Abstract
Rationale
The interactions between Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) during chronic treatment, and at equivalent doses, are not well characterised in animal models.
Objectives
The aim of this study is to examine whether the behavioural effects of THC, and blood and brain THC levels are affected by pre-treatment with equivalent CBD doses.
Methods
Adolescent rats were treated with ascending daily THC doses over 21 days (1 then 3 then 10 mg/kg). Some rats were given equivalent CBD doses 20 min prior to each THC injection to allow examination of possible antagonistic effects of CBD. During dosing, rats were assessed for THC and CBD/THC effects on anxiety-like behaviour, social interaction and place conditioning. At the end of dosing, blood and brain levels of THC, and CB1 and 5-HT1A receptor binding were assessed.
Results
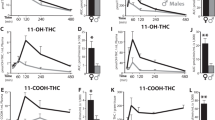
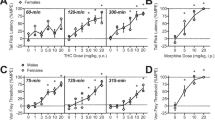
CBD potentiated an inhibition of body weight gain caused by chronic THC, and mildly augmented the anxiogenic effects, locomotor suppressant effects and decreased social interaction seen with THC. A trend towards place preference was observed in adolescent rats given CBD/THC but not those given THC alone. With both acute and chronic administration, CBD pre-treatment potentiated blood and brain THC levels, and lowered levels of THC metabolites (THC-COOH and 11-OH-THC). CBD co-administration did not alter the THC-induced decreases in CB1 receptor binding and no drug effects on 5-HT1A receptor binding were observed.
Conclusions
CBD can potentiate the psychoactive and physiological effects of THC in rats, most likely by delaying the metabolism and elimination of THC through an action on the CYP450 enzymes that metabolise both drugs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves FH, Crestani CC, Gomes FV, Guimaraes FS, Correa FM, Resstel LB (2010) Cannabidiol injected into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis modulates baroreflex activity through 5-HT1A receptors. Pharmacol Res 62:228–236
Bhattacharyya S, Morrison PD, Fusar-Poli P, Martin-Santos R, Borgwardt S, Winton-Brown T, Nosarti C, O'Connel CM, Seal M, Allen P, Mehta MA, Stone JM, Tunstall N, Giampietro V, Kapur S, Murray RM, Zuardi AW, Crippa JA, Atkan Z, McGuire PK (2010) Opposite effect of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol on human brain function and psychopathology. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:764–774
Bornheim LM, Correia MA (1989) Effect of cannabidiol on cytochrome P-450 isoenzymes. Biochem Pharmacol 38:2789–2794
Bornheim LM, Correia MA (1990) Selective inactivation of mouse liver cytochrome P-450IIIA by cannabidiol. Mol Pharmacol 38:319–326
Bornheim LM, Correia MA (1991) Purification and characterization of the major hepatic cannabinoid hydroxylase in the mouse: a possible member of the cytochrome P-450IIC subfamily. Mol Pharmacol 40:228–234
Bornheim LM, Kim K, Beatrice J, Perotti Y, Benet L (1995) Effect of cannabidiol pretreatment on the kinetic of tetrahydrocannabinol metabolites in mouse brain. Drug Metab Dispos 23:825–831
Breivogel CS, Childers SR, Deadwyler SA, Hampson RE, Vogt LJ, Sim-Selley LJ (1999) Chronic delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol treatment produces a time-dependent loss of cannabinoid receptors and cannabinoid receptor-activated G proteins in rat brain. J Neurochem 73:2447–2459
Campos AC, Guimaraes FS (2008) Involvement of 5HT1A receptors in the anxiolytic-like effects of cannabidiol injected into the dorsolateral periaqueductal gray of rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 199:223–230
Dalton GD, Smith FL, Smith PA, Dewey WL (2005) Chronic delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol treatment produces antinociceptive tolerance in mice without altering protein kinase A activity in mouse brain and spinal cord. Biochem Pharmacol 70:152–160
