Abstract
Rationale
Prepulse inhibition (PPI) refers to the reduction of the startle response magnitude when a startling stimulus is closely preceded by a weak stimulus. PPI is commonly used to measure sensorimotor gating. In rats, the PPI reduction induced by the dopamine agonist apomorphine can be reversed by systemic administration of nicotine. A high concentration of nicotinic receptors is found in the lateral habenula (LHb), an epithalamic structure with efferent projections to brain regions involved in the modulation of PPI, which has been shown to regulate the activity of midbrain dopamine neurons.
Objectives
The prospective role of nicotinic receptors in the LHb in the regulation of PPI was assessed in this study, using different pharmacological models of sensorimotor gating deficits.
Methods
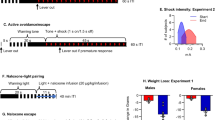
Interactions between systemic amphetamine and haloperidol and intra-LHb infusions of mecamylamine (10 μg/side) or nicotine (30 μg/side) on PPI were analyzed in Experiments 1 and 2. Intra-LHb infusions of different nicotine doses (25, and 50 μg/side) and their interactions with systemic administration of amphetamine or dizocilpine on PPI were examined in Experiments 3 and 4.
Results
Infusions of nicotine into the LHb dose-dependently attenuated amphetamine-induced PPI deficits but had no effect on PPI disruptions caused by dizocilpine. Intra-LHb mecamylamine infusions did not affect PPI nor interact with dopaminergic manipulations.
Conclusions
These results are congruent with previous reports of systemic nicotine effects on PPI, suggesting a role of the LHb in the attenuation of sensorimotor gating deficits caused by the hyperactivity of dopamine systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler LE, Hoffer LJ, Griffith J, Waldo MC, Freedman R (1992) Normalization by nicotine of deficient auditory sensory gating in the relatives of schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 32:607–616
Adler LE, Hoffer LD, Wiser A, Freedman R (1993) Normalization of auditory physiology by cigarette smoking in schizophrenic patients. Am J Psychiatry 150:1856–1861
Bakshi VP, Geyer MA (1998) Multiple limbic regions mediate the disruption of prepulse inhibition produced in rats by the noncompetitive NMDA antagonist dizocilpine. J Neurosci 18:8394–8401
Bell DD, Zucker I (1971) Sex differences in body weight and eating: organization and activation by gonadal hormones in the rat. Physiol Behav 7:27–34
Bubser M, Koch M (1994) Prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response of rats is reduced by 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the medial prefrontal cortex. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 113:487–492
Carlson S, Willott JF (1996) The behavioral salience of tones as indicated by prepulse inhibition of the startle response: relationship to hearing loss and central neural plasticity in C57BL/6J mice. Hear Res 99:168–175
Christoph GR, Leonzio RJ, Wilcox KS (1986) Stimulation of the lateral habenula inhibits dopamine-containing neurons in the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area of the rat. J Neurosci 6:613–619
Craft RM, Millholland RB (1998) Sex differences in cocaine- and nicotine-induced antinociception in the rat. Brain Res 809:137–140
Curzon P, Kim DJB, Decker MW (1994) Effect of nicotine, lobeline, and mecamylamine on sensory gating in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 49:877–882
Decker MW, Majchrzak MJ (1992) Effects of systemic and intracerebroventricular administration of mecamylamine, a nicotinic cholinergic antagonist, on spatial memory in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 107:530–534
Decker MW, Curzon P, Brioni JD (1995) Influence of separate and combined septal and amygdala lesions on memory, acoustic startle, anxiety, and locomotor activity in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 64:156–168
Fendt M (1999) Enhancement of prepulse inhibition after blockade of GABA activity within the superior colliculus. Brain Res 833:81–85
Heldt SA, Ressler KJ (2006) Lesions of the habenula produce stress- and dopamine-dependent alterations in prepulse inhibition and locomotion. Brain Res 1073–4:229–239
Hikosaka O, Sesack SR, Lecourtier L, Shepard PD (2008) Habenula: crossroad between the basal ganglia and the limbic system. J Neurosci 28:11825–11829
Japha K, Koch M (1999) Picrotoxin in the medial prefrontal cortex impairs sensorimotor gating in rats: reversal by haloperidol. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 144:347–354
Jaskiw GE, Weinberger DR (1987) The prefrontal cortex-accumbens circuit: who’s in charge? Behav Brain Sci 10:217–218
Jaskiw GE, Weinberger DR, Crawley JN (1991) Microinjection of apomorphine into the prefrontal cortex of the rat reduces dopamine metabolite concentrations in microdialysate from the caudate nucleus. Biol Psychiatry 29:703–706
Jones CK, Shannon HE (2000) Muscarinic cholinergic modulation of prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294:1017–1023
Keith VA, Mansbach RS, Geyer MA (1991) Failure of haloperidol to block the effects of phencyclidine and dizocilpine on prepulse inhibition of startle. Biol Psychiatry 30:557–566
Koch M (1998) Sensorimotor gating changes across the estrous cycle in female rats. Physiol Behav 64:625–628
Koch M (1999) The neurobiology of startle. Prog Neurobiol 59:107–128
Kodsi MH, Swerdlow NR (1997) Regulation of prepulse inhibition by ventral pallidal projections. Brain Res Bull 43:219–228
