Abstract
Rationale
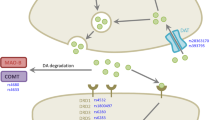
Pharmacogenetic studies on antipsychotic-induced movement disorders (MD) in schizophrenia so far have focused mainly on tardive dyskinesia. Only a few examined the more acute antipsychotic-induced MD such as parkinsonism and akathisia. Notably, all MD relate to deregulation of the dopamine system.
Objective
This study aimed to replicate previously reported associations in candidate genes for acute and tardive antipsychotic-induced MD in a young Caucasian sample.
Methods
In 402 patients (median age 26 years), a total of 13 polymorphisms were genotyped in eight dopamine-related candidate genes selected a priori from the literature (regarding dopamine and serotonin receptors, dopamine degradation, and free radicals scavenging enzymes pathways).
Results
Patients with MD used on average a higher haloperidol dose equivalent when compared to those without MD. The prevalence of MD was high and did not differ between first- and second-generation antipsychotics. Significant associations were found between (a) the TaqI_D polymorphism and akathisia (OR = 2.3, p = 0.001 for each extra C-allele) and (b) the −141C polymorphism and tardive dyskinesia (OR = 0.20, p = 0.001 for each extra Del allele). The other polymorphisms were not significantly associated with an MD.
Conclusions
Two associations were found between genetic variation TaqI_D and the −141C polymorphisms in the DRD2 gene and antipsychotic-induced MD; one with acute akathisia and one with tardive dyskinesia. These were previously reported to be associated with tardive dyskinesia and acute parkinsonism, respectively. These results suggest that the contribution of these DRD2 gene variants in the vulnerability of antipsychotic-induced MD takes place in a more general or pleiotropic way.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberg K, Adkins DE, Bukszar J, Webb BT, Caroff SN, del Miller D, Sebat J, Stroup S, Fanous AH, Vladimirov VI, McClay JL, Lieberman JA, Sullivan PF, van den Oord EJ (2010) Genomewide association study of movement-related adverse antipsychotic effects. Biol Psychiatry 67:279–282
Al Hadithy AF, Wilffert B, Stewart RE, Looman NM, Bruggeman R, Brouwers JR, Matroos GE, van Os J, Hoek HW, van Harten PN (2008) Pharmacogenetics of parkinsonism, rigidity, rest tremor, and bradykinesia in African-Caribbean inpatients: differences in association with dopamine and serotonin receptors. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 147B:890–897
Al Hadithy AF, Ivanova SA, Pechlivanoglou P, Semke A, Fedorenko O, Kornetova E, Ryadovaya L, Brouwers JR, Wilffert B, Bruggeman R, Loonen AJ (2009) Tardive dyskinesia and DRD3, HTR2A and HTR2C gene polymorphisms in Russian psychiatric inpatients from Siberia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:475–481
Al Hadithy AF, Ivanova SA, Pechlivanoglou P, Wilffert B, Semke A, Fedorenko O, Kornetova E, Ryadovaya L, Brouwers JR, Loonen AJ (2010) Missense polymorphisms in three oxidative-stress enzymes (GSTP1, SOD2, and GPX1) and dyskinesias in Russian psychiatric inpatients from Siberia. Hum Psychopharmacol 25:84–91
Al-Janabi I, Arranz MJ, Blakemore AI, Saiz PA, Susce MT, Glaser PE, Clark D, de Leon J (2009) Association study of serotonergic gene variants with antipsychotic-induced adverse reactions. Psychiatr Genet 19:305–311
Alkelai A, Greenbaum L, Rigbi A, Kanyas K, Lerer B (2009) Genome-wide association study of antipsychotic-induced parkinsonism severity among schizophrenia patients. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 206:491–499
Andreasen NC, Pressler M, Nopoulos P, Miller D, Ho BC (2010) Antipsychotic dose equivalents and dose-years: a standardized method for comparing exposure to different drugs. Biol Psychiatry 67:255–262
Arinami T, Gao M, Hamaguchi H, Toru M (1997) A functional polymorphism in the promoter region of the dopamine D2 receptor gene is associated with schizophrenia. Hum Mol Genet 6:577–582