Deveaux V, Cadoudal T, Ichigotani Y, Teixeira-Clerc F, Louvet A, Manin S, Nhieu JT, Belot MP, Zimmer A, Even P, Cani PD, Knauf C, Burcelin R, Bertola A, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Gual P, Mallat A, Lotersztajn S (2009) Cannabinoid CB2 receptor potentiates obesity-associated inflammation, insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis. PLoS ONE 4:e5844
Di Forti M, Morgan C, Dazzan P, Pariante C, Mondelli V, Marques TR, Handley R, Luzi S, Russo M, Paparelli A, Butt A, Stilo SA, Wiffen B, Powell J, Murray RM (2009) High-potency cannabis and the risk of psychosis. Br J Psychiatry 195:488–491
Fernandes M, Warning N, Christ W, Hill R (1973) Interactions of several cannabinoids with the hepatic drug metabolizing system. Biochem Pharmacol 22:2981–2987
Fernandes M, Schabarek A, Cooper H, Hill R (1974) Modification of delta9-THC actions by cannabinol and cannabidiol in the rat. Psychopharmacologia 38:329–338
Genn RF, Tucci S, Marco EM, Viveros MP, File SE (2004) Unconditioned and conditioned anxiogenic effects of the cannabinoid receptor agonist CP 55,940 in the social interaction test. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 77:567–573
Gomes FV, Resstel LB, Guimaraes FS (2011) The anxiolytic-like effects of cannabidiol injected into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis are mediated by 5-HT1A receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 213:465–473
Guilani D, Ferrari F, Ottani A (2000) The cannabinoid agonist HU 210 modifies rat behavioural responses to novelty and stress. Pharmacol Res 41:47–53
Guimaraes FS, Chiaretti TM, Graeff FG, Zuardi AW (1990) Antianxiety effect of cannabidiol in the elevated plus-maze. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 100:558–559
Gunasekaran N, Long L, Arnold JC, McGregor IS (2009) Reintoxication: the release of fat-stored delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) into blood is enhanced by food deprivation or ACTH exposure. British Journal of Pharmacology 158:1330–1337
Han M, Huang XF, du Bois TM, Deng C (2009) The effects of antipsychotic drugs administration on 5-HT1A receptor expression in the limbic system of the rat brain. Neuroscience 164:1754–1763
Hayakawa K, Mishima K, Nozako M, Ogata A, Hazekawa M, Liu A-X, Fujioka M, Abe K, Hasebe N, Egashira N, Iwasaki K, Fujiwara M (2007) Repeated treatment with cannabidiol but not delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol has a neuroprotective effect without the development of tolerance. Neuropharmacology 52:1079–1087
Hayakawa K, Mishima K, Hazekawa M, Sano K, Irie K, Orito K, Egawa T, Kitamura Y, Uchida N, Nishimura R, Egashira N, Iwasaki K, Fujiwara M (2008) Cannabidiol potentiates pharmacological effects of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol via a CB1 receptor-dependent mechanism. Brain Res 1188:157–164
Hollister LE, Gillespie H (1975) Interactions in man of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol, H-cannabinol and cannabidiol. Clin Pharmacol 18:329–338
Ignatowska-Jankowska B, Jankowski MM, Swiergiel AH (2011) Cannabidiol decreases body weight gain in rats: involvement of CB2 receptors. Neurosci Lett 490:82–84
Izzo AA, Borrelli F, Capasso R, Di Marzo V, Mechoulam R (2009) Non-psychotropic plant cannabinoids: new therapeutic opportunities from an ancient herb. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30:515–527
Jones G, Pertwee RG (1972) A metabolic interaction in vivo between cannabidiol and 1-tetrahydrocannabinol. Br J Pharmacol 45:375–377
Karniol IG, Carlini EA (1973) Pharmacological interaction between cannabidiol and delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Psychopharmacologia 33:53–70
Karniol IG, Shirakawa I, Kasinaki N, Carlini EA (1974) Cannabidiol interferes with the effects of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol in man. Eur J Pharmacol 28:172–177
Karschner EL, Darwin WD, McMahon RP, Liu F, Wright S, Goodwin RS, Huestis MA (2011a) Subjective and physiological effects after controlled Sativex and oral THC administration. Clin Pharmacol Ther 89:400–407
