Abstract
Rationale
Previous studies reported that bupropion, an effective antidepressant, exerts modulatory actions on serotonin (5-HT) and norepinephrine (NE) neurons.
Objectives
This study examined effects of bupropion administration on 5-HT and NE neurotransmission in hippocampus.
Methods
Electrophysiological recordings were obtained from anesthetized Sprague–Dawley rats. Subcutaneously implanted minipumps delivered saline or bupropion (30 mg/kg/day) for 2 and 14 days.
Results
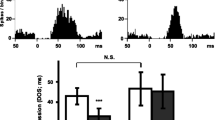
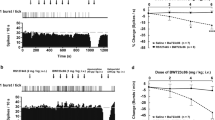
Although sustained bupropion administration did not alter the sensitivity of 5-HT1A and α2-adrenergic receptors, the tonic activation of postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors by endogenous 5-HT was enhanced in 14-day bupropion-treated rats to a greater extent than in the 2-day and control rats, as revealed by the greater disinhibitory action of the 5-HT1A antagonist WAY-100635 on hippocampus pyramidal neurons. The function of terminal 5-HT1B autoreceptors was not changed as determined by the unaltered effectiveness of different frequencies of stimulation of the ascending 5-HT fibers. The function of α2-adrenergic receptors on 5-HT terminals was, however, diminished, as indicated by the lesser effect of the α2-adrenoceptor agonist clonidine. Tonic activation of postsynaptic α2- and α1-adrenoceptors by endogenous NE was also increased in 14-day bupropion-treated rats, as indicated by the greater effect of the α2- and α1-adrenoceptor antagonists idazoxan and prazosin, respectively, on pyramidal firing. The function of terminal α2-adrenergic autoreceptors was attenuated since increasing frequency of stimulation of the ascending NE pathway produced a lesser degree of suppression of pyramidal neurons in rats administered bupropion than the control.
Conclusion
Enhancement of 5-HT and NE transmissions in hippocampus by prolonged bupropion may account for its effectiveness in major depression.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 5-HT:
-
5-Hydroxytryptamine
- DR:
-
Dorsal raphe
- LC:
-
Locus coeruleus
- NE:
-
Norepinephrine
- SSRI:
-
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
- WAY-100635:
-
N-{2-[4(2-methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl] ethyl}-N-(2-pyridinyl) cyclohexanecarboxamide trihydrochloride
References
Argyelan M, Szabo Z, Kanyo B, Tanacs A, Kovacs Z, Janka Z, Pavics L (2005) Dopamine transporter availability in medication free and in bupropion treated depression: a 99mTc-TRODAT-1 SPECT study. J Affect Disord 89:115–123
Besson A, Haddjeri N, Blier P, de Montigny C (2000) Effects of the co-administration of mirtazapine and paroxetine on serotonergic neurotransmission in the rat brain. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 10:177–188
Blier P, Bouchard C (1994) Modulation of 5-HT release in the guinea-pig brain following long-term administration of antidepressant drugs. Br J Pharmacol 113:485–495
Blier P, Chaput Y, de Montigny C (1988) Long-term 5-HT reuptake blockade, but not monoamine oxidase inhibition, decreases the function of terminal 5-HT autoreceptors: an electrophysiological study in the rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 337:246–254
Blier P, Ramdine R, Galzin AM, Langer SZ (1989) Frequency-dependence of serotonin autoreceptor but not alpha 2-adrenoceptor inhibition of [3H]-serotonin release in rat hypothalamic slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 339:60–64
Chaput Y, Blier P, de Montigny C (1986) In vivo electrophysiological evidence for the regulatory role of autoreceptors on serotonergic terminals. J Neurosci 6:2796–2801
Chaput Y, de Montigny C, Blier P (1991) Presynaptic and postsynaptic modifications of the serotonin system by long-term administration of antidepressant treatments. An in vivo electrophysiologic study in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 5:219–229
Cooper BR, Wang CM, Cox RF, Norton R, Shea V, Ferris RM (1994) Evidence that the acute behavioral and electrophysiological effects of bupropion (Wellbutrin) are mediated by a noradrenergic mechanism. Neuropsychopharmacology 11:133–141
Cryan JF, Dalvi A, Jin SH, Hirsch BR, Lucki I, Thomas SA (2001) Use of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase-deficient mice to determine the role of norepinephrine in the mechanism of action of antidepressant drugs. Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:651–657
Cryan JF, O'Leary OF, Jin SH, Friedland JC, Ouyang M, Hirsch BR, Page ME, Dalvi A, Thomas SA, Lucki I (2004) Norepinephrine-deficient mice lack responses to antidepressant drugs, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:8186–8191
Curet O, de Montigny C (1988a) Electrophysiological characterization of adrenoceptors in the rat dorsal hippocampus. II. Receptors mediating the effect of synaptically released norepinephrine. Brain Res 475:47–57
Curet O, de Montigny C (1988b) Electrophysiological characterization of adrenoceptors in the rat dorsal hippocampus. I. Receptors mediating the effect of microiontophoretically applied norepinephrine. Brain Res 475:35–46
Curet O, de Montigny C (1989) Electrophysiological characterization of adrenoceptors in the rat dorsal hippocampus. III. Evidence for the physiological role of terminal α2-adrenergic autoreceptors. Brain Res 499:18–26
