Abstract.
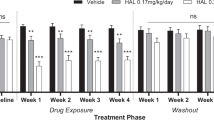
Chronic haloperidol treatment for 4–12 months gradually induces spontaneous, irregular, purposeless oral chewing movements (CMs), apparently involuntary, in some but not all treated rats. Based on phenomenologic and pharmacologic similarities, this laboratory preparation has been used as an animal model of tardive dyskinesia (TD), which is the human hyperkinetic motor syndrome associated with chronic antipsychotic administration. This putative animal model has received the most severe challenge to its validity by claims that its oral movements can be suppressed by anticholinergic treatments, since resistance to anticholinergic suppression is an accepted pharmacologic feature of TD. In this experiment, we challenged a group of haloperidol-treated rats with CMs using three doses of scopolamine (0.1, 0.3, 1.0 mg/kg) and placebo and rated the change in dyskinetic movements. Each scopolamine dose reduced CMs by a similar magnitude, without any dose effect; the saline dose also reduced CMs to an equivalent degree. Therefore, we concluded that some component of the experiment, not the scopolamine, reduced the CMs. The handling component of the procedure was identified as a likely confound, and we tested this further. Rats with CMs were handled at several levels of "severity"; and the dyskinesias were rated at 1 and 3 h later. CMs were reduced by the experimental handling, in relation to the strength of the handling. Minimal handling produced modest CM reductions with quick recovery; whereas, the "strongest" handling plus the placebo injection produced the greatest CM reduction, evident over 3 h, resembling the CM reductions seen in the scopolamine and placebo experiment. Overall, these results suggest that anticholinergic drugs do not suppress chronic haloperidol-induced rat CMs. However, the movements are sensitive to stressful handling situations, and diminish with stress. In both of these characteristics, rat CMs resemble human TD, further supporting a role for this model in studies of human TD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakai, K., Gao, XM. & Tamminga, C. Scopolamine fails to diminish chronic haloperidol-induced purposeless chewing in rats. Psychopharmacology 153, 191–195 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000570
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000570