Abstract
Rationale
Cocaine addiction is associated with high rates of relapse, and stress has been identified as a major risk factor. We have previously demonstrated that acupuncture reduces drug self-administration and dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens (NAc), a brain structure implicated in stress-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior.
Objective
This study was conducted to investigate the effects of acupuncture on footshock-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking and the expression of c-Fos and the transcription factor cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) in the NAc, used as markers of neuronal activation in conditions of stress-induced reinstatement to cocaine.
Methods
Male Sprague–Dawley rats were trained to self-administer cocaine (1.0 mg/kg) for 14 days, followed by extinction and then footshock stress. Acupuncture was applied at bilateral Shenmen (HT7) points for 1 min after footshock stress.
Results and conclusions
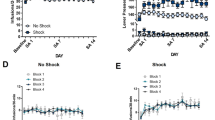
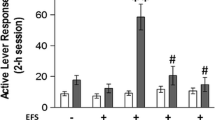
Acute footshock stress reinstated cocaine-seeking behavior and enhanced c-Fos expression and phosphorylated CREB (pCREB) activation in the NAc shell in cocaine pre-exposed rats. On the other hand, acupuncture at HT7, but not at control point (LI5), markedly reduced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking (86.5 % inhibition vs. control value), c-Fos expression (81.7% inhibition), and pCREB activation (79.3% inhibition) in the NAc shell. These results suggest that acupuncture attenuates stress-induced relapse by regulating neuronal activation in the NAc shell.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson SM, Bari AA, Pierce RC (2003) Administration of the D1-like dopamine receptor antagonist SCH-23390 into the medial nucleus accumbens shell attenuates cocaine priming-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 168:132–8
Ashby CR Jr, Rohatgi R, Ngosuwan J, Borda T, Gerasimov MR, Morgan AE, Kushner S, Brodie JD, Dewey SL (1999) Implication of the GABA(B) receptor in gamma vinyl-GABA’s inhibition of cocaine-induced increases in nucleus accumbens dopamine. Synapse 31:151–3
Bachtell RK, Whisler K, Karanian D, Self DW (2005) Effects of intra-nucleus accumbens shell administration of dopamine agonists and antagonists on cocaine-taking and cocaine-seeking behaviors in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 183:41–53
Backstrom P, Bachteler D, Koch S, Hyytia P, Spanagel R (2004) mGluR5 antagonist MPEP reduces ethanol-seeking and relapse behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:921–8
Boutrel B, Kenny PJ, Specio SE, Martin-Fardon R, Markou A, Koob GF, de Lecea L (2005) Role for hypocretin in mediating stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:19168–73
Brebner K, Phelan R, Roberts DC (2000) Intra-VTA baclofen attenuates cocaine self-administration on a progressive ratio schedule of reinforcement. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66:857–62
Brog JS, Salyapongse A, Deutch AY, Zahm DS (1993) The patterns of afferent innervation of the core and shell in the “accumbens” part of the rat ventral striatum: immunohistochemical detection of retrogradely transported fluoro-gold. J Comp Neurol 338:255–78
Brown RM, Short JL, Lawrence AJ (2010) Identification of brain nuclei implicated in cocaine-primed reinstatement of conditioned place preference: a behaviour dissociable from sensitization. PLoS One 5:e15889
Campbell UC, Lac ST, Carroll ME (1999) Effects of baclofen on maintenance and reinstatement of intravenous cocaine self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 143:209–14
Chan J, Briscomb D, Waterhouse E, Cannaby AM (2002) An uncontrolled pilot study of HT7 for ‘stress’. Acupunct Med 20:74–7
Chen Y, Fenoglio KA, Dube CM, Grigoriadis DE, Baram TZ (2006) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of hippocampal activation by acute stress are age-dependent. Mol Psychiatry 11:992–1002
