Abstract
Rationale
Inosine is a naturally occurring purine nucleoside formed by adenosine breakdown. This nucleoside is reported to exert potent effects on memory and learning, possibly through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions.
Objective
The objective is to evaluate the effects of inosine on the behavioral and neurochemical parameters in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) induced by streptozotocin (STZ).
Methods
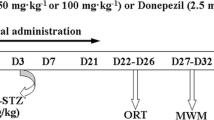
Adult male rats were divided into four groups: control (saline), STZ, STZ plus inosine (50 mg/kg), and STZ plus inosine (100 mg/kg). STZ (3 mg/kg) was administered by bilateral intracerebroventricular injection. The animals were treated intraperitoneally with inosine for 25 days. Memory, oxidative stress, ion pump activities, acetylcholinesterase (AChE), and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) activities and expression were evaluated in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus.
Results
The memory impairment induced by STZ was prevented by inosine. An increase in the Na+, K+-ATPase, and Mg-ATPase activities and a decrease in the Ca2+-ATPase activity were induced by STZ in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex, and inosine could prevent these alterations in ion pump activities. Inosine also prevented the increase in AChE activity and the alterations in AChE and ChAT expression induced by STZ. STZ increased the reactive oxygen species, nitrite levels, and superoxide dismutase activity and decreased the catalase and glutathione peroxidase activities. Inosine treatment conferred protection from these oxidative alterations in the brain.
Conclusions
Our findings demonstrate that inosine affects brain multiple targets suggesting that this molecule may have therapeutic potential against cognitive deficit and tissue damage in AD.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Agostinho P, Cunha RA, Oliveira C (2010) Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Curr Pharm Des 16:2766–2778
Aksenov MY, Markesbery WR (2001) Changes in thiol content and expression of glutathione redox system genes in the hippocampus and cerebellum in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 302:141–145
Ali SF, LeBel CP, Bondy SC (1992) Reactive oxygen species formation as a biomarker of methyl mercury and trimethyltin neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicol 13:637–648
Andreadou E, Nikolaou C, Gournaras F et al (2009) Serum uric acid levels in patients with Parkinson's disease: their relationship to treatment and disease duration. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 111:724–728
Apell HJ, Hitzler T, Schreiber G (2017) Modulation of the Na,K-ATPase by magnesium ions. Biochemistry 56:1005–1016
Aperia A (2007) New roles for an old enzyme: Na,K-ATPase emerges as an interesting drug target. J Intern Med 261:44–52
Assmann CE, Cadoná FC, Bonadiman BDSR, Dornelles EB, Trevisan G, Cruz IBMD (2018) Tea tree oil presents in vitro antitumor activity on breast cancer cells without cytotoxic effects on fibroblasts and on peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Biomed Pharmacother 103:1253–1261
Benarroch E (2011) Na+, K+-ATPase: functions in the nervous system and involvement in neurologic disease. Neurology 76:287–293
Carvalho FB, Gutierres JM, Bohnert C, Zago AM, Abdalla FH, Vieira JM, Palma HE, Oliveira SM, Spanevello RM, Duarte MM, Lopes ST, Aiello G, Amaral MG, Pippi NL, Andrade CM (2015) Anthocyanins suppress the secretion of proinflammatory mediators and oxidative stress, and restore ion pump activities in demyelination. J Nutr Biochem 26:378–390
Chen YG (2018) Research progress in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Chin Med J 131:1618–1624
Cinalli A, Guarracino J, Fernadez V et al (2013) Inosine induces presynaptic inhibition of acetylcholine release by activation of A3 adenosine receptors at the mouse neuromuscular junction. Br J Pharmacol 169:1810–1823
Dachir S, Shabashov D, Trembovler V, Alexandrovich AG, Benowitz LI, Shohami E (2014) Inosine improves functional recovery after experimental traumatic brain injury. Brain Res 1555:78–88
Darlington DN, Gann DS (2005) Purine nucleosides stimulate Na/K ATPase and prolong survival in hemorrhagic shock. J Trauma 58:1055–1060
Deiana S, Platt B, Riedel G (2011) The cholinergic system and spatial learning. Behav Brain Res 10:389–411