Arranz MJ, de Leon J (2007) Pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics of schizophrenia: a review of last decade of research. Mol Psychiatry 12:707–747
Bakker PR, van Harten PN, van Os J (2006) Antipsychotic-induced tardive dyskinesia and the Ser9Gly polymorphism in the DRD3 gene: a meta analysis. Schizophr Res 83:185–192
Bakker PR, van Harten PN, van Os J (2008) Antipsychotic-induced tardive dyskinesia and polymorphic variations in COMT, DRD2, CYP1A2 and MnSOD genes: a meta-analysis of pharmacogenetic interactions. Mol Psychiatry 13:544–556
Barnes TR (1989) A rating scale for drug-induced akathisia. Br J Psychiatry 154:672–676
Bartko JJ (1991) Measurement and reliability: statistical thinking considerations. Schizophr Bull 17:483–489
Bertolino A, Fazio L, Caforio G, Blasi G, Rampino A, Romano R, Di Giorgio A, Taurisano P, Papp A, Pinsonneault J, Wang D, Nardini M, Popolizio T, Sadee W (2009) Functional variants of the dopamine receptor D2 gene modulate prefronto-striatal phenotypes in schizophrenia. Brain 132:417–425
Casey DE (1995) Tardive dyskinesia: pathophysiology. In: Bloom FE, Kupfer DJ (eds) Psychopharmacology: the fourth generation of progress. Raven, New York, pp 1497–1502
Casey DE (2004) Pathophysiology of antipsychotic drug-induced movement disorders. J Clin Psychiatry 65(Suppl 9):25–28
Chakos MH, Alvir JM, Woerner MG, Koreen A, Geisler S, Mayerhoff D, Sobel S, Kane JM, Borenstein M, Lieberman JA (1996) Incidence and correlates of tardive dyskinesia in first episode of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53:313–319
Correll CU, Schenk EM (2008) Tardive dyskinesia and new antipsychotics. Curr Opin Psychiatry 21:151–156
Correll CU, Leucht S, Kane JM (2004) Lower risk for tardive dyskinesia associated with second-generation antipsychotics: a systematic review of 1 year studies. Am J Psychiatry 161:414–425
de Leon J, Susce MT, Pan RM, Koch WH, Wedlund PJ (2005) Polymorphic variations in GSTM1, GSTT1, PgP, CYP2D6, CYP3A5, and dopamine D2 and D3 receptors and their association with tardive dyskinesia in severe mental illness. J Clin Psychopharmacol 25:448–456
Duan J, Wainwright MS, Comeron JM, Saitou N, Sanders AR, Gelernter J, Gejman PV (2003) Synonymous mutations in the human dopamine receptor D2 (DRD2) affect mRNA stability and synthesis of the receptor. Hum Mol Genet 12:205–216
Eichhammer P, Albus M, Borrmann-Hassenbach M, Schoeler A, Putzhammer A, Frick U, Klein HE, Rohrmeier T (2000) Association of dopamine D3-receptor gene variants with neuroleptic induced akathisia in schizophrenic patients: a generalization of Steen’s study on DRD3 and tardive dyskinesia. Am J Med Genet 96:187–191
Frackiewicz EJ, Sramek JJ, Herrera JM, Kurtz NM, Cutler NR (1997) Ethnicity and antipsychotic response. Ann Pharmacother 31:1360–1369
Gerlach J (2002) Improving outcome in schizophrenia: the potential importance of EPS and neuroleptic dysphoria. Ann Clin Psychiatry 14:47–57
Glazer WM (2000) Review of incidence studies of tardive dyskinesia associated with typical antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry 61(Suppl 4):15–20
Greenbaum L, Strous RD, Kanyas K, Merbl Y, Horowitz A, Karni O, Katz E, Kotler M, Olender T, Deshpande SN, Lancet D, Ben-Asher E, Lerer B (2007) Association of the RGS2 gene with extrapyramidal symptoms induced by treatment with antipsychotic medication. Pharmacogenet Genomics 17:519–528
Greenbaum L, Smith RC, Rigbi A, Strous R, Teltsh O, Kanyas K, Korner M, Lancet D, Ben-Asher E, Lerer B (2009) Further evidence for association of the RGS2 gene with antipsychotic-induced parkinsonism: protective role of a functional polymorphism in the 3′-untranslated region. Pharmacogenomics J 9:103–110
Greenbaum L, Alkelai A, Rigbi A, Kohn Y, Lerer B (2010) Evidence for association of the GLI2 gene with tardive dyskinesia in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Mov Disord 25:2809–2817
