Abstract
A reliable PCR reference assay for relative genetically modified organism (GMO) quantification must be specific for the target taxon and amplify uniformly along the commercialised varieties within the considered taxon. Different reference assays for maize (Zea mays L.) are used in official methods for GMO quantification. In this study, we evaluated the reliability of eight existing maize reference assays, four of which are used in combination with an event-specific polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay validated and published by the Community Reference Laboratory (CRL). We analysed the nucleotide sequence variation in the target genomic regions in a broad range of transgenic and conventional varieties and lines: MON 810 varieties cultivated in Spain and conventional varieties from various geographical origins and breeding history. In addition, the reliability of the assays was evaluated based on their PCR amplification performance. A single base pair substitution, corresponding to a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) reported in an earlier study, was observed in the forward primer of one of the studied alcohol dehydrogenase 1 (Adh1) (70) assays in a large number of varieties. The SNP presence is consistent with a poor PCR performance observed for this assay along the tested varieties. The obtained data show that the Adh1 (70) assay used in the official CRL NK603 assay is unreliable. Based on our results from both the nucleotide stability study and the PCR performance test, we can conclude that the Adh1 (136) reference assay (T25 and Bt11 assays) as well as the tested high mobility group protein gene assay, which also form parts of CRL methods for quantification, are highly reliable. Despite the observed uniformity in the nucleotide sequence of the invertase gene assay, the PCR performance test reveals that this target sequence might occur in more than one copy. Finally, although currently not forming a part of official quantification methods, zein and SSIIb assays are found to be highly reliable in terms of nucleotide stability and PCR performance and are proposed as good alternative targets for a reference assay for maize.

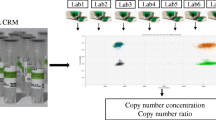
Comparison of performance of reference assays in worldwide collection of varieties. Each scatter plot was constructed by plotting the copy numbers determined with one reference assay (x-axis) against the copy numbers determined with another reference assay (y-axis) after the genewise normalisation of copy number data. The red line in each scatter plot denotes a perfect correlation (r = 1) of copy numbers between the two assays. The individual correlation coefficients between the assays are also shown in the squares diagonally opposite to individual plots





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Adh1 :
-
Alcohol dehydrogenase 1 gene
- BLAST:
-
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool
- Bp:
-
Base pairs
- CE:
-
Capillary electrophoresis
- CRL:
-
Community Reference Laboratory
- CRMs:
-
Certified reference materials
- CSCE:
-
Conformation sensitive capillary electrophoresis
- CSIC:
-
Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- dNTP:
-
Deoxynucleotide triphosphate
- EC:
-
European Commission
- EU:
-
European Union
- GM:
-
Genetically modified
- GMO:
-
Genetically modified organism
- Hmg :
-
High mobility group protein gene
- ILVO:
-
Institute for Agricultural and Fisheries Research
- Indel:
-
Insertion/deletion
- IRMM:
-
Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements
- Ivr :
-
Invertase gene
- JRC:
-
Joint Research Centre
- NIB:
-
National Institute of Biology
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- RA:
-
Reference assay
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- SSIIb :
-
Zea mays starch synthetase type B gene
References
James C (2009) Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops in 2008. ISAAA Brief 39: Executive Summary
Directive 2001/18/EC of the European Parliament and the Council of 12 March 2001 on the deliberate release into the environment of genetically modified organisms and repealing Council Directive 90/220/EEC. Off J Eur Union L106:1–38
Regulation (EC) No. 1829/2003 of the European Parliament and the Council of 22 September 2003 on genetically modified food and feed. Off J Eur Union L266:1–23
Regulation (EC) No. 1830/2003 of the European Parliament and the Council of 22 September 2003 concerning the traceability and labelling of genetically modified organisms and the traceability of food and feed products produced from genetically modified organisms and amending Directive 2001/18/EC. Off J Eur Union L266:24–28
Commission Regulation (EC) No 641/2004 of 6 April 2004 on detailed rules for the implementation of Regulation (EC) No 1829/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards the application for the authorisation of new genetically modified food and feed, the notification of existing products and adventitious or technically unavoidable presence of genetically modified material which has benefited from a favourable risk evaluation. Off J Eur Union L102:14–25