Dekosky S, Scheff S (1990) Synapse loss in frontal cortex biopsies in Alzheimer's disease: correlation with cognitive severity. Ann Neurob 27:457–464
Dellu F, Fauchey V, LeMoal M, Simon H (1997) Extension of a new two-trial memory task in the rat: influence of environmental context on recognition processes. Neur Learn Memory 67:112–120
Deshmukh R, Kaudal M, Bansal V et al (2016) Caffeic acid attenuates oxidative stress, learning and memory deficit in intra-cerebroventricular streptozotocin induced experimental dementia in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 81:56–62
Dixon A, Gubitz A, Sirinathsinghji D et al (1996) Tissue distribution of adenosine receptor mRNAs in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 118:14–16
Doyle C, Cristofaro V, Sullivan MP, Adam RM (2018) Inosine-a multifunctional treatment for complications of neurologic injury. Cell Physiol Biochem 49:2293–2303
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V et al (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Esterbauer H, Cheeseman KH (1990) Determination of aldehydic lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 186:407–421
Euser SM, Hofman A, Westendorp RG, Breteler MM (2009) Serum uric acid and cognitive function and dementia. Brain 132:377–382
Gamaro GD, Suyenaga E, Borsoi M et al (2011) Effect of rosmarinic and caffeic acids on inflammatory and nociception process in rats. Pharmacol 451682
Glantzounis GK, Tsimoyiannis EC, Kappas AM, Galaris DA (2005) Uric acid and oxidative stress. Curr Pharm Des 11:4145–4151
Grieb P (2016) Intracerebroventricular streptozotocin injections as a model of Alzheimer’s disease: in search of a relevant mechanism. Mol Neurobiol 53:1741–1752
Grünblatt E, Salkovic-Petrisic M, Osmanovic J, Riederer P, Hoyer S (2007) Brain insulin system dysfunction in streptozotocin intracerebroventricularly treated rats generates hyperphosphorylated tau protein. J Neurochem 101:757–770
Gudkov SV, Shtarkman IN, Smirnova VS, Chernikov AV, Bruskov VI (2006) Guanosine and inosine as natural antioxidants and radioprotectors for mice exposed to lethal doses of γ-radiation. Dokl Biochem Biophys 407:47–50
Gulyaeva NV, Bobkova NV, Kolosova NG et al (2017) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of sporadic Alzheimer's disease: studies on rodent models in vivo. Biochem 82:1088–1102
Gumusyayla S, Vural G, Bektas H et al (2016) A novel oxidative stress marker in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: dynamic thiol-disulphide homeostasis. Acta Neuropsychiatr 28:315–320
Gutierres JM, Carvalho FB, Schetinger MRC, Marisco P, Agostinho P, Rodrigues M, Rubin MA, Schmatz R, da Silva CR, de P Cognato G, Farias JG, Signor C, Morsch VM, Mazzanti CM, Bogo M, Bonan CD, Spanevello R (2014) Anthocyanins restore behavioral and biochemical changes caused by streptozotocin-induced sporadic dementia of Alzheimer’s type. Life Sci 96:7–17
Haskó G, Sitkovsky MV, Szabó C (2004) Immunomodulatory and neuroprotective effects of inosine. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25:152–157
Herman JP, Watson SJ (1987) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates (2nd edn) by George Paxinos and Charles Watson. Trends Neurosci 10:439–439
Hitschke K, Btihler R, Apell G (1994) Stark inactivation of the Na, K-ATPase by radiation-induced free. Evidence for a radical-chain mechanism. FEBS Lett 353:297–300
Huang WC, Lin YS, Wang CY et al (2009) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 negatively regulates anti-inflammatory interleukin-10 for lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS/NO biosynthesis and RANTES production in microglial cells. Immunol 128:275–286
Huang WJ, Zhang X, Chen WW (2016) Role of oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease (review). Biomed Rep 4:519–522
Ibanez V, Pietrini P, Alexander G et al (1998) Regional glucose metabolismo absnormalities are not the result of atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 50:1585–1593
Jeong S (2017) Molecular and cellular basis of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s. Dis Mol Cells 40:613–620
Jin X, Shephered R, Duling B et al (1997) Inosine binds to A3 adenosine receptors and stimulates mast cell degranulation. J Clin Invest 100:2849–2857
Koch M, De Keyser J (2006) Uric acid in multiple sclerosis. Neurol Res 28:316–319
