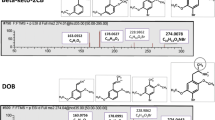
Abstract
In the last decade, liquid chromatography coupled to (tandem) mass spectrometry (LC–MS(−MS)) has become a versatile technique with many routine applications in clinical and forensic toxicology. However, it is well-known that ionization in LC–MS(−MS) is prone to so-called matrix effects, i.e., alteration in response due to the presence of co-eluting compounds that may increase (ion enhancement) or reduce (ion suppression) ionization of the analyte. Since the first reports on such matrix effects, numerous papers have been published on this matter and the subject has been reviewed several times. However, none of the existing reviews has specifically addressed aspects of matrix effects of particular interest and relevance to clinical and forensic toxicology, for example matrix effects in methods for multi-analyte or systematic toxicological analysis or matrix effects in (alternative) matrices almost exclusively analyzed in clinical and forensic toxicology, for example meconium, hair, oral fluid, or decomposed samples in postmortem toxicology. This review article will therefore focus on these issues, critically discussing experiments and results of matrix effects in LC–MS(−MS) applications in clinical and forensic toxicology. Moreover, it provides guidance on performance of studies on matrix effects in LC–MS(−MS) procedures in systematic toxicological analysis and postmortem toxicology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Segura J, Ventura R, Jurado C (1998) Derivatization procedures for gas chromatographic–mass spectrometric determination of xenobiotics in biological samples, with special attention to drugs of abuse and doping agents. J Chromatogr B 713(1):61–90
Drummer OH (1999) Chromatographic screening techniques in systematic toxicological analysis. J Chromatogr B 733(1–2):27–45
Maurer HH (2000) Screening procedures for simultaneous detection of several drug classes used in the high throughput toxicological analysis and doping control [review]. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 3:461–474
Maurer HH (2004) Position of chromatographic techniques in screening for detection of drugs or poisons in clinical and forensic toxicology and/or doping control [review]. Clin Chem Lab Med 42(11):1310–1324
Maurer HH (2007) Current role of liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry in clinical and forensic toxicology. Anal Bioanal Chem 388(7):1315–1325
Maurer HH (2005) Multi-analyte procedures for screening for and quantification of drugs in blood, plasma, or serum by liquid chromatography–single stage or tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS or LC–MS/MS) relevant to clinical and forensic toxicology [review]. Clin Biochem 38(4):310–318
Hoja H, Marquet P, Verneuil B, Lotfi H, Penicaut B, Lachatre G (1997) Applications of liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry in analytical toxicology: a review. J Anal Toxicol 21(2):116–126
Marquet P (2002) Progress of LC–MS in clinical and forensic toxicology. Ther Drug Monit 24(2):255–276
Vogeser M, Seger C (2010) Pitfalls associated with the use of liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry in the clinical laboratory. Clin Chem 56(8):1234–1244
Taylor PJ (2005) Matrix effects: the Achilles heel of quantitative high-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray–tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Biochem 38(4):328–334
Shah VP, Midha KK, Findlay JW, Hill HM, Hulse JD, McGilveray IJ, McKay G, Miller KJ, Patnaik RN, Powell ML, Tonelli A, Viswanathan CT, Yacobi A (2000) Bioanalytical method validation – a revisit with a decade of progress. Pharm Res 17(12):1551–1557
Annesley TM (2003) Ion suppression in mass spectrometry. Clin Chem 49(7):1041–1044
Van Eeckhaut A, Lanckmans K, Sarre S, Smolders I, Michotte Y (2009) Validation of bioanalytical LC–MS/MS assays: evaluation of matrix effects. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 877(23):2198–2207
Gosetti F, Mazzucco E, Zampieri D, Gennaro MC (2010) Signal suppression/enhancement in high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1217(25):3929–3937
