Abstract
Rationale
Recreational use of ecstasy (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine [MDMA]) has been associated with memory impairments. Functional neuroimaging studies with cross-sectional designs reported altered memory-related hippocampal functioning in ecstasy-polydrug users. However, differences might be pre-existing or related to the concomitant use of amphetamine.
Objective
To prospectively investigate the specific effects of ecstasy on memory-related hippocampal functioning.
Methods
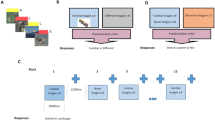
We used an associative memory task and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in 40 ecstasy and/or amphetamine users at baseline (t1) and after 12 months (t2). At t1, all subjects had very limited amphetamine and/or ecstasy experience (less than 5 units lifetime dose). Based on the reported drug use at t2, subjects with continued ecstasy and/or amphetamine use (n = 17) were compared to subjects who stopped use after t1 (n = 12).
Results
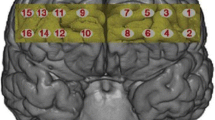
Analysis of repeated measures revealed that encoding-related activity in the left parahippocampal gyrus changed differentially between the groups. Activity in this region increased in abstinent subjects from t1 to t2, however, decreased in subjects with continued use. Decreases within the left parahippocampal gyrus were associated with the use of ecstasy, but not amphetamine, during the follow-up period. However, there were no significant differences in memory performance.
Conclusions
The current findings suggest specific effects of ecstasy use on memory-related hippocampal functioning. However, alternative explanations such as (sub-)acute cannabis effects are conceivable.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker B, Wagner D, Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E, Spuentrup E, Daumann J (2010) Altered parahippocampal functioning in cannabis users is related to the frequency of use. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 209:361–74
Bedi G, Redman J (2008) Ecstasy use and higher-level cognitive functions: weak effects of ecstasy after control for potential confounds. Psychol Med 38:1319–30
Brown J, McKone E, Ward J (2010) Deficits of long-term memory in ecstasy users are related to cognitive complexity of the task. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 209:51–67
Buchert R, Thomasius R, Wilke F, Petersen K, Nebeling B, Obrocki J, Schulze O, Schmidt U, Clausen M (2004) A voxel-based PET investigation of the long-term effects of "Ecstasy" consumption on brain serotonin transporters. Am J Psychiatry 161:1181–9
Carusone LM, Srinivasan J, Gitelman DR, Mesulam MM, Parrish TB (2002) Hemodynamic response changes in cerebrovascular disease: implications for functional MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1222–8
Colado MI, Granados R, O'Shea E, Esteban B, Green AR (1998) Role of hyperthermia in the protective action of clomethiazole against MDMA ('ecstasy')-induced neurodegeneration, comparison with the novel NMDA channel blocker AR-R15896AR. Br J Pharmacol 124:479–84
Daumann J, Fimm B, Willmes K, Thron A, Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E (2003) Cerebral activation in abstinent ecstasy (MDMA) users during a working memory task: a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 16:479–87
Daumann J Jr, Fischermann T, Heekeren K, Thron A, Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E (2004) Neural mechanisms of working memory in ecstasy (MDMA) users who continue or discontinue ecstasy and amphetamine use: evidence from an 18-month longitudinal functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Biol Psychiatry 56:349–55
Daumann J, Fischermann T, Heekeren K, Henke K, Thron A, Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E (2005) Memory-related hippocampal dysfunction in poly-drug ecstasy (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine) users. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 180:607–11
de Win MM, Reneman L, Jager G, Vlieger EJ, Olabarriaga SD, Lavini C, Bisschops I, Majoie CB, Booij J, den Heeten GJ, van den Brink W (2007) A prospective cohort study on sustained effects of low-dose ecstasy use on the brain in new ecstasy users. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:458–70
de Win MM, Jager G, Booij J, Reneman L, Schilt T, Lavini C, Olabarriaga SD, den Heeten GJ, van den Brink W (2008) Sustained effects of ecstasy on the human brain: a prospective neuroimaging study in novel users. Brain 131:2936–45
Eldreth DA, Matochik JA, Cadet JL, Bolla KI (2004) Abnormal brain activity in prefrontal brain regions in abstinent marijuana users. NeuroImage 23:914–20
EMCDDA Annual report: the state of the drugs problem in Europe (2007): European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction [online] http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/html.cfm/index44682EN.html.