Cusack B, Nelson A, Richelson E (1994) Binding of antidepressants to human brain receptors: focus on newer generation compounds. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 114:559–565
de Montigny C (1984) Electroconvulsive shock treatments enhance responsiveness of forebrain neurons to serotonin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 228:230–234
Debonnel G, Saint-André E, Hébert C, de Montigny C, Lavoie N, Blier P (2007) Differential physiological effects of a low dose and high doses of venlafaxine in major depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 10:51–61
Dong J, Blier P (2001) Modification of norepinephrine and serotonin, but not dopamine, neuron firing by sustained bupropion treatment. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 155:52–57
El Mansari M, Ghanbari R, Janssen S, Blier P (2008) Sustained administration of bupropion alters the neuronal activity of serotonin, norepinephrine but not dopamine neurons in the rat brain. Neuropharmacology 55:1191–1198
Evans L, Golshan S, Kelsoe J, Rapaport M, Resovsky K, Sutton L, Gillin JC (2002) Effects of rapid tryptophan depletion on sleep electroencephalogram and mood in subjects with partially remitted depression on bupropion. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:1016–1026
Ferris RM, Beaman OJ (1983) Bupropion: a new antidepressant drug, the mechanism of action of which is not associated with down-regulation of postsynaptic beta-adrenergic, serotonergic (5-HT2), alpha 2-adrenergic, imipramine and dopaminergic receptors in brain. Neuropharmacology 22:1257–1267
Ferris RM, White HL, Cooper BR, Maxwell RA, Tang FLM, Beaman OJ, Russell A (1981) Some neurochemical properties of a new antidepressant, bupropion hydrochloride (Wellbutrin). Drug Dev Res 1:21–35
Fletcher A, Forster EA, Bill DJ, Brown G, Cliffe IA, Hartley JE, Jones DE, McLenachan A, Stanhope KJ, Critchley DJ, Childs KJ, Middlefell VC, Lanfumey L, Corradetti R, Laporte AM, Gozlan H, Hamon M, Dourish CT (1996) Electrophysiological, biochemical, neurohormonal and behavioural studies with WAY-100635, a potent, selective and silent 5-HT1A receptor antagonist. Behav Brain Res 73:337–353
Frankhuijzen AL, Mulder AH (1982) Pharmacological characterization of presynaptic α-adrenoceptors modulating 3H-NA and 3H-5-HT release from slices of the hippocampus of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 81:97–106
Freedman JE, Aghajanian GK (1985) Opiate and alpha 2-adrenoceptor responses of rat amygdaloid neurons: co-localization and interactions during withdrawal. J Neurosci 5:3016–3024
Gandolfi O, Barbaccia ML, Chuang DM, Costa E (1983) Daily bupropion injections for 3 weeks attenuate the NE stimulation of adenylate cyclase and the number of beta-adrenergic recognition sites in rat frontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 22:927–929
Ghanbari R, El Mansari M, Blier P (2010) Electrophysiological effects of the co-administration of escitalopram and bupropion on rat serotonin and norepinephrine neurons. J Psychopharmacol 24:39–50
Gobbi G, Slater S, Boucher N, Debonnel G, Blier P (2003) Neurochemical and psychotropic effects of bupropion in healthy male subjects. J Clin Psychopharmacol 23:233–239
Göthert M, Huth H, Schlicker E (1981) Characterization of the receptor subtype involved in alpha-adrenoceptor-mediated modulation of serotonin release from rat brain cortex slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 317:199–203
Haddjeri N, Blier P, de Montigny C (1998) Long-term antidepressant treatments result in a tonic activation of forebrain 5-HT1A receptors. J Neurosci 18:10150–10156
Hardebo JE (1992) Influence of impulse pattern on noradrenaline release from sympathetic nerves in cerebral and some peripheral vessels. Acta Physiol Scand 144:333–339
Kandel ER, Spencer WA (1961) Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. II. After-potentials and repetitive firing. J Neurophysiol 24:43–259
Khawaja X, Evans N, Reilly Y, Ennis C, Minchin MC (1995) Characterization of the binding of [3H]WAY-100635, a novel 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor antagonist, to rat brain. J Neurochem 64:2716–2726
Kugaya A, Seneca NM, Snyder PJ, Williams SA, Malison RT, Baldwin RM, Seibyl JP, Innis RB (2003) Changes in human in vivo serotonin and dopamine transporter availabilities during chronic antidepressant administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:413–420
Kwon S, Lee B, Kim M, Lee H, Park HJ, Hahm DH (2010) Antidepressant-like effect of the methanolic extract from Bupleurum falcatum in the tail suspension test. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34:265–270
Lacroix D, Blier P, Curet O, de Montigny C (1991) Effects of long-term desipramine administration on noradrenergic neurotransmission: electrophysiological studies in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257:1081–1090
Lam RW, Hossie H, Solomons K, Yatham LN (2004) Citalopram and bupropion-SR: combining versus switching in patients with treatment-resistant depression. J Clin Psychiatry 65:337–340
Learned-Coughlin SM, Bergstorm M, Savitcheva I, Ascher J, Schmith VD, Langstorm B (2003) In vivo activity of bupropion at the human dopamine transporter as measured by positron emission tomography. Biol Psychiatry 54:800–805
Li SX, Perry KW, Wong DT (2002) Influence of fluoxetine on the ability of bupropion to modulate extracellular dopamine and norepinephrine concentrations in three mesocorticolimbic areas of rats. Neuropharmacology 42:181–190
Maura G, Gemignani A, Raiteri M (1982) Noradrenaline inhibits central serotonin release through alpha 2-adrenoceptors located on serotonergic nerve terminals. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 320:272–274
Maura G, Gemignani A, Raiteri M (1985) Alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rat hypothalamus and cerebral cortex: functional evidence for pharmacologically distinct subpopulations. Eur J Pharmacol 116:335–339
Meyer JH, Goulding VS, Wilson AA, Hussey D, Christensen BK, Houle S (2002) Bupropion occupancy of the dopamine transporter is low during clinical treatment. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 163:102–105
Mongeau R, Blier P, de Montigny C (1993) In vivo electrophysiological evidence for tonic activation by endogenous noradrenaline of alpha 2-adrenoceptors on 5-hydroxytryptamine terminals in the rat hippocampus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 347:266–272
Mongeau R, de Montigny C, Blier P (1994) Electrophysiologic evidence for desensitization of alpha 2-adrenoceptors on serotonin terminals following long-term treatment with drugs increasing norepinephrine synaptic concentration. Neuropsychopharmacology 10:41–51
Nomikos GG, Damsma G, Wenkstern D, Fibiger HC (1992) Effects of chronic bupropion on interstitial concentrations of dopamine in rat nucleus accumbens and striatum. Neuropsychopharmacology 7:7–14
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 4th edn. Academic, New York
Perumal AS, Smith TM, Suckow RF, Cooper TB (1986) Down regulation of beta-receptors by bupropion and its major metabolite in mouse brain. Neuropharmacology 25:1323–1326
Piacentini MF, Clinckers R, Meeusen R, Sarre S, Ebinger G, Michotte Y (2003) Effect of bupropion on hippocampal neurotransmitters and on peripheral hormonal concentrations in the rat. J Appl Physiol 95:652–656
Pittenger C, Duman RS (2008) Stress, depression, and neuroplasticity: a convergence of mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:88–109
Ranck JB (1975) Behavioral correlates and firing repertoires of neurons in the dorsal hippocampal formation and septum of unrestrained rats. In: Isaacson RL, Pribram KH (eds) The hippocampus. Plenum, New York, pp 207–244
Rueter LE, De Montigny C, Blier P (1998) Electrophysiological characterization of the effect of long-term duloxetine administration on the rat serotonergic and noradrenergic systems. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 285:404–412
Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, Surget A, Battaglia F, Dulawa S, Weisstaub N, Lee J, Duman R, Arancio O, Belzung C, Hen R (2003) Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science 301:805–809
Seppala T, Linnoila M, Soundergaard I, Elonen E, Mattila MJ (1981) Tyramine pressor test and cardiovascular effects of chlorimipramine and nortriptyline in healthy volunteers. Biol Psychiatry 16:71–77
Starke K, Montel H (1973) Involvement of alpha-receptors in clonidine-induced inhibition of transmitter release from central monoamine neurones. Neuropharmacology 12:1073–1080
Szabo ST, Blier P (2001) Effects of the selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor reboxetine on norepinephrine and serotonin transmission in the rat hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 25:845–857
Tatsumi M, Groshan K, Blakely RD, Richelson E (1997) Pharmacological profile of antidepressants and related compounds at human monoamine transporters. Eur J Pharmacol 340:249–258
Wang RY, Aghajanian GK (1980) Enhanced sensitivity of amygdaloid neurons to serotonin and norepinephrine after chronic antidepressant treatment. Commun Psychopharmacol 4:83–90
Wolfe BB, Harden TK, Sporn JR, Molinoff PB (1978) Presynaptic modulation of beta adrenergic receptors in rat cerebral cortex after treatment with antidepressants. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 207:446–457
Zisook S, Rush AJ, Haight BR, Clines DC, Rockett CB (2006) Use of bupropion in combination with serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Biol Psychiatry 59:203–210
Acknowledgments
This research study was supported by the Canadian Institutes for Health Research grant (77838) to P. Blier, a Tier I Chair in Psychopharmacology from the Canadian Government, and an Endowed chair from the University of Ottawa Institute of Mental Health Research. P. Blier has received grants and/or honoraria from Astra Zeneca, Biovail, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Labopharm, Lundbeck/Takeda, Schering-Plough/Merck, Sepracor, Servier and Wyeth. R. Ghanbari and M. El Mansari have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghanbari, R., El Mansari, M. & Blier, P. Enhancement of serotonergic and noradrenergic neurotransmission in the rat hippocampus by sustained administration of bupropion. Psychopharmacology 217, 61–73 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2260-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2260-1