Cippitelli A, Damadzic R, Hansson AC, Singley E, Sommer WH, Eskay R, Thorsell A, Heilig M (2010) Neuropeptide Y (NPY) suppresses yohimbine-induced reinstatement of alcohol seeking. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 208:417–26
Cousins MS, Roberts DC, de Wit H (2002) GABA(B) receptor agonists for the treatment of drug addiction: a review of recent findings. Drug Alcohol Depend 65:209–20
Cui CL, Wu LZ, Luo F (2008) Acupuncture for the treatment of drug addiction. Neurochem Res 33:2013–22
Cullinan WE, Ziegler DR, Herman JP (2008) Functional role of local GABAergic influences on the HPA axis. Brain Struct Funct 213:63–72
Di Ciano P, Everitt BJ (2004) Contribution of the ventral tegmental area to cocaine-seeking maintained by a drug-paired conditioned stimulus in rats. Eur J Neurosci 19:1661–7
Doherty M, Gratton A (2007) Differential involvement of ventral tegmental GABA(A) and GABA(B) receptors in the regulation of the nucleus accumbens dopamine response to stress. Brain Res 1150:62–8
Erb S, Salmaso N, Rodaros D, Stewart J (2001) A role for the CRF-containing pathway from central nucleus of the amygdala to bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 158:360–5
Erb S, Lopak V, Smith C (2004) Cocaine pre-exposure produces a sensitized and context-specific c-fos mRNA response to footshock stress in the central nucleus of the AMYGDALA. Neuroscience 129:719–25
Finlay JM, Zigmond MJ, Abercrombie ED (1995) Increased dopamine and norepinephrine release in medial prefrontal cortex induced by acute and chronic stress: effects of diazepam. Neuroscience 64:619–28
Funk D, Li Z, Le AD (2006) Effects of environmental and pharmacological stressors on c-fos and corticotropin-releasing factor mRNA in rat brain: relationship to the reinstatement of alcohol seeking. Neuroscience 138:235–43
Giardino L, Zanni M, Pozza M, Bettelli C, Covelli V (1998) Dopamine receptors in the striatum of rats exposed to repeated restraint stress and alprazolam treatment. Eur J Pharmacol 344:143–7
Goeders NE (2003) The impact of stress on addiction. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 13:435–41
Guimaraes CM, Pinge MC, Yamamura Y, Mello LE (1997) Effects of acupuncture on behavioral, cardiovascular and hormonal responses in restraint-stressed Wistar rats. Braz J Med Biol Res 30:1445–50
Herman JP, Mueller NK, Figueiredo H (2004) Role of GABA and glutamate circuitry in hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical stress integration. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1018:35–45
Iwa M, Nakade Y, Pappas TN, Takahashi T (2006) Electroacupuncture elicits dual effects: stimulation of delayed gastric emptying and inhibition of accelerated colonic transit induced by restraint stress in rats. Dig Dis Sci 51:1493–500
Jindal V, Ge A, Mansky PJ (2008) Safety and efficacy of acupuncture in children: a review of the evidence. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 30:431–42
Kalivas PW, Duffy P (1995) Selective activation of dopamine transmission in the shell of the nucleus accumbens by stress. Brain Res 675:325–8
Kim MR, Kim SJ, Lyu YS, Kim SH, Lee Y, Kim TH, Shim I, Zhao R, Golden GT, Yang CH (2005) Effect of acupuncture on behavioral hyperactivity and dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens in rats sensitized to morphine. Neurosci Lett 387:17–21
Kim H, Park HJ, Han SM, Hahm DH, Lee HJ, Kim KS, Shim I (2009) The effects of acupuncture stimulation at PC6 (Neiguan) on chronic mild stress-induced biochemical and behavioral responses. Neurosci Lett 460:56–60
Kotlinska JH, Gibula-Bruzda E, Pachuta A, Kunce D, Witkowska E, Chung NN, Schiller PW, Izdebski J (2010) Influence of new deltorphin analogues on reinstatement of cocaine-induced conditioned place preference in rats. Behav Pharmacol 21:638–48
Kreibich AS, Blendy JA (2004) cAMP response element-binding protein is required for stress but not cocaine-induced reinstatement. J Neurosci 24:6686–92
Le AD, Poulos CX, Harding S, Watchus J, Juzytsch W, Shaham Y (1999) Effects of naltrexone and fluoxetine on alcohol self-administration and reinstatement of alcohol seeking induced by priming injections of alcohol and exposure to stress. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:435–44