Kuricova M, Ledecky V, Liptak T, Madari A, Grulova I, Slovinska L, Nagyova M, Cizkova D (2014) Oral administration of inosine promotes recovery after experimental spinal cord injury in rat. Neurol Sci 35:1785–1791
Lores Arnaiz GR, Ordieres MG (2014) Brain Na(+), K(+)-ATPase activity in aging and disease. Int J Biomed Sci 10:85–102
Lowry O, Rosebrough N, Farr A (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. Anal Biochem 217:220–230
Mabley JG, Pacher P, Murthy KGK, Williams W, Southan GJ, Salzman AL, Szabo C (2009) The novel inosine analogue INO-2002 exerts an anti-inflammatory effect in a murine model of acute lung injury. Shock 32:258–262
Markowitz CE, Spitsin S, Zimmerman V, Jacobs D, Udupa JK, Hooper DC, Koprowski H (2009) The treatment of multiple sclerosis with inosine. J Altern Complement Med 15:619–625
Martini F, Rosa SG, Klann IP, Fulco BCW, Carvalho FB, Rahmeier FL, Fernandes MC, Nogueira CW (2019) A multifunctional compound ebselen reverses memory impairment, apoptosis and oxidative stress in a mouse model of sporadic Alzheimer's disease. J Psychiatr Res 109:107–117
Mata A, Sepulveda R (2010) Plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPases in the nervous system during development and ageing. World J Biol Chem 26:229–234
Mata A, Berrocal M, Sepulveda M (2011) Impairment of the activity of the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase in Alzheimer's disease. Send to Biochem Soc Trans 39:819–822
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175
Mosconi L (2005) Brain glucose metabolism in the early and specific diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 32:486–510
Muto J, Lee H, Lee H et al (2015) Oral administration of inosine produces antidepressant-like effects in mice. Sci Rep 4:4199
Pacheco SM, Soares MSP, Gutierres JM, Gerzson MFB, Carvalho FB, Azambuja JH, Schetinger MRC, Stefanello FM, Spanevello RM (2018) Anthocyanins as a potential pharmacological agent to manage memory deficit, oxidative stress and alterations in ion pump activity induced by experimental sporadic dementia of Alzheimer’s type. J Nutr Biochem 56:193–204
Rentzos M, Nikolaou C, Anagnostouli M et al (2006) Serum uric acid and multiple sclerosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 108:527–531
Ruhal P, Dhingra D (2018) Inosine improves cognitive function and decreases aging-induced oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in aged female rats. Inflammopharmacol 26:1317–1329
Sonntag KC, Ryu WI, Amirault KM et al (2017) Late-onset Alzheimer’s disease is associated with inherent changes in bioenergetics profiles. Sci Rep 7:1–13
Soreq H, Seidman S (2001) Acetylcholinesterase: new roles for an old actor. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:294–302
Sorial ME, Sayed NSED (2017) Protective effect of valproic acid in streptozotocin-induced sporadic Alzheimer’s disease mouse model: possible involvement of the cholinergic system. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 390:581–593
Squadrito GL, Cueto R, Splenser AE, Valavanidis A, Zhang H, Uppu RM, Pryor WA (2000) Reaction of uric acid with peroxynitrite and implications for the mechanism of neuroprotection by uric acid. Arch Biochem Biophys 376:333–337
Welihinda AA, Kaur M, Greene K, Zhai Y, Amento EP (2016) The adenosine metabolite inosine is a functional agonist of the adenosine A2A receptor with a unique signaling bias. Cell Signal 28:552–560
Yao Z, Zhang Y, Lin L et al (2010) Abnormal cortical networks in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS Comput Biol 18:e1001006
Zaidi A, Michaelis ML (1999) Effects of reactive oxygen species on brain synaptic plasma membrane Ca(2+)-ATPase. Free Radic Biol Med 27:810–821
Zhang LN, Sun YJ, Pan S et al (2013) Na+-K+-ATPase, a potent neuroprotective modulator against Alzheimer disease. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 27:96–103
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS). This study was financed in part by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior-Brasil (CAPES)—Finance code 001. R.M.S. is recipient of CNPq fellowship (309299/2017-9).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teixeira, F.C., Gutierres, J.M., Soares, M.S.P. et al. Inosine protects against impairment of memory induced by experimental model of Alzheimer disease: a nucleoside with multitarget brain actions. Psychopharmacology 237, 811–823 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05419-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05419-5