Abstract
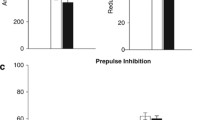
Prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustic startle response (ASR) is impaired by dopamine (DA) overactivity in the nucleus accumbens and anteromedial striatum. Since there is evidence that DA in the medial prefrontal cortex exerts an inhibitory control on striatal DA systems, it was investigated whether depletion of prefrontal DA reduces PPI. Rats were tested for PPI both before and after injections (2 × 1 µl per side) of vehicle, a low (3.0 µg/µl) or a high (6.0 µg/µl) dose of 6-hydroxydopamine hydrobromide (6-OHDA) into the prefrontal cortex. Only the high dose of 6-OHDA, leading to an 87% depletion of prefrontal DA, impaired PPI. The ability of an acoustic prepulse (75 dB, 10 kHz) to reduce the response to a startle pulse (100 dB noise burst) was maintained in sham lesioned rats, but was significantly disturbed in rats lesioned with the high dose of 6-OHDA. The 6-OHDA treatment did not affect the ASR amplitude in the absence of a prepulse. The reduction of PPI in lesioned rats correlated with the extent of DA depletion. These results suggest that the DA innervation of the prefrontal cortex is involved in the modulation of the ASR and they provide further evidence for opposite actions of prefrontal and subcortical DA systems in the control of behaviour. The present findings are discussed with regard to the potential role of prefrontal DA in schizophrenia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bean AJ, Roth RH (1991) Effects of haloperidol administration on in vivo extracellular dopamine in striatum and prefrontal cortex after partial dopamine lesions. Brain Res 549:155–158
Beckstead RM (1979) An autoradiographic examination of corticocortical and subcortical projections of the mediodorsal-projection (prefrontal) cortex in the rat. J Comp Neurol 184:43–62
Berger B, Thierry AM, Tassin JP, Moyne MA (1976) Dopaminergic innervation of the rat prefrontal cortex: a fluorescence histochemical study. Brain Res 106:133–145
Björklund A, Lindvall O (1984) Dopamine-containing systems in the CNS. In: Björklund A, Hökfelt T (eds) Handbook of chemical neuroanatomy, vol 2. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 55–122
Braff DL, Stone C, Callaway E, Geyer MA, Glick ID, Bali L (1978) Prestimulus effects on human startle reflex in normals and schizophrenics. Psychophysiology 15:339–343
Breese GR, Traylor TD (1971) Depletion of brain noradrenaline and dopamine by 6-hydroxydopamine. Br J Pharmacol 42:88–99
Bubser M (1992) Verhaltenspharmakologische und neurochemische Charakterisierung der Funktion von Dopamin im medialen präfrontalen Cortex der Ratte. PhD-thesis, Universität Stuttgart
Bubser M, Keseberg U, Notz PK, Schmidt WJ (1992) Differential behavioural and neurochemical effects of competitive and non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonists in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 229:75–82
Caine SB, Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR (1992) Hippocampal modulation of acoustic startle and prepulse inhibition in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:1201–1208
Carter CJ, Pycock CJ (1980) Behavioural and biochemical effects of dopamine and noradrenaline depletion within the medial prefrontal cortex of the rat. Brain Res 192:163–176
Clarke PBS, Jakubovic A, Fibiger HC (1988) Anatomical analysis of the involvement of mesolimbocortical dopamine in the locomotor stimulant actions ofd-amphetamine and apomorphine. Psychopharmacology 96:511–520
Davis M (1988) Apomorphine,d-amphetamine, strychnine and yohimbine do not alter prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex. Psychopharmacology 95:151–156
Deutch AY, Clark WA, Roth RH (1990) Prefrontal cortical dopamine depletion enhances the responsiveness of mesolimbic dopamine neurons to stress. Brain Res 521:311–315
Ferron A, Thierry AM, LeDouarin C, Glowinski J (1984) Inhibitory influence of the mesocortical dopaminergic system on spontaneous activity or excitatory response induced from the thalamic mediodorsal nucleus in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Brain Res 302:257–265
Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR, Mansbach RS, Braff DL (1990) Startle response models of sensorimotor gating and habituation deficits in schizophrenia. Brain Res Bull 25:485–498
Glowinski J, Tassin JP, Thierry AM (1984) The mesocortico-prefrontal dopaminergic neurons. TINS 7:415–418
Grace AA (1991) Phasic versus tonic dopamine release and the modulation of dopamine system responsivity: a hypothesis for the etiology of schizophrenia. Neuroscience 41:1–24
Hammond GR (1974) Frontal cortical lesions and prestimulus inhibition of the rat's acoustic startle reaction. Physiol Psychol 2:151–156
Heffner TG, Hartman JA, Seiden LS (1980) A rapid method for the regional dissection of the rat brain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 13:453–456
Hoffman HS, Ison JR (1980) Reflex modification in the domain of startle: I. some empirical findings and their implications for how the nervous system processes sensory input. Psychol Rev 2:175–189
Jaskiw GE, Weinberger DR (1987) The prefrontal cortex-accumbens circuit: who's in charge? Behav Brain Sci 10:217–218