Trufelli H, Palma P, Famiglini G, Cappiello A (2011) An overview of matrix effects in liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom Rev 30(3):491–509
Enke CG (1997) A predictive model for matrix and analyte effects in electrospray ionization of singly-charged ionic analytes. Anal Chem 69(23):4885–4893
King R, Bonfiglio R, Fernandez-Metzler C, Miller-Stein C, Olah T (2000) Mechanistic investigation of ionization suppression in electrospray ionization. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 11(11):942–950
Beaudry F, Vachon P (2006) Electrospray ionization suppression, a physical or a chemical phenomenon? Biomed Chromatogr 20(2):200–205
Dams R, Huestis MA, Lambert WE, Murphy CM (2003) Matrix effect in bio-analysis of illicit drugs with LC–MS/MS: influence of ionization type, sample preparation, and biofluid. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 14(11):1290–1294
Liang HR, Foltz RL, Meng M, Bennett P (2003) Ionization enhancement in atmospheric pressure chemical ionization and suppression in electrospray ionization between target drugs and stable-isotope-labeled internal standards in quantitative liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 17(24):2815–2821
Mallet CR, Lu Z, Mazzeo JR (2004) A study of ion suppression effects in electrospray ionization from mobile phase additives and solid-phase extracts. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 18(1):49–58
Matuszewski BK, Constanzer ML, Chavez-Eng CM (2003) Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC–MS/MS. Anal Chem 75(13):3019–3030
Schuhmacher J, Zimmer D, Tesche F, Pickard V (2003) Matrix effects during analysis of plasma samples by electrospray and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry: practical approaches to their elimination. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 17(17):1950–1957
Souverain S, Rudaz S, Veuthey JL (2004) Matrix effect in LC–ESI–MS and LC–APCI–MS with off-line and on-line extraction procedures. J Chromatogr A 1058(1–2):61–66
Remane D, Meyer MR, Wissenbach DK, Maurer HH (2010) Ion suppression and enhancement effects of co-eluting analytes in multi-analyte approaches: systematic investigation using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry with atmospheric-pressure chemical ionization or electrospray ionization. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 24(21):3103–3108
Remane D, Wissenbach DK, Meyer MR, Maurer HH (2010) Systematic investigation of ion suppression and enhancement effects of fourteen stable-isotope-labeled internal standards by their native analogues using atmospheric-pressure chemical ionization and electrospray ionization and the relevance for multi-analyte liquid chromatographic/mass spectrometric procedures. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 24(7):859–867
Ikonomou MG, Blades AT, Kebarle P (1990) Investigations of the elctrospray interface for liquid chromatography/mass spectroemtry. Anal Chem 62:957–967
Couchman L, Morgan PE (2011) LC–MS in analytical toxicology: some practical considerations. Biomed Chromatogr 25(1–2):100–123
Bonfiglio R, King RC, Olah TV, Merkle K (1999) The effects of sample preparation methods on the variability of the electrospray ionization response for model drug compounds. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 13(12):1175–1185
Buhrman DL, Price PI, Rudewicz PJ (1996) Quantitation of SR 27417 in human plasma using electrospray liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry: a study of ion suppression. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 7:1099–1105
Matuszewski BK, Constanzer ML, Chavez-Eng CM (1998) Matrix effect in quantitative LC/MS/MS analyses of biological fluids: a method for determination of finasteride in human plasma at picogram per milliliter concentrations. Anal Chem 70(5):882–889
Peters FT, Drummer OH, Musshoff F (2007) Validation of new methods. Forensic Sci Int 165(2–3):216–224
Peters FT (2006) Method validation using LC–MS. In: Polettini A (ed) Applications of liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry in toxicology, vol 1st, Method validation using LC–MS. Pharmaceutical Press, London, pp 71–95