Karschner EL, Darwin WD, Goodwin RS, Wright S, Huestis MA (2011b) Plasma cannabinoid pharmacokinetics following controlled oral delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and oromucosal cannabis extract administration. Clin Chem 57:66–75
Kmietowicz Z (2010) Cannabis based drug is licensed for spasticity in patients with MS. BMJ 340:c3363
Long LE, Chesworth R, Huang XF, McGregor IS, Arnold JC, Karl T (2010) A behavioural comparison of acute and chronic delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol in C57BL/6JArc mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 13:861–876
Mallet PE, Beninger PJ (1998) Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol, but not the endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand anandamide, produces conditioned place avoidance. Life Sci 62:2431–2434
Malone DT, Jongejan D, Taylor DA (2009) Cannabidiol reverses the reduction in social interaction produced by low dose of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 93:91–96
McGregor IS, Issakidis CN, Prior G (1996) Aversive effects of the synthetic cannabinoid CP 55,940 in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 53:657–664
McLaren J, Swift W, Dillon P, Allsop S (2008) Cannabis potency and contamination: a review of the literature. Addiction 103:1100–1109
Mechoulam R (1986) The pharmacohistory of Cannabis sativa. In: Mechoulam R (ed) Cannabinoids as therapeutic agents. CRC, Boca Raton, p 19
Mishima K, Hayakawa K, Abe K, Ikeda T, Egashira N, Iwasaki K, Fujiwara M (2005) Cannabidiol prevents cerebral infarction via a serotonergic 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor-dependent mechanism. Stroke 36:1071–1076
Moreira FA, Aguiar DC, Guimaraes FS (2006) Anxiolytic-like effect of cannabidiol in the rat Vogel conflict test. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30:1466–1471
Morgan CJ, Curran HV (2008) Effects of cannabidiol on schizophrenia-like symptoms in people who use cannabis. Br J Psychiatry 192:306–307
Morgan CJ, Freeman TP, Schafer GL, Curran HV (2010a) Cannabidiol attenuates the appetitive effects of delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol in humans smoking their chosen cannabis. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:1879–1885
Morgan CJ, Schafer G, Freeman TP, Curran HV (2010b) Impact of cannabidiol on the acute memory and psychotomimetic effects of smoked cannabis: naturalistic study. Br J Psychiatry 197:285–290
Nadulski T, Pragst F, Weinberg G, Roser P, Schnelle M, Fronk EM, Stadelmann AM (2005) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study about the effects of cannabidiol (CBD) on the pharmacokinetics of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) after oral application of THC verses standardized cannabis extract. Ther Drug Monit 27:799–810
Onaivi ES, Green MR, Martin BR (1990) Pharmacological effects of cannabinoids in the elevated plus-maze. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 253:1002–1009
Oviedo A, Glowa J, Herkenham M (1993) Chronic cannabinoid administration alters cannabinoid receptor binding in rat brain: a quantitative autoradiographic study. Brain Res 616:293–302
Parker LA, Burton P, Sorge RE, Yakiwchuk C, Mechoulam R (2004) Effect of low doses of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol on the extinction of cocaine-induced and amphetamine-induced conditioned place preference learning in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 175:360–366
Pertwee RG (2004) The pharmacology and therapeutic potential of cannabidiol. In: Marzo VD (ed) Cannabinoids. Kluwer/Plenum, New York, p 51
Pertwee RG (2008) The diverse CB1 and CB2 receptor pharmacology of three plant cannabinoids: delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and delta9-tetrahydrocannabivarin. Br J Pharmacol 153:199–215
Pertwee RG, Thomas A (2007) Therapeutic applications for agents that act at CB1 and CB2 receptor. In: Reggio PH (ed) The cannabinoid receptors. Humana, Totowa
Potter DJ, Clark P, Brown MB (2008) Potency of delta 9-THC and other cannabinoids in cannabis in England in 2005: implications for psychoactivity and pharmacology. J Forensic Sci 53:90–94