Commission Recommendation 2004/787/EC of 4 October 2004 on technical guidance for sampling and detection of genetically modified organisms and material produced from genetically modified organisms as or in products in the context of Regulation (EC) No 1830/2003. Off J Eur Union L348:18–26
Commission Regulation (EC) No 1981/2006 of 22 December 2006 on detailed rules for the implementation of Article 32 of Regulation (EC) No 1829/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards the community reference laboratory for genetically modified organisms. Off J Eur Union L386:99–109
Community Reference Laboratory official website: http://www.crl-gmo.europa.eu
OECD (2003) Consensus document on the biology of Zea mays subsp. Mays (maize). Series on harmonization of regulatory oversight in biotechnology No.27. JT00147699
European Commission (2006) The common catalogue of varieties of agricultural plant species. Off J Eur Union C 68A/01
Hernandez M, Duplan M, Berthier G, Vaïtilingom M, Hauser W, Freyer R, Pla M, Bertheau Y (2004) J Agric Food Chem 52:4632
Taverniers I (2005) Development and implementation of strategies for GMO quantification in an evolving European context. PhD thesis. University of Ghent, ISBN 90-5989-049-3, p 346
Kuribara H, Shindo Y, Matsuoka T, Takubo K, Futo S, Aoki N, Hirao T, Akiyama H, Goda Y, Toyoda M, Hino A (2002) J AOAC Int 85:1077
Shindo Y, Kuribara H, Matsuoka T, Futo S, Sawada C, Shono J, Akiyama H, Goda Y, Toyoda M, Hino A (2002) J AOAC Int 85:1119
Yoshimura T, Kuribara H, Matsuoka T, Kodama T, Iida M, Watanabe T, Akiyama H, Maitani T, Furui S, Hino A (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:2052
Brunner S, Fengler K, Morgante M, Tingey S, Rafalski A (2005) The Plant Cell 17:343
Emrich SJ, Li L, Wen T, Yandeau-Nelson M, Fu Y, Guo L, Chou H, Aluru S, Ashlock D, Schnable P (2007) Genetics 175:429
Liu K, Goodman M, Muse S, Smith JS, Buckler E, Doebley J (2003) Genetics 165:2117
Bhattramakki D, Dolan M, Hanafey M, Wineland R, Vaske D, Register J III, Tingey S, Rafalski A (2002) Plant Mol Biol 48:539
Tenaillon M, Sawkins M, Anderson L, Stack S, Doebley J, Gaut B (2002) Genetics 162:1401
Broothaerts W, Corbisier P, Schimmel H, Trapmann S, Vincent S, Emons H (2008) J Agric Food Chem 56:8825
Bru D, Martin-Laurent D, Philippot L (2008) Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1660
Ghedira R, Papazova N, Vuylsteke M, Ruttink T, Taverniers I, De Loose M (2009) Assessment of primer/template mismatch effects on real-time PCR amplification of target taxa for GMO quantification. J Agric Food Chem 57(20):9370
Zhang D, Corlet A, Fouilloux S (2008) Transgenic Res 17:393
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Molecular biology. Humana Press, Totowa, p 365
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:208
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn P, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Genome Biol 3: research0034.1–0034.11. Available from http://genomebiology.com/2002/3/7/research/0034.1
Papazova N, Ghedira R, Van Glabeke S, Bategi A, Windels P, Taverniers I, Roldan-Ruiz I, Van Bockstaele E, Milcamps A, Van den Eede G, Depicker A, De Loose M (2008) Plant Cell Rep 27:749
Sachs M, Dennis E, Gerlach W, Peacock W (1986) Genetics 113:449
Ceddia M, Rodriguez-Cerezo E (2008) A descriptive analysis of conventional, organic and GM crop and certified seed production in the EU. EUR 23443 EN
Vigouroux Y, Mitchell S, Matsuoka Y, Hamblin M, Kresovich S, Smith JSC, Jaqueth J, Smith OS, Doebley J (2005) Genetics 169:1617
Moor D (2005) Reliability of the Maize and Soybean Endogenous Reference Genes used in GMO Analysis if Food. PhD thesis, University of Bern, p 128
Chaouachi M, Giancola S, Romaniuk M, Laval V, Bertheau Y, Brunel D (2007) J Agric Food Chem 55:8003
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the European Commission through the Sixth Framework Programme, integrated project Co-Extra (http://www.coextra.eu), contract FOOD-2005-CT-007158 and by the Slovenian Research Agency Programme Plant biotechnology and systems biology P4-0165. Maria Pla (CSIC, Spain) and Zoran Čergan (Agricultural Institute of Slovenia) are acknowledged for providing seed and DNA material from maize varieties. We are very thankful to Cindy Merckaert and Kato Platteau for the excellent experimental work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Nina Papazova and David Zhang contributed equally to this paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 463 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papazova, N., Zhang, D., Gruden, K. et al. Evaluation of the reliability of maize reference assays for GMO quantification. Anal Bioanal Chem 396, 2189–2201 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3386-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3386-4