Abstract.
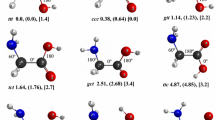
The potential energy hypersurface of protonated glycine, GH+, has been investigated. The calculated G2(MP2) value for the proton affinity (PA) of glycine, PA calc=895kJ mol−1, is in good agreement with the experimental value which has been estimated to lie in the range 864kJ mol−1 < PA exp <891kJ mol−1. Ab initio quantum chemical calculations of relevant parts of the potential energy surface of GH+ give a reaction model which is consistent with the observed mass spectrometric fragmentation pattern. The lowest energy unimolecular reactions of GH+ are two distinct processes: (1) loss of CO, which has a substantial barrier for the reverse reaction, and (2) loss of CO plus H2O, which has no barrier for the reverse reaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 November 1996 / Accepted: 6 May 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uggerud, E. The unimolecular chemistry of protonated glycine and the proton affinity of glycine: a computational model. Theor Chem Acta 97, 313–316 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002140050266
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002140050266