Kretschmer BD, Koch M (1998) The ventral pallidum mediates disruption of prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response induced by dopamine agonists, but not by NMDA antagonists. Brain Res 798:204–210
Kusljic S, Copolov DL, van den Buuse M (2003) Differential role of serotonergic projections arising from the dorsal and median raphe nuclei in locomotor hyperactivity and prepulse inhibition. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:2138–2147
Kutlu MG, Burke D, Slade S, Hall BJ, Rose JE, Levin ED (2013) Role of insular cortex D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in nicotine self-administration in rats. Behav Brain Res 256:273–278
Larrauri JA, Levin ED (2012a) The α2-adrenergic antagonist idazoxan counteracts prepulse inhibition deficits caused by amphetamine or dizocilpine in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 219:99–108
Larrauri JA, Levin ED (2012b) Differential effects of the antidepressant mirtazapine on amphetamine- and dizocilpine-induced PPI deficits. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 102:82–87
Lingenhöhl K, Friauf E (1994) Giant neurons in the rat reticular formation: a sensorimotor interface in the elementary acoustic startle circuit? J Neurosci 14:1176–1194
Louilot A, Le Moal M, Simon H (1989) Opposite influences of dopaminergic pathways to the prefrontal cortex or the septum on the dopaminergic transmission in the nucleus accumbens. An in vivo voltammetric study. Neuroscience 29:45–56
Lowry CA, Hale MW, Evans AK, Heerkens J, Staub DR, Gasser PJ, Shekhar A (2008) Serotonergic systems, anxiety, and affective disorder: focus on the dorsomedial part of the dorsal raphe nucleus. Ann NY Acad Sci 1148:86–94
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA (1989) Effects of phencyclidine and phencyclidine biologs on sensorimotor gating in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 2:299–308
Matsumoto M, Hikosaka O (2007) Lateral habenula as a source of negative reward signals in dopamine neurons. Nature 447:1111–1115
Rainbow TC, Schwartz RD, Parsons B, Kellar KJ (1984) Quantitative autoradiography of nicotinic [3H]acetylcholine binding sites in rat brain. Neurosci Lett 50:193–196
Sanders D, Simkiss D, Braddy D, Baccus S, Morton T, Cannady R, Weaver N, Rose JE, Levin ED (2010) Nicotinic receptors in the habenula: importance for memory. Neuroscience 166:386–390
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1967) Statistical methods. Ames, Iowa
Suemaru K, Yasuda K, Umeda K, Araki H, Choshi T, Hibino S, Gomita Y (2004) Nicotine blocks apomorphine-induced disruption of prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle in rats: possible involvement of central nicotinic α7 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 142:843–850
Swanson LW (1982) The projections of the ventral tegmental area and adjacent regions: a combined fluorescent retrograde tracer and immunofluorescence study in the rat. Brain Res Bull 9:321–353
Swerdlow N, Braff D, Masten V, Geyer M (1990a) Schizophrenic-like sensorimotor gating abnormalities in rats following dopamine infusion into the nucleus accumbens. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 101:414–420
Swerdlow NR, Mansbach RS, Geyer MA, Pulvirenti L, Koob GF, Braff DL (1990b) Amphetamine disruption of prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle is reversed by depletion of mesolimbic dopamine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 100:413–416
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990c) GABAergic projection from nucleus accumbens to ventral pallidum mediates dopamine-induced sensorimotor gating deficits of acoustic startle in rats. Brain Res 532:146–150
Swerdlow NR, Caine SB, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1992) The neural substrates of sensorimotor gating of the startle reflex: a review of recent findings and their implications. J Psychopharmacol 6:176–190
Swerdlow NR, Auerbach P, Monroe SM, Hartston H, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1993) Men are more inhibited than women by weak prepulses. Biol Psychiatry 34:253–260
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Geyer MA (2000) Animal models of deficient sensorimotor gating: what we know, what we think we know, and what we hope to know soon. Behav Pharmacol 11:185–204
Toth E, Vizi ES, Lajtha A (1993) Effect of nicotine on levels of extracellular amino acids in regions of the rat brain in vivo. Neuropharmacology 32:827–832
Yoshioka M, Matsumoto M, Togashi H, Saito H (1996) Effect of conditioned fear stress on dopamine release in the rat prefrontal cortex. Neurosci Lett 209:201–203
Zhang J, Engel JA, Hjorth S, Svensson L (1995) Changes in the acoustic startle response and prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle in rats after local injection of pertussis toxin into the ventral tegmental area. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 119:71–78
Acknowledgments
This research was sponsored by the Wallace Research Foundation. Supported by NIDA P50 grant DA027840.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larrauri, J.A., Burke, D.A., Hall, B.J. et al. Role of nicotinic receptors in the lateral habenula in the attenuation of amphetamine-induced prepulse inhibition deficits of the acoustic startle response in rats. Psychopharmacology 232, 3009–3017 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-3940-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-3940-z