GROUP (2010) Evidence that familial liability for psychosis is expressed as differential sensitivity to cannabis: an analysis of patient-sibling and sibling-control pairs. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68(2):138–147
Gunes A, Scordo MG, Jaanson P, Dahl ML (2007) Serotonin and dopamine receptor gene polymorphisms and the risk of extrapyramidal side effects in perphenazine-treated schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 190:479–484
Gunes A, Dahl ML, Spina E, Scordo MG (2008) Further evidence for the association between 5-HT2C receptor gene polymorphisms and extrapyramidal side effects in male schizophrenic patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 64:477–482
Guy E (1976) Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale, ECDEU assessment manual for psychopharmacology. National institute of mental Health, U.S. Department Health and Human Services, National institute of mental Health, U.S. Department Health and Human Services
Guzey C, Scordo MG, Spina E, Landsem VM, Spigset O (2007) Antipsychotic-induced extrapyramidal symptoms in patients with schizophrenia: associations with dopamine and serotonin receptor and transporter polymorphisms. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 63:233–241
Hori H, Ohmori O, Shinkai T, Kojima H, Nakamura J (2001) Association between three functional polymorphisms of dopamine D2 receptor gene and tardive dyskinesia in schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet 105:774–778
Inada T, Koga M, Ishiguro H, Horiuchi Y, Syu A, Yoshio T, Takahashi N, Ozaki N, Arinami T (2008) Pathway-based association analysis of genome-wide screening data suggest that genes associated with the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor signaling pathway are involved in neuroleptic-induced, treatment-resistant tardive dyskinesia. Pharmacogenet Genomics 18:317–323
Jonsson EG, Nothen MM, Grunhage F, Farde L, Nakashima Y, Propping P, Sedvall GC (1999) Polymorphisms in the dopamine D2 receptor gene and their relationships to striatal dopamine receptor density of healthy volunteers. Mol Psychiatry 4:290–296
Jorgensen AL, Williamson PR (2008) Methodological quality of pharmacogenetic studies: issues of concern. Stat Med 27:6547–6569
Kahn RS, Fleischhacker WW, Boter H, Davidson M, Vergouwe Y, Keet IP, Gheorghe MD, Rybakowski JK, Galderisi S, Libiger J, Hummer M, Dollfus S, Lopez-Ibor JJ, Hranov LG, Gaebel W, Peuskens J, Lindefors N, Riecher-Rossler A, Grobbee DE (2008) Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in first-episode schizophrenia and schizophreniform disorder: an open randomized clinical trial. Lancet 371:1085–1097
Kaiser R, Tremblay PB, Klufmoller F, Roots I, Brockmoller J (2002) Relationship between adverse effects of antipsychotic treatment and dopamine D(2) receptor polymorphisms in patients with schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 7:695–705
Kane JM (2006) Tardive dyskinesia circa 2006. Am J Psychiatry 163:1316–1318
Kane JM (2007) Treatment adherence and long-term outcomes. CNS Spectr 12:21–26
Kane JM, Smith JM (1982) Tardive dyskinesia: prevalence and risk factors, 1959 to 1979. Arch Gen Psychiatry 39:473–481
Kane JM, Fleischhacker WW, Hansen L, Perlis R, Pikalov A 3rd, Assuncao-Talbott S (2009) Akathisia: an updated review focusing on second-generation antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry 70:627–643
Kang SG, Lee HJ, Choi JE, An H, Rhee M, Kim L (2009) Association study between glutathione S-transferase GST-M1, GST-T1, and GST-P1 polymorphisms and tardive dyskinesia. Hum Psychopharmacol 24:55–60
Kapur S, Mamo D (2003) Half a century of antipsychotics and still a central role for dopamine D2 receptors. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27:1081–1090
Kapur S, Zipursky RB, Remington G (1999) Clinical and theoretical implications of 5-HT2 and D2 receptor occupancy of clozapine, risperidone, and olanzapine in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 156:286–293