Lee HJ, Lee B, Choi SH, Hahm DH, Kim MR, Roh PU, Pyun KH, Golden G, Yang CH, Shim I (2004) Electroacupuncture reduces stress-induced expression of c-fos in the brain of the rat. Am J Chin Med 32:795–806
Lee B, Han SM, Shim I (2009) Acupuncture attenuates cocaine-induced expression of behavioral sensitization in rats: possible involvement of the dopaminergic system in the ventral tegmental area. Neurosci Lett 449:128–32
Lee JH, Kim HY, Jang EY, Choi SH, Han CH, Lee BH, Yang CH (2011) Effect of acupuncture on naloxone-precipitated withdrawal syndrome in morphine-experienced rats: the mediation of GABA receptors. Neurosci Lett 504:301–5
Li J, Bian W, Dave V, Ye JH (2011) Blockade of GABA(A) receptors in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus attenuates voluntary ethanol intake and activates the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenocortical axis. Addict Biol 16:600–14
Liu S, Zhou W, Liu H, Yang G, Zhao W (2005) Electroacupuncture attenuates morphine withdrawal signs and c-Fos expression in the central nucleus of the amygdala in freely moving rats. Brain Res 1044:155–63
Liu X, Weiss F (2002) Additive effect of stress and drug cues on reinstatement of ethanol seeking: exacerbation by history of dependence and role of concurrent activation of corticotropin-releasing factor and opioid mechanisms. J Neurosci 22:7856–61
Mansour A, Khachaturian H, Lewis ME, Akil H, Watson SJ (1988) Anatomy of CNS opioid receptors. Trends Neurosci 11:308–14
Margolis EB, Fields HL, Hjelmstad GO, Mitchell JM (2008) Delta-opioid receptor expression in the ventral tegmental area protects against elevated alcohol consumption. J Neurosci 28:12672–81
McFarland K, Davidge SB, Lapish CC, Kalivas PW (2004) Limbic and motor circuitry underlying footshock-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior. J Neurosci 24:1551–60
Mello NK, Negus SS (1996) Preclinical evaluation of pharmacotherapies for treatment of cocaine and opioid abuse using drug self-administration procedures. Neuropsychopharmacology 14:375–424
Mogenson GJ, Jones DL, Yim CY (1980) From motivation to action: functional interface between the limbic system and the motor system. Prog Neurobiol 14:69–97
Napadow V, Makris N, Liu J, Kettner NW, Kwong KK, Hui KK (2005) Effects of electroacupuncture versus manual acupuncture on the human brain as measured by fMRI. Hum Brain Mapp 24:193–205
Orsini C, Izzo E, Koob GF, Pulvirenti L (2002) Blockade of nitric oxide synthesis reduces responding for cocaine self-administration during extinction and reinstatement. Brain Res 925:133–40
Peuker E, Cummings M (2003) Anatomy for the acupuncturist—facts & fiction. 3: Upper & lower extremity. Acupunct Med 21:122–32
Schmidt HD, Pierce RC (2006) Cooperative activation of D1-like and D2-like dopamine receptors in the nucleus accumbens shell is required for the reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in the rat. Neuroscience 142:451–61
Schoen AM (2001) Veterinary acupuncture: ancient art to modern medicine, 2nd edn. Mosby, St. Louis
Shaham Y, Stewart J (1995) Stress reinstates heroin-seeking in drug-free animals: an effect mimicking heroin, not withdrawal. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 119:334–41
Shaham Y, Erb S, Stewart J (2000) Stress-induced relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking in rats: a review. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 33:13–33
Shaham Y, Shalev U, Lu L, De Wit H, Stewart J (2003) The reinstatement model of drug relapse: history, methodology and major findings. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 168:3–20
Sheng M, McFadden G, Greenberg ME (1990) Membrane depolarization and calcium induce c-fos transcription via phosphorylation of transcription factor CREB. Neuron 4:571–82
Shoaib M, Swanner LS, Beyer CE, Goldberg SR, Schindler CW (1998) The GABAB agonist baclofen modifies cocaine self-administration in rats. Behav Pharmacol 9:195–206
Sinha R (2001) How does stress increase risk of drug abuse and relapse? Psychopharmacology (Berl) 158:343–59