Viswanathan CT, Bansal S, Booth B, DeStefano AJ, Rose MJ, Sailstad J, Shah VP, Skelly JP, Swann PG, Weiner R (2007) Quantitative bioanalytical methods validation and implementation: best practices for chromatographic and ligand binding assays. Pharm Res 24(10):1962–1973
Wille SMR, Peters FT, Di Fazio V, Samyn N (2011) Practical aspects concerning validation and quality control for forensic and clinical bioanalytical quantitative methods. Accred Qual Assur 16(6):279–292
Peters FT, Hartung M, Herbold M, Schmitt G, Daldrup T, Musshoff F (2009) Anhang B zur Richtilinie der GTFCh zur Qualitätssicherung bei forensisch-toxikologischen Untersuchungen – Anforderungen an die Validierung von Analysenmethoden. Toxichem Krimtech 76(3):185–208
Matuszewski BK (2006) Standard line slopes as a measure of a relative matrix effect in quantitative HPLC–MS bioanalysis. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 830(2):293–300
Concheiro M, Simoes SM, Quintela O, de Castro A, Dias MJ, Cruz A, Lopez-Rivadulla M (2007) Fast LC–MS/MS method for the determination of amphetamine, methamphetamine, MDA, MDMA, MDEA, MBDB and PMA in urine. Forensic Sci Int 171(1):44–51
Gustavsson E, Andersson M, Stephanson N, Beck O (2007) Validation of direct injection electrospray LC–MS/MS for confirmation of opiates in urine drug testing. J Mass Spectrom 42(7):881–889
Feng J, Wang L, Dai I, Harmon T, Bernert JT (2007) Simultaneous determination of multiple drugs of abuse and relevant metabolites in urine by LC–MS–MS. J Anal Toxicol 31(7):359–368
Concheiro M, De Castro A, Quintela O, Cruz A, Lopez-Rivadulla M (2007) Determination of illicit drugs and their metabolites in human urine by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry including relative ion intensity criterion. J Anal Toxicol 31(9):573–580
Berg T, Lundanes E, Christophersen AS, Strand DH (2009) Determination of opiates and cocaine in urine by high pH mobile phase reversed phase UPLC–MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 877(4):421–432
del Mar Ramirez Fernandez M, Laloup M, Wood M, De Boeck G, Lopez-Rivadulla M, Wallemacq P, Samyn N (2007) Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous analysis of multiple hallucinogens, chlorpheniramine, ketamine, ritalinic acid, and metabolites, in urine. J Anal Toxicol 31(8):497–504
Qiu P, Chen X, Lin L, Ai C (2008) Simultaneous determination of five toxic alkaloids in body fluids by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 875(2):471–477
Pichini S, Pujadas M, Marchei E, Pellegrini M, Fiz J, Pacifici R, Zuccaro P, Farre M, de la Torre R (2008) Liquid chromatography–atmospheric pressure ionization electrospray mass spectrometry determination of "hallucinogenic designer drugs" in urine of consumers. J Pharm Biomed Anal 47(2):335–342
Cheng WC, Yau TS, Wong MK, Chan LP, Mok VK (2006) A high-throughput urinalysis of abused drugs based on a SPE–LC–MS/MS method coupled with an in-house developed post-analysis data treatment system. Forensic Sci Int 162(1–3):95–107
Quintela O, Sauvage FL, Charvier F, Gaulier JM, Lachatre G, Marquet P (2006) Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for detection of low concentrations of 21 benzodiazepines, metabolites, and analogs in urine: method with forensic applications. Clin Chem 52(7):1346–1355
Dulaurent S, Saint-Marcoux F, Marquet P, Lachatre G (2006) Simultaneous determination of six dialkylphosphates in urine by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 831(1–2):223–229
Wohlfarth A, Weinmann W, Dresen S (2010) LC–MS/MS screening method for designer amphetamines, tryptamines, and piperazines in serum. Anal Bioanal Chem 396(7):2403–2414
Sauvage FL, Gaulier JM, Lachatre G, Marquet P (2006) A fully automated turbulent-flow liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry technique for monitoring antidepressants in human serum. Ther Drug Monit 28(1):123–130
Ferreiros Bouzas N, Dresen S, Munz B, Weinmann W (2009) Determination of basic drugs of abuse in human serum by online extraction and LC–MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 395(8):2499–2507