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Laruelle M (1998) Imaging dopamine transmission in schizophrenia. A review and meta-analysis. Q J Nucl Med 42:211–221
Lerer B (2002) Pharmacogenetics of psychotropic drugs. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lerer B, Segman RH, Fangerau H, Daly AK, Basile VS, Cavallaro R, Aschauer HN, McCreadie RG, Ohlraun S, Ferrier N, Masellis M, Verga M, Scharfetter J, Rietschel M, Lovlie R, Levy UH, Meltzer HY, Kennedy JL, Steen VM, Macciardi F (2002) Pharmacogenetics of tardive dyskinesia: combined analysis of 780 patients supports association with dopamine D3 receptor gene Ser9Gly polymorphism. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:105–119
Lieberman JA, Bymaster FP, Meltzer HY, Deutch AY, Duncan GE, Marx CE, Aprille JR, Dwyer DS, Li XM, Mahadik SP, Duman RS, Porter JH, Modica-Napolitano JS, Newton SS, Csernansky JG (2008) Antipsychotic drugs: comparison in animal models of efficacy, neurotransmitter regulation, and neuroprotection. Pharmacol Rev 60:358–403
Marsalek M (2000) Tardive drug-induced extrapyramidal syndromes. Pharmacopsychiatry 33(Suppl 1):14–33
Marsden CD, Jenner P (1980) The pathophysiology of extrapyramidal side-effects of neuroleptic drugs. Psychol Med 10:55–72
Martinez-Martin P, Gil-Nagel A, Gracia LM, Gomez JB, Martinez-Sarries J, Bermejo F (1994) Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale characteristics and structure. The Cooperative Multicentric Group. Mov Disord 9:76–83
Masand PS, Roca M, Turner MS, Kane JM (2009) Partial adherence to antipsychotic medication impacts the course of illness in patients with schizophrenia: a review. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry 11:147–154
Miyamoto S, Duncan GE, Marx CE, Lieberman JA (2005) Treatments for schizophrenia: a critical review of pharmacology and mechanisms of action of antipsychotic drugs. Mol Psychiatry 10:79–104
Morgenstern H, Glazer WM (1993) Identifying risk factors for tardive dyskinesia among long-term outpatients maintained with neuroleptic medications. Results of the Yale Tardive Dyskinesia Study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 50:723–733
Ng F, Berk M, Dean O, Bush AI (2008) Oxidative stress in psychiatric disorders: evidence base and therapeutic implications. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:851–876
Pohjalainen T, Nagren K, Syvalahti EK, Hietala J (1999) The dopamine D2 receptor 5′-flanking variant,−141C Ins/Del, is not associated with reduced dopamine D2 receptor density in vivo. Pharmacogenetics 9:505–509
Potvin S, Blanchet P, Stip E (2009) Substance abuse is associated with increased extrapyramidal symptoms in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Schizophr Res 113:181–188
Ritchie T, Noble EP (2003) Association of seven polymorphisms of the D2 dopamine receptor gene with brain receptor-binding characteristics. Neurochem Res 28:73–82
Rummel-Kluge C, Komossa K, Schwarz S, Hunger H, Schmid F, Kissling W, Davis JM, Leucht S (2011) Second-generation antipsychotic drugs and extrapyramidal side effects: a systematic review and meta-analysis of head-to-head comparisons. Schizophr Bull. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbq042
Sachdev PS (2005) Neuroleptic-induced movement disorders: an overview. Psychiatr Clin North Am 28:255–274
Schooler NR, Kane JM (1982) Research diagnoses for tardive dyskinesia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 39:486–487
Schwartz JC, Diaz J, Pilon C, Sokoloff P (2000) Possible implications of the dopamine D(3) receptor in schizophrenia and in antipsychotic drug actions. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 31:277–287