Sinha R (2007) The role of stress in addiction relapse. Curr Psychiatry Rep 9:388–95
Steffensen SC, Stobbs SH, Colago EE, Lee RS, Koob GF, Gallegos RA, Henriksen SJ (2006) Contingent and non-contingent effects of heroin on mu-opioid receptor-containing ventral tegmental area GABA neurons. Exp Neurol 202:139–51
Stewart J (2000) Pathways to relapse: the neurobiology of drug- and stress-induced relapse to drug-taking. J Psychiatry Neurosci 25:125–36
Stux G, Pomeranz B (1998) Basics of acupuncture, 4th edn. Springer, Berlin
Ulett GA, Han S, Han JS (1998) Electroacupuncture: mechanisms and clinical application. Biol Psychiatry 44:129–38
Wang Q, Mao L, Han J (1990a) Analgesic electrical stimulation of the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus: tolerance and its cross-tolerance to 2 Hz or 100 Hz electroacupuncture. Brain Res 518:40–6
Wang Q, Mao L, Han J (1990b) The arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus mediates low but not high frequency electroacupuncture analgesia in rats. Brain Res 513:60–6
Wang B, Shaham Y, Zitzman D, Azari S, Wise RA, You ZB (2005) Cocaine experience establishes control of midbrain glutamate and dopamine by corticotropin-releasing factor: a role in stress-induced relapse to drug seeking. J Neurosci 25:5389–96
Ward SJ, Roberts DC (2007) Microinjection of the delta-opioid receptor selective antagonist naltrindole 5′-isothiocyanate site specifically affects cocaine self-administration in rats responding under a progressive ratio schedule of reinforcement. Behav Brain Res 182:140–4
Xi ZX, Stein EA (1998) Nucleus accumbens dopamine release modulation by mesolimbic GABAA receptors-an in vivo electrochemical study. Brain Res 798:156–65
Xi ZX, Gilbert J, Campos AC, Kline N, Ashby CR Jr, Hagan JJ, Heidbreder CA, Gardner EL (2004) Blockade of mesolimbic dopamine D3 receptors inhibits stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 176:57–65
Yamamoto H, Kawada T, Kamiya A, Miyazaki S, Sugimachi M (2011) Involvement of the mechanoreceptors in the sensory mechanisms of manual and electrical acupuncture. Auton Neurosci 160:27–31
Yang CH, Lee BB, Jung HS, Shim I, Roh PU, Golden GT (2002) Effect of electroacupuncture on response to immobilization stress. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 72:847–55
Yang CH, Lee BH, Sohn SH (2008) A possible mechanism underlying the effectiveness of acupuncture in the treatment of drug addiction. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 5:257–66
Yang CH, Yoon SS, Hansen DM, Wilcox JD, Blumell BR, Park JJ, Steffensen SC (2010) Acupuncture inhibits GABA neuron activity in the ventral tegmental area and reduces ethanol self-administration. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34:2137–46
Yoon SS, Kwon YK, Kim MR, Shim I, Kim KJ, Lee MH, Lee YS, Golden GT, Yang CH (2004) Acupuncture-mediated inhibition of ethanol-induced dopamine release in the rat nucleus accumbens through the GABAB receptor. Neurosci Lett 369:234–8
Yoon SS, Kim H, Choi KH, Lee BH, Lee YK, Lim SC, Choi SH, Hwang M, Kim KJ, Yang CH (2010) Acupuncture suppresses morphine self-administration through the GABA receptors. Brain Res Bull 81:625–30
Zhao ZQ (2008) Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia. Prog Neurobiol 85:355–75
Zhao RJ, Yoon SS, Lee BH, Kwon YK, Kim KJ, Shim I, Choi KH, Kim MR, Golden GT, Yang CH (2006) Acupuncture normalizes the release of accumbal dopamine during the withdrawal period and after the ethanol challenge in chronic ethanol-treated rats. Neurosci Lett 395:28–32
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants (K08010 and K11010) from Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine (KIOM), South Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Seong Shoon Yoon and Eun Jin Yang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, S.S., Yang, E.J., Lee, B.H. et al. Effects of acupuncture on stress-induced relapse to cocaine-seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 222, 303–311 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2683-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2683-3