Quintela O, Cruz A, Castro A, Concheiro M, Lopez-Rivadulla M (2005) Liquid chromatography–electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry for the determination of nine selected benzodiazepines in human plasma and oral fluid. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 825(1):63–71
Laloup M, Ramirez Fernandez Mdel M, De Boeck G, Wood M, Maes V, Samyn N (2005) Validation of a liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of 26 benzodiazepines and metabolites, zolpidem and zopiclone, in blood, urine, and hair. J Anal Toxicol 29(7):616–626
Beyer J, Peters FT, Kraemer T, Maurer HH (2007) Detection and validated quantification of toxic alkaloids in human blood plasma—comparison of LC–APCI–MS with LC–ESI–MS/MS. J Mass Spectrom 42(5):621–633
Beyer J, Peters FT, Kraemer T, Maurer HH (2007) Detection and validated quantification of nine herbal phenalkylamines and methcathinone in human blood plasma by LC–MS/MS with electrospray ionization. J Mass Spectrom 42(2):150–160
Li S, Liu G, Jia J, Liu Y, Pan C, Yu C, Cai Y, Ren J (2007) Simultaneous determination of ten antiarrhythic drugs and a metabolite in human plasma by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 847(2):174–181
Sergi M, Bafile E, Compagnone D, Curini R, D'Ascenzo G, Romolo FS (2009) Multiclass analysis of illicit drugs in plasma and oral fluids by LC–MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 393(2):709–718
Ferreiros N, Dresen S, Alonso RM, Weinmann W (2007) Validated quantitation of angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARA-II) in human plasma by liquid-chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry using minimum sample clean-up and investigation of ion suppression. Ther Drug Monit 29(6):824–834
Ishida T, Kudo K, Hayashida M, Ikeda N (2009) Rapid and quantitative screening method for 43 benzodiazepines and their metabolites, zolpidem and zopiclone in human plasma by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry with a small particle column. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 877(25):2652–2657
de Castro A, Ramirez Fernandez Mdel M, Laloup M, Samyn N, De Boeck G, Wood M, Maes V, Lopez-Rivadulla M (2007) High-throughput on-line solid-phase extraction–liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous analysis of 14 antidepressants and their metabolites in plasma. J Chromatogr A 1160(1–2):3–12
Remane D, Meyer MR, Peters FT, Wissenbach DK, Maurer HH (2010) Fast and simple procedure for liquid–liquid extraction of 136 analytes from different drug classes for development of a liquid chromatographic–tandem mass spectrometric quantification method in human blood plasma. Anal Bioanal Chem 397(6):2303–2314
Favretto D, Frison G, Maietti S, Ferrara SD (2007) LC–ESI–MS/MS on an ion trap for the determination of LSD, iso-LSD, nor-LSD and 2-oxo-3-hydroxy-LSD in blood, urine and vitreous humor. Int J Legal Med 121(4):259–265
Oiestad EL, Johansen U, Stokke Opdal M, Bergan S, Christophersen AS (2009) Determination of digoxin and digitoxin in whole blood. J Anal Toxicol 33(7):372–378
Roman M, Kronstrand R, Lindstedt D, Josefsson M (2008) Quantitation of seven low-dosage antipsychotic drugs in human postmortem blood using LC–MS–MS. J Anal Toxicol 32(2):147–155
Simonsen KW, Hermansson S, Steentoft A, Linnet K (2010) A validated method for simultaneous screening and quantification of twenty-three benzodiazepines and metabolites plus zopiclone and zaleplone in whole blood by liquid–liquid extraction and ultra-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol 34(6):332–341
Sorensen LK (2012) Determination of metformin and other biguanides in forensic whole blood samples by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed Chromatogr 26(1):1–5
Taylor K, Elliott S (2009) A validated hybrid quadrupole linear ion-trap LC–MS method for the analysis of morphine and morphine glucuronides applied to opiate deaths. Forensic Sci Int 187(1–3):34–41