Segman RH, Heresco-Levy U, Finkel B, Inbar R, Neeman T, Schlafman M, Dorevitch A, Yakir A, Lerner A, Goltser T, Shelevoy A, Lerer B (2000) Association between the serotonin 2 C receptor gene and tardive dyskinesia in chronic schizophrenia: additive contribution of 5-HT2Cser and DRD3gly alleles to susceptibility. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 152:408–413
Segman RH, Heresco-Levy U, Finkel B, Goltser T, Shalem R, Schlafman M, Dorevitch A, Yakir A, Greenberg D, Lerner A, Lerer B (2001) Association between the serotonin 2A receptor gene and tardive dyskinesia in chronic schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 6:225–229
Stephens M, Donnelly P (2003) A comparison of bayesian methods for haplotype reconstruction from population genotype data. Am J Hum Genet 73:1162–1169
Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P (2001) A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet 68:978–989
Suzuki M, Hurd YL, Sokoloff P, Schwartz JC, Sedvall G (1998) D3 dopamine receptor mRNA is widely expressed in the human brain. Brain Res 779:58–74
Swartz JR, Burgoyne K, Smith M, Gadasally R, Ananth J, Ananth K (1997) Tardive dyskinesia and ethnicity: review of the literature. Ann Clin Psychiatry 9:53–59
Tenback DE, van Harten PN, Slooff CJ, van Os J (2006) Evidence that early extrapyramidal symptoms predict later tardive dyskinesia: a prospective analysis of 10,000 patients in the European Schizophrenia Outpatient Health Outcomes (SOHO) study. Am J Psychiatry 163:1438–1440
Tenback DE, van Harten PN, van Os J (2009) Non-therapeutic risk factors for onset of tardive dyskinesia in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Mov Disord 24(16):2309–2315
Tsai G, Goff DC, Chang RW, Flood J, Baer L, Coyle JT (1998) Markers of glutamatergic neurotransmission and oxidative stress associated with tardive dyskinesia. Am J Psychiatry 155:1207–1213
van den Oord EJ, Sullivan PF (2003a) False discoveries and models for gene discovery. Trends Genet 19:537–542
van den Oord EJ, Sullivan PF (2003b) A framework for controlling false discovery rates and minimizing the amount of genotyping in the search for disease mutations. Hum Hered 56:188–199
Waddington JL, Cross AJ, Gamble SJ, Bourne RC (1983) Spontaneous orofacial dyskinesia and dopaminergic function in rats after 6 months of neuroleptic treatment. Science 220:530–532
Waeber C, Palacios JM (1994) Binding sites for 5-hydroxytryptamine-2 receptor agonists are predominantly located in striosomes in the human basal ganglia. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 24:199–209
Warrens M (2010) Inequalities between multi-rater kappas. Adv Data Anal Classif: 271–286
Weiden P (1994) Neuroleptic-induced parkinsonism. American Psychiatric Association (APA), American Psychiatric Association (APA)
Weiden PJ (2007) Understanding and addressing adherence issues in schizophrenia: from theory to practice. J Clin Psychiatry 68(Suppl 14):14–19
Wilffert B, Al Hadithy AF, Sing VJ, Matroos G, Hoek HW, van Os J, Bruggeman R, Brouwers JR, van Harten PN (2009) The role of dopamine D3, 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor variants as pharmacogenetic determinants in tardive dyskinesia in African-Caribbean patients under chronic antipsychotic treatment: Curacao extrapyramidal syndromes study IX. J Psychopharmacol 23:652–659
Wu SN, Gao R, Xing QH, Li HF, Shen YF, Gu NF, Feng GY, He L (2006) Association of DRD2 polymorphisms and chlorpromazine-induced extrapyramidal syndrome in Chinese schizophrenic patients. Acta Pharmacol Sin 27:966–970
Zai CC, Hwang RW, De Luca V, Muller DJ, King N, Zai GC, Remington G, Meltzer HY, Lieberman JA, Potkin SG, Kennedy JL (2007) Association study of tardive dyskinesia and 12 DRD2 polymorphisms in schizophrenia patients. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 10:639–651
Zai CC, Tiwari AK, Muller DJ, de Luca V, Shinkai T, Shaikh S, Ni X, Sibony D, Voineskos AN, Meltzer HY, Lieberman JA, Potkin SG, Remington G, Kennedy JL (2010) The catechol-O-methyl-transferase gene in tardive dyskinesia. World J Biol Psychiatry 11:803–812
