Abstract
Rationale
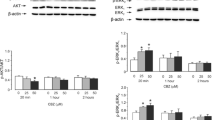
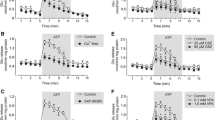
Common biological effects by all three conventional anti-bipolar drugs, the lithium ion (Li+), carbamazepine, and valproic acid, are important because identical effects may provide information about the pathophysiology of affective disorders. It has been reported that chronic treatment with either drug in vivo down-regulates the turnover of arachidonic acid in brain. This reaction is catalyzed by Ca2+-dependent phospholipase A2 (cPLA2), the expression of which was down-regulated by Li+ or carbamazepine but not by valproic acid; expression of two other PLA subtypes, iPLA2 and sPLA2 was unaffected. cPLA2 is amply expressed in astrocytes, and in the present study, effects of 1–4 weeks of treatment with clinically relevant concentrations of each of the three anti-bipolar drugs on cPLA2, iPLA2, and sPLA2 mRNA and protein expression were determined in primary cultures of mouse astrocytes by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and immunoblotting.
Results
Two or more weeks treatment with Li+ concentrations below 2 mM, carbamazepine or valproic acid up-regulated mRNA and protein expression of cPLA2, but had no effect on iPLA2 and sPLA2, showing enzyme specificity. The effect occurred more rapidly at higher than lower concentrations but also tended to end after 4 weeks at the higher concentrations. Two millimolar Li+ caused an initial increase of cPLA2 followed by a decrease after 3 and 4 weeks. Topiramate had no effect, indicating specificity for anti-bipolar drugs.
Conclusions
Both up- and down-regulation of cPLA2 gene expression are involved in the mechanisms of action of anti-bipolar drugs; astrocytes are a target for these drugs.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloisio S, Aiello R, Ferroni S, Nobile M (2006) Potentiation of native and recombinant P2X7-mediated calcium signaling by arachidonic acid in cultured cortical astrocytes and human embryonic kidney 293 cells. Mol Pharmacol 69:1975–1983
Balboa MA, Varela-Nieto I, Lucas KK, Dennis EA (2002) Expression and function of phospholipase A2 in brain. FEBS Lett 531:12–17
Basselin M, Chang L, Seemann R, Bell JM, Rapoport SI (2005) Chronic lithium administration to rats selectively modifies 5-HT2A/2C receptor-mediated brain signaling via arachidonic acid. Neuropsychopharmacol 30:461–472
Bazinet RP, Rao JS, Chang L, Rapoport SI, Lee HJ (2005) Chronic valproate does not alter the kinetics of docosahexaenoic acid within brain phospholipids of the unanesthetized rat. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 182:180–185
Bazinet RP, Rao JS, Chang L, Rapoport SI, Lee HJ (2006) Chronic carbamazepine decreases the incorporation rate and turnover of arachidonic acid but not docosahexaenoic acid in brain phospholipids of the unanesthetized rat: relevance to bipolar disorder. Biol Psychiatry 59:401–407
Bialer M, Levy RH, Perucca E (1998) Does carbamazepine have a narrow therapeutic plasma concentration range? Ther Drug Monit 20:56–59
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chang MC, Grange E, Rabin O, Bell JM, Allen DD, Rapoport SI (1996) Lithium decreases turnover of arachidonate in several brain phospholipids. Neurosci Lett 220:171–174
Chang MC, Contreras MA, Rosenberger TA, Rintala JJ, Bell JM, Rapoport SI (2001) Chronic valproate treatment decreases the in vivo turnover of arachidonic acid in brain phospholipids: a possible common effect of mood stabilizers. J Neurochem 77:796–803
Cornell-Bell AH, Jung P, Trinkaus-Randall V (2004) Decoding calcium wave signaling. In Hertz L (ed) Non-neuronal cells of the nervous system: function and dysfunction. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 661–687
Di Daniel E, Cheng L, Maycox PR, Mudge AW (2006) The common inositol-reversible effect of mood stabilizers on neurons does not involve GSK3 inhibition, myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase or the sodium-dependent myo-inositol transporters. Mol Cell Neurosci 32:27–36
El Marjou M, Montalescot V, Buzyn A, Geny B (2000) Modifications in phospholipase D activity and isoform expression occur upon maturation and differentiation in vivo and in vitro in human myeloid cells. Leukemia 14:2118–2127
Fiacco TA, McCarthy KD (2006) Astrocyte calcium elevations: properties, propagation, and effects on brain signaling. Glia 54:676–690
Friis ML, Christiansen J, Hvidberg EF (1978) Brain concentrations of carbamazepine and carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide in epileptic patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 14:47–51
Garcia MC, Kim HY (1997) Mobilization of arachidonate and docosahexaenoate by stimulation of the 5-HT2Areceptor in rat C6 glioma cells. Brain Res 768:43–48
Ghelardoni S, Tomita YA, Bell JM, Rapoport SI, Bosetti F (2004) Chronic carbamazepine selectively downregulates cytosolic phospholipase A2 expression and cyclooxygenase activity in rat brain. Biol Psychiatry 56:248–254
Ghosh M, Tucker DE, Burchett SA, Leslie CC (2006) Properties of the Group IV phospholipase A2 family. Prog Lipid Res 45:487–510
Goodnick PJ (2006) Anticonvulsants in the treatment of bipolar mania. Expert Opin Pharmacother 7:401–410
Haas B, Schipke CG, Peters O, Sohl G, Willecke K, Kettenmann H (2006) Activity-dependent ATP-waves in the mouse neocortex are independent from astrocytic calcium waves. Cereb Cortex 16:237–246
Hansson E, Rönnbäck L (2004) Astrocytic receptors and second messenger systems. In: Hertz L (ed) Non-Neuronal Cells of the Nervous System: Function and Dysfunction. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 475–501
Hertz L, Schousboe A, Boechler N, Mukerji S, Fedoroff S (1978) Kinetic characteristics of the glutamate uptake into normal astrocytes in cultures. Neurochem Res 3:1–14
Hertz L, Juurlink BHJ, Szuchet S (1985) Cell cultures. In: A Lajtha A (ed) Handbook of neurochemistry (2nd ed, Vol. 8) Plenum, New York, pp 603–661
Hertz L, Bender AS, Woodbury D, White SA (1989) Potassium induced calcium uptake in astrocytes and its potent inhibition by a calcium channel blocker. J Neurosci Res 22:209–215
Hertz L, Peng L, Lai JC (1998) Functional studies in cultured astrocytes. Methods 16:293–310
Hertz L, Chen Y, Bersudsky Y, Wolfson M (2004) Shared effects of all three conventional anti-bipolar drugs on the phosphoinositide system in astrocytes. In: Hertz L (ed) Non-neuronal cells of the nervous system: function and dysfunction. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1033–1048
Hewett SJ (1999) Interferon-gamma reduces cyclooxygenase-2-mediated prostaglandin E2 production from primary mouse astrocytes independent of nitric oxide formation. J Neuroimmunol 94:134–143
Ivanov A, Pero RS, Scheck A, Romanousky AA (2002) Prostaglandin E2-synthesizing enzymes in fever: differential transcriptional regulation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 283:R1104–R1117
Kennedy BP, Payette P, Mudgett J, Vadas P, Pruzanski W, Kwan M, Tang C, Rancourt DE, Cromlish WA (1995) A natural disruption of the secretory group II phospholipase A2 gene in inbred mouse strains. J Biol Chem 22:22378–22385
Kong EKC, Peng L, Chen Y, Yu ACH, Hertz L (2002) Up-regulation of 5-HT2B receptor density and receptor-mediated glycogenolysis in mouse astrocytes by long-term fluoxetine administration. Neurochem Int 27:113–120
Lautens LL, Chiou XG, Sharp JD, Young WS 3rd, Sprague DL, Ross LS, Felder CC (1998) Cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) distribution in murine brain and functional studies indicate that cPLA2 does not participate in muscarinic receptor-mediated signaling in neurons. Brain Res 809:18–30
Lindbom J, Ljungman AG, Lindahl M, Tagesson C (2001) Expression of members of the phospholipase A2 family of enzymes in human nasal mucosa. Eur Respir J 18:130–138
Lubrich B, van Calker D (1999) Inhibition of the high-affinity myo-inositol uptake: a common mechanism of action of anti-bipolar drugs? Neuropsychopharmacol 21:519–529
Maida ME, Hurley SD, Daeschner JA, Moore AH, O’Banion M (2006) Cytosolic prostaglandin E2 synthase (cPGES) expression is decreased in discrete cortical regions in psychiatric disease. Brain Res 1103:164–172
Meier E, Hertz L, Schousboe A (1991) Neurotransmitters as developmental signals. Neurochem Int 19:1–15
Moore CM, Demopulos CM, Henry ME, Steingard RJ, Zamvil L, Katic A, Breeze JL, Moore JC, Cohen BM, Renshaw PF (2002) Brain-to-serum lithium ratio and age: an in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Am J Psychiatry 159:1240–1242
Peng L, Juurlink BHJ, Hertz L (1991) Differences in transmitter release, morphology, and ischemia-induced cell injury between cerebellar granule cell cultures developing in the presence and in the absence of a depolarizing potassium concentration. Dev Brain Res 63:1–12
Petit P, Lonjon R, Cociglio M, Sluzewska A, Blayac JP, Hue B, Alric R, Pouget R (1991) Carbamazepine and its 10,11-epoxide metabolite in acute mania: clinical and pharmacokinetic correlates. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 41:541–546
Purdon AD, Rosenberger TA, Shetty HU, Rapoport SI (2002) Energy consumption by phospholipid metabolism in mammalian brain. Neurochem Res 27:1641–1647
Rapoport SI, Bosetti F (2002) Do lithium and anticonvulsants target the brain arachidonic acid cascade in bipolar disorder? Arch Gen Psychiatry 59:592–596
Rintala J, Seemann R, Chandrasekaran K, Rosenberger TA, Chang L, Contreras MA, Rapoport SI, Chang MC (1999) 85 kDa cytosolic phospholipase A2 is a target for chronic lithium in rat brain. Neuroreport 10:3887–3890
Scemes E, Giaume C (2006) Astrocyte calcium waves: what they are and what they do. Glia 54:716–725
Schou M (2001) Lithium treatment at 52. J Affect Disord 67:21–32
Sergeeva M, Strokin M, Wang H, Ubl JJ, Reiser G (2003) Arachidonic acid in astrocytes blocks Ca(2+) oscillations by inhibiting store-operated Ca(2+) entry, and causes delayed Ca(2+) influx. Cell Calcium 33:283–292
Soares JC, Boada F, Spencer S, Mallinger AG, Dippold CS, Wells KF, Frank E, Keshavan MS, Gershon S, Kupfer DJ (2001) Brain lithium concentrations in bipolar disorder patients: preliminary (7)Li magnetic resonance studies at 3 T. Biol Psychiatry 49:437–443
Sproule B (2002) Lithium in bipolar disorder: can drug concentrations predict therapeutic effect? Clin Pharmacokinet 41:639–660
Stephenson DT, Manetta JV, White DL, Chiou XG, Cox L, Gitter B, May PC, Sharp JD, Kramer RM, Clemens JA (2004) Phospholipase A2 in the central nervous system: implication for neurodegeneration diseases. J Lipid Res 46:205–213
Sun GY, Xu J, Jensen MD, Yu S, Wood WG, Gonzalez FA, Simonyi A, Sun, AY, Weisman GA (2005) Phospholipase A2 in astrocytes: responses to oxidative stress, inflammation, and G protein-coupled receptor agonists. Mol Neurobiol 31:27–41
Vajda FJ, Donnan GA, Phillips J, Bladin PF (1981) Human brain, plasma, and cerebrospinal fluid concentration of sodium valproate after 72 h of therapy. Neurology 31:486–487
Weerasinghe GR, Rapoport SI, Bosetti F (2004) The effect of chronic lithium on arachidonic acid release and metabolism in rat brain does not involve secretory phospholipase A2 or lipoxygenase/cytochrome P450 pathways. Brain Res Bull 63:485–489
Wieser HG (1994) Comparison of valproate level in human plasma, cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue following administration of various preparations of valproate and valpromide. Schweiz Rundsch Med Prax 83:1111–1116
Williams V, Grossman RG, