscione JM, Park J, Ilic BR, Mooney DJ, Reed MA, Fahmy TM (2010) Label-free biomarker detection from whole blood. Nat Nanotechnol 5:138–142
Chikkaveeraiah BV, Mani V, Patel V, Gutkind JS, Rusling JF (2011) Microfluidic electrochemical immunoarray for ultrasensitive detection of two cancer biomarker proteins in serum. Biosens Bioelectron 26:4477–4483
Li Q, Tang D, Tang J, Su B, Chen G, Wei M (2011) Magneto-controlled electrochemical immunosensor for direct detection of squamous cell carcinoma antigen by using serum as supporting electrolyte. Biosens Bioelectron 27:153–159
Fragoso A, Latta D, Laboria N, Germar F, Hansen-Hagge T, Kemmner W, Gärtner C, Klemm R, Dreseb K, O’Sullivan C (2011) Integrated microfluidic platform for the electrochemical detection of breast cancer markers in patient serum samples. Lab Chip 11:625–631
Kellner C, Botero ML, Latta D, Drese K, Fragoso A, O’Sullivan C (2011) Automated microsystem for electrochemical detection of cancer markers. Electrophoresis 32:926–930
Choi S, Chae C (2009) A microfluidic biosensor based on competitive protein adsorption for thyroglobulin detection. Biosens Bioelectron 25:118–123
Jeon S, Kim SU, Jeon W, Shin CB (2009) Fabrication of multicomponent protein microarrays with microfluidic devices of poly(dimethylsiloxane). Macromol Res 17:192–196
Cheng CM, Martinez AW, Gong J, Mace CR, Phillips ST, Carrilho EC, Mirica KA, Whitesides GM (2010) Millimeter-scale contact printing of aqueous solutions using a stamp made out of paper and tape. Lab on a Chip 10:3201–3205
Martinez AW, Phillips ST, Butte MJ, Whitesides GM (2007) Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low-volume, portable bioassays. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:1318–1320
Sia SK, Linder V, Parviz B, Siegel A, Whitesides GM (2004) An integrated approach to a portable and low-cost immunoassay for resource-poor settings. Angew Chem 116:504–508
Liu H, Crooks RM (2012) A paper-based electrochemical sensing platform with integral battery and electrochromic read-out. Anal Chem 84:2528–2532
Ge L, Yan J, Song X, Yan M, Ge S, Yu J (2012) Three-dimensional paper-based electrochemiluminescence immunodevice for multiplexed measurement of biomarkers and point-of-care testing. Biomaterials 33:1024–1031
Delaney JL, Hogan CF, Tian J, Shen W (2011) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence detection in paper-based microfluidic sensors. Anal Chem 83:1300–1306
Pittet P, Lu G, Galvan J, Ferrigno R, Blum L, Leca-Bouvier B (2008) PCB technology-based electrochemiluminescence microfluidic device for low-cost portable analytical systems. IEEE Sensors Journal 8:565–571
Pittet P, Lu G, Galvan J, Ferrigno R, Blum L, Leca-Bouvier B (2007) PCB-based integration of electrochemiluminescence detection for microfluidic systems. Analyst 132:409–411
Niskanen AJ, Ylinen-Hinkka T, Kulmala S, Franssila S (2011) Integrated microelectrode hot electron electrochemiluminescent sensor for microfluidic applications. Sensors and Actuators B 152:56–62
Malhotra R, Patel V, Chikkaveeraiah BV, Munge BS, Cheong SC, Zain RB, Abraham MT, Dey DK, Gutkind JS, Rusling JF (2012) Oral cancer detection in the clinic using an ultrasensitive microfluidic array for a panel of biomarker proteins. Anal Chem 84:6249–6255
Tang CK, Vaze A, Rusling JF (2011) Fabrication of immunosensor microwell arrays from gold compact discs for detection of cancer biomarker proteins. Lab Chip 12:281–286
Debad JB, Glezer EN, Leland JK, Sigal GB, Wholstadter J (2011) In: Bard, AJ (eds) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp. 359–396
Miao WJ (2008) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence and its biorelated applications. Chem Rev 108:2506–2553
Richter MM (2004) Electrochemiluminescence (ECL). Chem Rev 104:3003–3036
Forster RJ, Bertoncello P, Keyes TE (2009) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence. Annu Rev Anal Chem 2:359–385
Healy DA, Hayes CJ, Leonard P, McKenna L, O’Kennedy R (2007) Biosensor developments: application to prostate-specific antigen detection. Trends Biotechnol 25:125–131
Yu X, Munge B, Patel V, Jensen G, Bhirde A, Gong JD, Kim SN, Gillespie J, Gutkind JS, Papadimitrakopoulos F, Rusling JF (2006) Carbon nanotube amplification strategies for highly sensitive immunodetection of cancer biomarkers. J Am Chem Soc 128:11199–11205
Kim SN, Rusling JF, Papadimitrakopolous F (2007) Carbon nanotubes for electronic and electrochemical detection of biomolecules. Adv Mater 19:3214–3228
Rusling JF, Yu X, Munge BS, Kim SN, Papadimitrakopoulos F (2009) Engineering the bioelectronic interface. In: Davis, J (eds) Royal Society of Chemistry, London, pp. 94–118
Sardesai NP, Pan S, Rusling JF (2009) Electrochemiluminescent immunosensor for detection of protein cancer biomarkers using carbon nanotube forests and [Ru-(bpy)3]2+-doped silica nanoparticles. Chem Commun 4968–4970
Sardesai NP, Barron J, Rusling JF (2011) Carbon nanotube microwell array for sensitive electrochemiluminescent detection of cancer biomarker proteins. Anal Chem 83:6698–6703
Kai J, Puntambekar A, Santiago N, Lee SH, Sehy DW, Moore V, Han J, Ahn C (2012) A novel microfluidic microplate as the next generation assay platform for enzyme linked immunoassays (ELISA). Lab on a Chip 12:4257–4262. doi:10.1039/C2LC40585G
Miao W, Choi JP, Bard AJ (2002) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence 69: the tris(2,2′-bipyridine)ruthenium(II), (Ru(bpy)3 2+)/tri-n-propylamine (TPrA) system revisited-a new route involving TPrA*+ cation radicals. J Am Chem Soc 124:14478
Malhotra R, Papadimitrakopoulos F, Rusling JF (2010) Sequential layer analysis of protein immunosensors based on single wall carbon nanotube forests. Langmuir 26:15050–15056
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant no. EB014586 from the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, NIH. We also acknowledge FAPESP Proc. No. 11/02259-6 for financial support to Dr. R.C. Faria for a sabbatical visit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Bioelectroanalysis with guest editors Nicolas Plumeré, Magdalena Gebala, and Wolfgang Schuhmann.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 3577 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sardesai, N.P., Kadimisetty, K., Faria, R. et al. A microfluidic electrochemiluminescent device for detecting cancer biomarker proteins. Anal Bioanal Chem 405, 3831–3838 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6656-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6656-5