Quinn HR, Matsumoto I, Callaghan PD, Long LE, Arnold JC, Gunasekaran N, Thompson MR, Dawson B, Mallet PE, Kashem MA, Matsuda-Matsumoto H, Iwazaki T, McGregor IS (2008) Adolescent rats find repeated delta(9)-THC less aversive than adult rats but display greater residual cognitive deficits and changes in hippocampal protein expression following exposure. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:1113–1126
Reid MJ, Bornheim LM (2001) Cannabinoid-induced alterations in brain disposition of drugs of abuse. Biochem Pharmacol 61:1357–1367
Resstel LB, Tavares RF, Lisboa SF, Joca SR, Correa FM, Guimaraes FS (2009) 5-HT1A receptors are involved in the cannabidiol-induced attenuation of behavioural and cardiovascular responses to acute restraint stress in rats. Br J Pharmacol 156:181–188
Robson P (2005) Human studies of cannabinoids and medicinal cannabis. In: Pertwee RG (ed) Cannabinoids. Handbook of experimental pharmacology. Springer, Heidelberg, p 37
Russo E, Guy GW (2006) A tale of two cannabinoids: the therapeutic rationale for combining tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol. Med Hypotheses 66:234–246
Sjoden PO, Jarbe TU, Henriksson BG (1973) Influence of tetrahydrocannabinols (delta8-THC and delta9-THC) on body weight, food, and water intake in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1:395–399
South T, Huang XF (2008) Temporal and site-specific brain alterations in CB1 receptor binding in high fat diet-induced obesity in C57Bl/6 mice. J Neuroendocrinol 20:1288–1294
Spear LP (2000) The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:417–463
Teixeira D, Pestana D, Faria A, Calhau C, Azevedo I, Monteiro R (2010) Modulation of adipocyte biology by delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol. Obesity (Silver Spring) 18:2077–2085
Thomas A, Baillie GL, Phillips AM, Razdan RK, Ross RA, Pertwee RG (2007) Cannabidiol displays unexpectedly high potency as an antagonist of CB1 and CB2 receptor agonists in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 150:613–623
Vann RE, Gamage TF, Warner JA, Marshall EM, Taylor NL, Martin BR, Wiley JL (2008) Divergent effects of cannabidiol on the discriminative stimulus and place conditioning effects of delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol. Drug Alcohol Depend 94:191–198
Varvel SA, Wiley JL, Yang R, Bridgen DT, Long K, Lichtman AH, Martin BR (2006) Interactions between THC and cannabidiol in mouse models of cannabinoid activity. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 186:226–234
Zanelati TV, Biojone C, Moreira FA, Guimaraes FS, Joca SR (2010) Antidepressant-like effects of cannabidiol in mice: possible involvement of 5-HT1A receptors. Br J Pharmacol 159:122–128
Zavitsanou K, Wang H, Dalton VS, Nguyen V (2010) Cannabinoid administration increases 5HT1A receptor binding and mRNA expression in the hippocampus of adult but not adolescent rats. Neuroscience 169:315–324
Zuardi AW, Finkelfarb E, Bueno OF, Musty RE, Karniol IG (1981) Characteristics of the stimulus produced by the mixture of cannabidiol with delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Thér 249:137–146
Zuardi AW, Shirakawa I, Finkelfarb E, Karniol IG (1982) Action of cannabidiol on the anxiety and other effects produced by delta9-THC in normal subjects. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 76:245–250
Acknowledgements
Supported by research grants from the Australian Research Council (ISM) and National Health and Medical Research Council (TK, ISM and JCA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klein, C., Karanges, E., Spiro, A. et al. Cannabidiol potentiates Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) behavioural effects and alters THC pharmacokinetics during acute and chronic treatment in adolescent rats. Psychopharmacology 218, 443–457 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2342-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2342-0