Bjork MK, Nielsen MK, Markussen LO, Klinke HB, Linnet K (2010) Determination of 19 drugs of abuse and metabolites in whole blood by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 396(7):2393–2401
Kristoffersen L, Oiestad EL, Opdal MS, Krogh M, Lundanes E, Christophersen AS (2007) Simultaneous determination of 6 beta-blockers, 3 calcium-channel antagonists, 4 angiotensin-II antagonists and 1 antiarrhythmic drug in post-mortem whole blood by automated solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Method development and robustness testing by experimental design. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 850(1–2):147–160
Gergov M, Nokua P, Vuori E, Ojanpera I (2009) Simultaneous screening and quantification of 25 opioid drugs in post-mortem blood and urine by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci Int 186(1–3):36–43
Bugey A, Rudaz S, Staub C (2006) A fast LC–APCI/MS method for analyzing benzodiazepines in whole blood using monolithic support. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 832(2):249–255
Saar E, Gerostamoulos D, Drummer OH, Beyer J (2009) Comparison of extraction efficiencies and LC–MS–MS matrix effects using LLE and SPE methods for 19 antipsychotics in human blood. Anal Bioanal Chem 393(2):727–734
Rosano TG, Wood M, Swift TA (2011) Postmortem drug screening by non-targeted and targeted ultra-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry technology. J Anal Toxicol 35(7):411–423
Ariffin MM, Anderson RA (2006) LC/MS/MS analysis of quaternary ammonium drugs and herbicides in whole blood. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 842(2):91–97
Oiestad EL, Johansen U, Christophersen AS (2007) Drug screening of preserved oral fluid by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem 53(2):300–309
Wood M, Laloup M, Ramirez Fernandez Mdel M, Jenkins KM, Young MS, Ramaekers JG, De Boeck G, Samyn N (2005) Quantitative analysis of multiple illicit drugs in preserved oral fluid by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci Int 150(2–3):227–238
Concheiro M, de Castro A, Quintela O, Cruz A, Lopez-Rivadulla M (2008) Determination of illicit and medicinal drugs and their metabolites in oral fluid and preserved oral fluid by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 391(6):2329–2338
Kintz P, Villain M, Concheiro M, Cirimele V (2005) Screening and confirmatory method for benzodiazepines and hypnotics in oral fluid by LC–MS/MS. Forensic Sci Int 150(2–3):213–220
Concheiro M, de Castro A, Quintela O, Cruz A, Lopez-Rivadulla M (2007) Confirmation by LC–MS of drugs in oral fluid obtained from roadside testing. Forensic Sci Int 170(2–3):156–162
Badawi N, Simonsen KW, Steentoft A, Bernhoft IM, Linnet K (2009) Simultaneous screening and quantification of 29 drugs of abuse in oral fluid by solid-phase extraction and ultraperformance LC–MS/MS. Clin Chem 55(11):2004–2018
de Castro A, Concheiro M, Quintela O, Cruz A, Lopez-Rivadulla M (2008) LC–MS/MS method for the determination of nine antidepressants and some of their main metabolites in oral fluid and plasma. Study of correlation between venlafaxine concentrations in both matrices. J Pharm Biomed Anal 48(1):183–193
Concheiro M, Gray TR, Shakleya DM, Huestis MA (2010) High-throughput simultaneous analysis of buprenorphine, methadone, cocaine, opiates, nicotine, and metabolites in oral fluid by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 398(2):915–924
Laloup M, Fernandez Mdel M, Wood M, Maes V, De Boeck G, Vanbeckevoort Y, Samyn N (2007) Detection of diazepam in urine, hair and preserved oral fluid samples with LC–MS–MS after single and repeated administration of Myolastan and Valium. Anal Bioanal Chem 388(7):1545–1556
Wang IT, Feng YT, Chen CY (2010) Determination of 17 illicit drugs in oral fluid using isotope dilution ultra-high performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry with three atmospheric pressure ionizations. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 878(30):3095–3105
Coulter C, Garnier M, Moore C (2011) Synthetic cannabinoids in oral fluid. J Anal Toxicol 35(7):424–430