Zaykin DV, Westfall PH, Young SS, Karnoub MA, Wagner MJ, Ehm MG (2002) Testing association of statistically inferred haplotypes with discrete and continuous traits in samples of unrelated individuals. Hum Hered 53:79–91
Zhang JP, Lencz T, Malhotra AK (2010) D2 receptor genetic variation and clinical response to antipsychotic drug treatment: a meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry 167:763–772
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the generosity of time and effort by the patients and their families, healthy subjects, and all researchers who make this GROUP project possible.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Funding
The infrastructure for the GROUP study is funded through the Geestkracht programme of the Dutch Health Research Council (ZON-MW, grant number 10-000-1002), and matching funds from participating pharmaceutical companies (Lundbeck, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Janssen Cilag) and universities and mental health care organizations (Amsterdam: Academic Psychiatric Centre of the Academic Medical Centre and the mental health institutions: GGZ Ingeest, Arkin, Dijk en Duin, Rivierduinen, Erasmus Medical Centre, GGZ Noord Holland Noord. Maastricht: Maastricht University Medical Centre and the mental health institutions: GGZ Eindhoven, GGZ Midden-Brabant, GGZ Oost-Brabant, GGZ Noord- Midden Limburg, Mondriaan Zorggroep, Prins Clauscentrum Sittard, RIAGG Roermond, Universitair Centrum Sint-Jozef Kortenberg, CAPRI University of Antwerp, PC Ziekeren Sint-Truiden, PZ Sancta Maria Sint-Truiden, GGZ Overpelt, OPZ Rekem. Groningen: University Medical Center Groningen and the mental health institutions: Lentis, GGZ Friesland,GGZ Drenthe, Dimence, Mediant, GGZ De Grote Rivieren and Parnassia psycho-medical centre (The Hague). Utrecht: University Medical Centre Utrecht and the mental health institutions Altrecht, Symfora, Meerkanten, Riagg Amersfoort and Delta.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Additional information
GROUP investigators are: René S. Kahn, MD, PhD, Department of Psychiatry, Rudolf Magnus Institute of Neuroscience, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, the Netherlands; Don H. Linszen, MD, PhD, Department of Psychiatry, Academic Medical Centre, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, the Netherlands; Jim van Os, MD, PhD, South Limburg Mental Health Research and Teaching Network, EURON, Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht, the Netherlands, and King’s College London, King’s Health Partners, Department of Psychosis Studies, Institute of Psychiatry, London, England; Durk Wiersma, PhD, Department of Psychiatry, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, Groningen, the Netherlands; Richard Bruggeman, MD, PhD, Department of Psychiatry, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen; Wiepke Cahn, MD, PhD, Department of Psychiatry, Rudolf Magnus Institute of Neuroscience, University Medical Center Utrecht; Lieuwe de Haan, MD, PhD, Department of Psychiatry, Academic Medical Centre, University of Amsterdam; Lydia Krabbendam, PhD, South Limburg Mental Health Research and Teaching Network, EURON, Maastricht University Medical Centre; and Inez Myin-Germeys, PhD, South Limburg Mental Health Research and Teaching Network, EURON, Maastricht University Medical Centre.
Jeroen P. Koning and Jelle Vehof contributed equally in joint first authorship. Peter N. van Harten and Harold Snieder contributed equally to the manuscript.
Correspondence must be addressed to Richard Bruggeman.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koning, J.P., Vehof, J., Burger, H. et al. Association of two DRD2 gene polymorphisms with acute and tardive antipsychotic-induced movement disorders in young Caucasian patients. Psychopharmacology 219, 727–736 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2394-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2394-1