Ferrington L, Kirilly E, McBean DE, Olverman HJ, Bagdy G, Kelly PA (2006) Persistent cerebrovascular effects of MDMA and acute responses to the drug. Eur J Neurosci 24:509–19
Fischer C, Hatzidimitriou G, Wlos J, Katz J, Ricaurte G (1995) Reorganization of ascending 5-HT axon projections in animals previously exposed to the recreational drug (+/−)3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, "ecstasy"). J Neurosci 15:5476–85
Fox HC, McLean A, Turner JJ, Parrott AC, Rogers R, Sahakian BJ (2002) Neuropsychological evidence of a relatively selective profile of temporal dysfunction in drug-free MDMA ("ecstasy") polydrug users. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 162:203–14
Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E, Daumann J (2006a) Neurotoxicity of methylenedioxyamphetamines (MDMA; ecstasy) in humans: how strong is the evidence for persistent brain damage? Addiction 101:348–61
Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E, Daumann J (2006b) The confounding problem of polydrug use in recreational ecstasy/MDMA users: a brief overview. J Psychopharmacol 20:188–93
Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E, Daumann J (2009) Neurotoxicity of drugs of abuse—the case of methylenedioxyamphetamines (MDMA, ecstasy), and amphetamines. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 11:305–17
Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E, Thimm B, Rezk M, Hensen G, Daumann J (2003) Memory impairment suggests hippocampal dysfunction in abstinent ecstasy users. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27:819–27
Green AR, Mechan AO, Elliott JM, O'Shea E, Colado MI (2003) The pharmacology and clinical pharmacology of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, "ecstasy"). Pharmacol Rev 55:463–508
Halpern JH, Pope HG Jr, Sherwood AR, Barry S, Hudson JI, Yurgelun-Todd D (2004) Residual neuropsychological effects of illicit 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) in individuals with minimal exposure to other drugs. Drug Alcohol Depend 75:135–47
Halpern JH, Sherwood AR, Hudson JI, Gruber S, Kozin D, Pope HG Jr (2011) Residual neurocognitive features of long-term ecstasy users with minimal exposure to other drugs. Addiction 106:777–86
Hatzidimitriou G, McCann UD, Ricaurte GA (1999) Altered serotonin innervation patterns in the forebrain of monkeys treated with (+/−)3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine seven years previously: factors influencing abnormal recovery. J Neurosci 19:5096–107
Henson RNA, Penny WD (2003) ANOVAs and SPM. Technical report, Wellcome Department of Imaging Neuroscience. [online] http://www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/~wpenny/biblio/Year/2003.complete.html
Jacobsen LK, Mencl WE, Pugh KR, Skudlarski P, Krystal JH (2004) Preliminary evidence of hippocampal dysfunction in adolescent MDMA ("ecstasy") users: possible relationship to neurotoxic effects. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 173:383–90
Jager G, van Hell MM, Kahn RS, van den Brink W, van Ree JM, Ramsey NF (2007) Effects of frequent cannabi suse on hippocampal activity during an associative memory task. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 17:289–97
Jager G, de Win MM, van der Tweel I, Schilt T, Kahn RS, van den Brink W, van Ree JM, Ramsey NF (2008) Assessment of cognitive brain function in ecstasy users and contributions of other drugs of abuse: results from an FMRI study. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:247–58
Kalechstein AD, De La Garza R 2nd, Mahoney JJ 3rd, Fantegrossi WE, Newton TF (2007) MDMA use and neurocognition: a meta-analytic review. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 189:531–7
Kish SJ, Fitzmaurice PS, Chang LJ, Furukawa Y, Tong J (2010) Low striatal serotonin transporter protein in a human polydrug MDMA (ecstasy) user: a case study. J Psychopharmacol 24:281–4
Lyvers M (2006) Recreational ecstasy use and the neurotoxic potential of MDMA: current status of the controversy and methodological issues. Drug Alcohol Rev 25:269–76
Maldjian JA, Laurienti PJ, Kraft RA, Burdette JH (2003) An automated method for neuroanatomic and cytoarchitectonic atlas-based interrogation of fMRI data sets. NeuroImage 19:1233–9
Maldjian JA, Laurienti PJ, Burdette JH (2004) Precentral gyrus discrepancy in electronic versions of the Talairach atlas. NeuroImage 21:450–5
Martin GW, Wilkinson DA, Kapur BM (1988) Validation of self-reported cannabis use by urine analysis. Addict Behav 13:147–50