Fritch D, Blum K, Nonnemacher S, Haggerty BJ, Sullivan MP, Cone EJ (2009) Identification and quantitation of amphetamines, cocaine, opiates, and phencyclidine in oral fluid by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol 33(9):569–577
Vogliardi S, Favretto D, Tucci M, Stocchero G, Ferrara SD (2011) Simultaneous LC–HRMS determination of 28 benzodiazepines and metabolites in hair. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(1):51–67
Scheidweiler KB, Huestis MA (2004) Simultaneous quantification of opiates, cocaine, and metabolites in hair by LC–APCI–MS/MS. Anal Chem 76(15):4358–4363
Rust KY, Baumgartner MR, Meggiolaro N, Kraemer T (2012) Detection and validated quantification of 21 benzodiazepines and 3 "z-drugs" in human hair by LC–MS/MS. Forensic Sci Int 215(1–3):64–72
Miller EI, Wylie FM, Oliver JS (2008) Simultaneous detection and quantification of amphetamines, diazepam and its metabolites, cocaine and its metabolites, and opiates in hair by LC–ESI–MS–MS using a single extraction method. J Anal Toxicol 32(7):457–469
Kim J, Lee S, In S, Choi H, Chung H (2011) Validation of a simultaneous analytical method for the detection of 27 benzodiazepines and metabolites and zolpidem in hair using LC–MS/MS and its application to human and rat hair. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 879(13–14):878–886
Broecker S, Herre S, Pragst F (2011) General unknown screening in hair by liquid chromatography–hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC–QTOF–MS). Forensic Sci Int. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2011.10.004
Hegstad S, Khiabani HZ, Kristoffersen L, Kunoe N, Lobmaier PP, Christophersen AS (2008) Drug screening of hair by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol 32(5):364–372
Concheiro M, Shakleya DM, Huestis MA (2011) Simultaneous analysis of buprenorphine, methadone, cocaine, opiates and nicotine metabolites in sweat by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(1):69–78
Thomas A, Deglon J, Steimer T, Mangin P, Daali Y, Staub C (2010) On-line desorption of dried blood spots coupled to hydrophilic interaction/reversed-phase LC/MS/MS system for the simultaneous analysis of drugs and their polar metabolites. J Sep Sci 33(6–7):873–879
Gray TR, Shakleya DM, Huestis MA (2009) A liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous quantification of 20 drugs of abuse and metabolites in human meconium. Anal Bioanal Chem 393(8):1977–1990
Pichini S, Pellegrini M, Gareri J, Koren G, Garcia-Algar O, Vall O, Vagnarelli F, Zuccaro P, Marchei E (2008) Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for fatty acid ethyl esters in meconium: assessment of prenatal exposure to alcohol in two European cohorts. J Pharm Biomed Anal 48(3):927–933
Sauvage FL, Saint-Marcoux F, Duretz B, Deporte D, Lachatre G, Marquet P (2006) Screening of drugs and toxic compounds with liquid chromatography–linear ion trap tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem 52(9):1735–1742
Pelander A, Ristimaa J, Rasanen I, Vuori E, Ojanpera I (2008) Screening for basic drugs in hair of drug addicts by liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Ther Drug Monit 30(6):717–724
Pelander A, Ristimaa J, Ojanpera I (2010) Vitreous humor as an alternative matrix for comprehensive drug screening in postmortem toxicology by liquid chromatography–time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol 34(6):312–318
Wissenbach DK, Meyer MR, Remane D, Weber AA, Maurer HH (2011) Development of the first metabolite-based LC–MS( n ) urine drug screening procedure—exemplified for antidepressants. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(1):79–88
Wissenbach DK, Meyer MR, Remane D, Philipp AA, Weber AA, Maurer HH (2011) Drugs of abuse screening in urine as part of a metabolite-based LC–MS(n) screening concept. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(10):3481–3489
Lee HK, Ho CS, Iu YP, Lai PS, Shek CC, Lo YC, Klinke HB, Wood M (2009) Development of a broad toxicological screening technique for urine using ultra-performance liquid chromatography and time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 649(1):80–90