Jaskiw GE, Weinberger DR, Crawley JN (1991) Microinjection of apomorphine into the prefrontal cortex of the rat reduces dopamine metabolite concentrations in microdialysate from the caudate nucleus. Biol Psychiatry 29:703–706
Jones GH, Robbins TW (1992) Differential effects of mesocortical, mesolimbic, and mesostriatal dopamine depletion on spontaneous, conditioned, and drug-induced locomotor activity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:887–895
Joyce EM, Stinus L, Iversen SD (1983) Effect of injection of 6-OHDA into either nucleus accumbens septi of frontal cortex on spontaneous and drug-induced activity. Neuropharmacology 22:1141–1145
Kerwin R (1992) A history of frontal and temporal lobe aspects of the neuropharmacology of schizophrenia. J Psychopharmacol 6:230–240
Koob GF, Simon H, Herman JP, Le Moal M (1984) Neuroleptic-like disruption of the conditioned avoidence response requires destruction of both the mesolimbic and nigrostriatal dopamine systems. Brain Res 303:319–329
Le Moal M, Simon H (1991) Mesocorticolimbic dopaminergic network: functional and regulatory roles. Physiol Rev 71:155–234
Leonard CM (1969) The prefrontal cortex of the rat. I. Cortical projection of the mediodorsal nucleus. II. Efferent connections. Brain Res 12:321–343
Louilot A, Le Moal M, Simon H (1989) Opposite influences of dopaminergic pathways to the prefrontal cortex or the septum on the dopaminergic transmission in the nucleus accumbens. An in vivo voltammetric study. Neuroscience 29:45–56
Oades RD, Taghzouti K, Rivet JM, Simon H, Le Moal M (1986) Locomotor activity in relation to dopamine and noradrenaline in the nucleus accumbens, septal and frontal areas: a 6-hydroxydopamine study. Neuropsychobiology 16:37–42
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Peterson SL, St Mary JS, Harding NR (1987) Cis-flupentixol antagonism of the rat prefrontal cortex neuronal response to apomorphine and ventral tegmental area input. Brain Res Bull 18:723–729
Pilz PKD, Schnitzler HU, Menne D (1987) Acoustic startle threshold of the albino rat (Rattus norvegicus). J Comp Psychol 101:67–72
Pycock CJ, Kerwin RW, Carter CJ (1980) Effect of lesion of cortical dopamine terminals on subcortical dopamine receptors in rats. Nature 286:74–77
Robbins TW (1990) The case for frontostriatal dysfunction in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 16:391–402
Romo R, Chéramy A, Godeheu G, Glowinski J (1986) In vivo presynaptic control of dopamine release in the cat caudate nucleus — III further evidence for the implication of corticostriatal glutamatergic neurons. Neuroscience 19:1091–1099
Sesack SR, Bunney BS (1989) Pharmacological characterization of the receptors mediating electrophysiological responses to dopamine in the rat medial prefrontal cortex: a microiontophoretic study. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 248:1323–1333
Sesack SR, Pickel VM (1992) Prefrontal cortical efferents in the rat synapse on unlabeled neuronal targets of catecholamine terminals in the nucleus accumbens septi and on dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area. J Comp Neurol 320:145–160
Sesack SR, Deutch AY, Roth RH, Bunney BS (1989) Topographical organization of the efferent projections of the medial prefrontal cortex in the rat: an anterograde tract-tracing study with Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin. J Comp Neurol 290:213–242
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Geyer MA, Koob GF (1986) Central dopamine hyperactivity in rats mimics abnormal acoustic startle response in schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 21:23–33
Swerdlow NJ, Braff DL, Masten VL, Geyer MA (1990) Schizophrenic-like sensorimotor gating abnormalities in rats following dopamine infusion into the nucleus accumbens. Psychopharmacology 101:414–420
Swerdlow NR, Caine SB, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1992a) The neural substrates of sensorimotor rating of the startle reflex: a review of recent findings and their implications. J Psychopharmacol 6:176–190
Swerdlow NR, Caine SB, Geyer MA (1992b) Regionally selective effects of intracerebral dopamine infusion on sensorimotor gating of the startle reflex in rats. Psychopharmacology 108:189–195
Taghzouti K, Simon H, Hervé D, Blanc G, Studler JM, Glowinski J, LeMoal M, Tassin JP (1988) Behavioural deficits induced by the electrolytic lesion of the rat ventral mesencephalic tegmentum are corrected by a superimposed lesion of the dorsal nordrenergic system. Brain Res 440:172–176
Tassin JP (1987) Dopamine and mental illness: and what about the mesocortical dopamine systems? Behav Brain Sci 10:224–225
Vezina P, Blanc G, Glowinski J, Tassin JP (1991) Opposed behavioural outputs of increased dopamine transmission in prefrontocortical and subcortical areas: a role for the cortical D-1 dopamine receptor. Eur J Neurosci 3:1001–1007
Youngren KD, Daly DA, Moghaddam B (1993) Distinct actions of endogenous excitatory amino acids on the outflow of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:289–293
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bubser, M., Koch, M. Prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response of rats is reduced by 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the medial prefrontal cortex. Psychopharmacology 113, 487–492 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245228
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245228