McCann UD, Szabo Z, Vranesic M, Palermo M, Mathews WB, Ravert HT, Dannals RF, Ricaurte GA (2008) Positron emission tomographic studies of brain dopamine and serotonin transporters in abstinent (+/−)3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine ("ecstasy") users: relationship to cognitive performance. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 200:439–50
Moeller FG, Steinberg JL, Dougherty DM, Narayana PA, Kramer LA, Renshaw PF (2004) Functional MRI study of working memory in MDMA users. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 177:185–94
Nestor L, Roberts G, Garavan H, Hester R (2008) Deficits in learning and memory: parahippocampal hyperactivity and frontocortical hypoactivity in cannabis users. NeuroImage 40:1328–39
Parrott AC (2000) Human research on MDMA (3,4-methylene- dioxymethamphetamine) neurotoxicity: cognitive and behavioural indices of change. Neuropsychobiology 42:17–24
Parrott AC (2004) MDMA (3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine) or ecstasy: the neuropsychobiological implications of taking it at dances and raves. Neuropsychobiology 50:329–35
Parrott AC, Lees A, Garnham NJ, Jones M, Wesnes K (1998) Cognitive performance in recreational users of MDMA of 'ecstasy': evidence for memory deficits. J Psychopharmacol 12:79–83
Pedersen W, Skrondal A (1999) Ecstasy and new patterns of drug use: a normal population study. Addiction 94:1695–706
Quednow BB, Jessen F, Kuhn KU, Maier W, Daum I, Wagner M (2006) Memory deficits in abstinent MDMA (ecstasy) users: neuropsychological evidence of frontal dysfunction. J Psychopharmacol 20:373–84
Raven J (2000) The Raven's progressive matrices: change and stability over culture and time. Cogn Psychol 41:1–48
Reneman L, Lavalaye J, Schmand B, de Wolff FA, van den Brink W, den Heeten GJ, Booij J (2001) Cortical serotonin transporter density and verbal memory in individuals who stopped using 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA or "ecstasy"): preliminary findings. Arch Gen Psychiatry 58:901–6
Reneman L, Schilt T, de Win MM, Booij J, Schmand B, van den Brink W, Bakker O (2006) Memory function and serotonin transporter promoter gene polymorphism in ecstasy (MDMA) users. J Psychopharmacol 20:389–399
Ricaurte GA, Finnegan KT, Irwin I, Langston JW (1990) Aminergic metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid of humans previously exposed to MDMA: preliminary observations. Ann N Y Acad Sci 600:699–708, discussion 708–10
Roberts GM, Nestor L, Garavan H (2009) Learning and memory deficits in ecstasy users and their neural correlates during a face-learning task. Brain Res 1292:71–81
Rosa-Neto P, Olsen AK, Gjedde A, Watanabe H, Cumming P (2004) MDMA-evoked changes in cerebral blood flow in living porcine brain: correlation with hyperthermia. Synapse 53:214–21
Rothe M, Pragst F, Spiegel K, Harrach T, Fischer K, Kunkel J (1997) Hair concentrations and self-reported abuse history of 20 amphetamine and ecstasy users. Forensic Sci Int 89:111–28
Schilt T, de Win MM, Koeter M, Jager G, Korf DJ, van den Brink W, Schmand B (2007) Cognition in novice ecstasy users with minimal exposure to other drugs: a prospective cohort study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64:728–36
Schilt T, de Win MM, Jager G, Koeter MW, Ramsey NF, Schmand B, van den Brink W (2008) Specific effects of ecstasy and other illicit drugs on cognition in poly-substance users. Psychol Med 38:1309–17
Smart RG, Ogborne AC (2000) Drug use and drinking among students in 36 countries. Addict Behav 25:455–60
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, Mazoyer B, Joliot M (2002) Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage 15:273–89
Ward MF, Wender PH, Reimherr FW (1993) The Wender Utah Rating Scale: an aid in the retrospective diagnosis of childhood attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Psychiatry 150:885–90
Zakzanis KK, Campbell Z, Jovanovski D (2007) The neuropsychology of ecstasy (MDMA) use: a quantitative review. Hum Psychopharmacol 22:427–35
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant to E. Gouzoulis-Mayfrank and J. Daumann from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG GO 717/6-1/2).
Conflicts of interest
None of the authors has declared any conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 41 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becker, B., Wagner, D., Koester, P. et al. Memory-related hippocampal functioning in ecstasy and amphetamine users. Psychopharmacology 225, 923–934 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2873-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2873-z