Mueller DM, Duretz B, Espourteille FA, Rentsch KM (2011) Development of a fully automated toxicological LC–MS(n) screening system in urine using online extraction with turbulent flow chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(1):89–100
Muller C, Schafer P, Stortzel M, Vogt S, Weinmann W (2002) Ion suppression effects in liquid chromatography–electrospray-ionisation transport-region collision induced dissociation mass spectrometry with different serum extraction methods for systematic toxicological analysis with mass spectra libraries. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 773(1):47–52
Stokvis E, Rosing H, Beijnen JH (2005) Stable isotopically labeled internal standards in quantitative bioanalysis using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry: necessity or not? Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 19(3):401–407
Lindegardh N, Annerberg A, White NJ, Day NP (2008) Development and validation of a liquid chromatographic–tandem mass spectrometric method for determination of piperaquine in plasma stable isotope labeled internal standard does not always compensate for matrix effects. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 862(1–2):227–236
Wang S, Cyronak M, Yang E (2007) Does a stable isotopically labeled internal standard always correct analyte response? A matrix effect study on a LC/MS/MS method for the determination of carvedilol enantiomers in human plasma. J Pharm Biomed Anal 43(2):701–707
Sojo LE, Lum G, Chee P (2003) Internal standard signal suppression by co-eluting analyte in isotope dilution LC–ESI–MS. Analyst 128(1):51–54
Remane D, Meyer MR, Wissenbach DK, Maurer HH (2011) Full validation and application of an ultra high performance liquid chromatographic–tandem mass spectrometric procedure for target screening and quantification of 34 antidepressants in human blood plasma as part of a comprehensive multi-analyte approach. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(7):2093–2107
Remane D, Meyer MR, Wissenbach DK, Maurer HH (2011) Ultra high performance liquid chromatographic–tandem mass spectrometric multi-analyte procedure for target screening and quantification in human blood plasma: validation and application for 31 neuroleptics, 28 benzodiazepines, and Z-drugs. Anal Bioanal Chem 401(4):1341–1352
Egge-Jacobsen W, Unger M, Niemann CU, Baluom M, Hirai S, Benet LZ, Christians U (2004) Automated, fast, and sensitive quantification of drugs in human plasma by LC/LC–MS: quantification of 6 protease inhibitors and 3 nonnucleoside transcriptase inhibitors. Ther Drug Monit 26(5):546–562
Hoizey G, Lamiable D, Trenque T, Robinet A, Binet L, Kaltenbach ML, Havet S, Millart H (2005) Identification and quantification of 8 sulfonylureas with clinical toxicology interest by liquid chromatography–ion-trap tandem mass spectrometry and library searching. Clin Chem 51(9):1666–1672
Tong X, Ita IE, Wang J, Pivnichny JV (1999) Characterization of a technique for rapid pharmacokinetic studies of multiple co-eluting compounds by LC/MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal 20(5):773–784
Neuvonen M, Neuvonen PJ (2008) Determination of oxycodone, noroxycodone, oxymorphone, and noroxymorphone in human plasma by liquid chromatography–electrospray–tandem mass spectrometry. Ther Drug Monit 30(3):333–340
Skelton H, Dann LM, Ong RT, Hamilton T, Ilett KF (1998) Drug screening of patients who deliberately harm themselves admitted to the emergency department. Ther Drug Monit 20(1):98–103
Wu AH, McKay C, Broussard LA, Hoffman RS, Kwong TC, Moyer TP, Otten EM, Welch SL, Wax P (2003) National academy of clinical biochemistry laboratory medicine practice guidelines: recommendations for the use of laboratory tests to support poisoned patients who present to the emergency department. Clin Chem 49(3):357–379
Maurer HH (1998) Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry in forensic and clinical toxicology [review]. J Chromatogr B: Biomed Sci Appl 713(1):3–25
Polettini A (1999) Systematic toxicological analysis of drugs and poisons in biosamples by hyphenated chromatographic and spectroscopic techniques. J Chromatogr B 733:47–63
Wood M, Laloup M, Samyn N, Mar Ramirez FM, De Bruijn EA, Maes RA, de Boeck G (2006) Recent applications of liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry in forensic science. J Chromatogr A 1130(1):3–15
Mueller CA, Weinmann W, Dresen S, Schreiber A, Gergov M (2005) Development of a multi-target screening analysis for 301 drugs using a QTrap liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry system and automated library searching. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 19(10):1332–1338
Dresen S, Ferreiros N, Gnann H, Zimmermann R, Weinmann W (2010) Detection and identification of 700 drugs by multi-target screening with a 3200 Q TRAP((R)) LC–MS/MS system and library searching. Anal Bioanal Chem 396(7):2425–2434
Dresen S, Gergov M, Politi L, Halter C, Weinmann W (2009) ESI–MS/MS library of 1,253 compounds for application in forensic and clinical toxicology. Anal Bioanal Chem 395(8):2521–2526
Pelander A, Ojanpera I, Laks S, Rasanen I, Vuori E (2003) Toxicological screening with formula-based metabolite identification by liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 75(21):5710–5718
Gergov M, Boucher B, Ojanpera I, Vuori E (2001) Toxicological screening of urine for drugs by liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry with automated target library search based on elemental formulas. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 15(8):521–526
Liu HC, Liu RH, Lin DL, Ho HO (2010) Rapid screening and confirmation of drugs and toxic compounds in biological specimens using liquid chromatography/ion trap tandem mass spectrometry and automated library search. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 24(1):75–84
Humbert L, Grisel F, Richeval C, Lhermitte M (2010) Screening of xenobiotics by ultra-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry using in-source fragmentation at increasing cone voltages: library constitution and an evaluation of spectral stability. J Anal Toxicol 34(9):571–580
Herrin GL, McCurdy HH, Wall WH (2005) Investigation of an LC–MS–MS (QTrap) method for the rapid screening and identification of drugs in postmortem toxicology whole blood samples. J Anal Toxicol 29(7):599–606
Broecker S, Herre S, Wust B, Zweigenbaum J, Pragst F (2011) Development and practical application of a library of CID accurate mass spectra of more than 2,500 toxic compounds for systematic toxicological analysis by LC–QTOF–MS with data-dependent acquisition. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(1):101–117
Broecker S, Pragst F, Bakdash A, Herre S, Tsokos M (2011) Combined use of liquid chromatography–hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC–QTOF–MS) and high performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array detector (HPLC–DAD) in systematic toxicological analysis. Forensic Sci Int 212(1–3):215–226
Gergov M, Ojanpera I, Vuori E (2003) Simultaneous screening for 238 drugs in blood by liquid chromatography–ion spray tandem mass spectrometry with multiple-reaction monitoring. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 795(1):41–53
Gosselin M, Ramirez Fernandez Mdel M, Wille SM, Samyn N, De Boeck G, Bourel B (2010) Quantification of methadone and its metabolite 2-ethylidene-1,5-dimethyl-3,3-diphenylpyrrolidine in third instar larvae of Lucilia sericata (Diptera: Calliphoridae) using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol 34(7):374–380
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Dirk K. Wissenbach for his assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the special issue Young Investigators in Analytical and Bioanalytical Science with guest editors S. Daunert, J. Bettmer, T. Hasegawa, Q. Wang and Y. Wei.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 239 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peters, F.T., Remane, D. Aspects of matrix effects in applications of liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry to forensic and clinical toxicology—a review. Anal Bioanal Chem 403, 2155–2172 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6035-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6035-2