Abstract
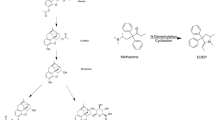
A high-performance liquid chromatography (LC)–tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) method has been developed and validated for the determination of 19 drugs of abuse and metabolites and used in whole blood. The following compounds were included: amphetamine, methylenedioxyamphetamine, methylenedioxyethylamphetamine, methylenedioxymethamphetamine, methamphetamine, cocaine, benzoylecgonine, morphine, 6-acetylmorphine, codeine, methadone, buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine, ketobemidone, tramadol, O-desmethyltramadol, zaleplone, zolpidem, and zopiclone. The sample pretreatment consisted of solid-phase extraction using mixed-mode columns (Isolute Confirm HCX). Deuterated analogues were used as internal standards for all analytes, except for ketobemidone and O-desmethyltramadol. The analytes were separated by a methanol/ammonium formate gradient using high-performance LC (Agilent HPLC 1100) with a 3 mm × 100 mm Varian Pursuit 3 C18 column, 3-µm particle size, and were quantified by MS/MS (Waters Quattro micro tandem quadrupole mass spectrometer) using multiple reaction monitoring in positive mode. Two transitions were used for all analytes, except for tramadol and O-desmethyltramadol. The run time of the method was 35 min including the equilibration time. For all analytes, responses were linear over the range investigated, with R 2 > 0.99. One-point calibration was found to be adequate by validation, thereby saving analysis of multiple calibrators. The limits of quantification (LOQs) for the analytes ranged from 0.0005 to 0.01 mg/kg. Absolute recoveries of the analytes were from 34 to 97%, except for zaleplone (6%). Both the interday precision and the intraday precision were less than 15% (20% at the LOQ) for all analytes, except buprenorphine, norburprenorphine, and zaleplone (less than 18%). Accuracy (bias) was within ±15% (±20% at the LOQ) for all analytes, except MDMA and O-desmethyltramadol (within ±19%). No ion suppression or enhancement was seen nor was suppression from coeluted analytes seen. Matrix effects were found to be less than 23% for all analytes, except zopiclone (64%). High-concentration and low-concentration quality control samples gave acceptable values, and the method has been tried in international proficiency test schemes with good results. The present LC-MS/MS method provides a simple, specific, and sensitive solution for the quantification of some of the most frequent drugs of abuse and their metabolites in whole blood. The quantification by LC-MS/MS was successfully applied to 412 forensic cases from October 2008 to mid February 2009, where 267 cases were related to zero-tolerance traffic legislation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moeller MR, Kraemer T (2002) Ther Drug Monit 24:210–221
Kraemer T, Paul LD (2007) Anal Bioanal Chem 388:1415–1435
Maurer HH (2009) Anal Bioanal Chem 393:97–107
Musshoff F, Trafkowski J, Kuepper U, Madea B (2006) J Mass Spectrom 41:633–640
Gergov M, Nokua P, Vuori E, Qjanpera I (2009) Forensic Sci Int 186:36–43
Johansen SS, Bhatia HM (2007) J Chromatogr B 852:338–344
Wood M, De Boeck G, Samyn N, Morris M, Cooper DP, Maes RA, de Bruijn EA (2003) J Anal Toxicol 27:78–87
Kratzsch C, Tenberken O, Peters FT, Weber AA, Kraemer T, Maurer HH (2004) J Mass Spectrom 39:856–872
Gunnar T, Ariniemi K, Lillsunde P (2005) J Mass Spectrom 40:739–753
Concheiro M, de Castro A, Quintela O, Lopez-Rivadulla M, Cruz A (2006) J Chromatogr B 832:81–89
Maralikova B, Weinmann W (2004) J Chromatogr B 811:21–30
European Commission (2002) Off J Eur Communities L 221:8
Peters FT, Drummer OH, Musshoff F (2007) Forensic Sci Int 165:216–224
Allen KR (2006) Clin Toxicol (Phila) 44:147–153
Sauvage FL, Gaulier JM, Lachatre G, Marquet P (2008) Clin Chem 54:1519–1527
Matuszewski BK, Constanzer ML, Chavez-Eng CM (2003) Anal Chem 75:3019–3030
Baselt RC (2008) Disposition of toxic drugs and chemicals in man. Biomedical Publications, Foster City
Winek CL, Wahba WW, Winek CL Jr, Balzer TW (2001) Forensic Sci Int 122:107–123
Schulz M, Schmoldt A (2003) Pharmazie 58:447–474
Peters FT, Maurer HH (2007) Anal Chem 79:4967–4976
Christophersen AS, Morland J (1997) Drug Alcohol Depend 47:125–135
Christophersen AS, Ceder G, Kristinsson J, Lillsunde P, Steentoft A (1999) Forensic Sci Int 106:173–190
Holmgren A, Holmgren P, Kugelberg FC, Jones AW, Ahlner J (2007) Traffic Inj Prev 8:361–367
Ojaniemi KK, Lintonen TP, Impinen AO, Lillsunde PM, Ostamo AI (2009) Accid Anal Prev 41:191–196
Walsh JM, de Gier JJ, Christopherson AS, Verstraete AG (2004) Traffic Inj Prev 5:241–253
Behrensdorff I, Steentoft A (2003) Accid Anal Prev 35:851–860
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Birthe Haue Christensen and Jytte Lundsby Jensen for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bjørk, M.K., Nielsen, M.K.K., Markussen, L.Ø. et al. Determination of 19 drugs of abuse and metabolites in whole blood by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 396, 2393–2401 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3268-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3268-9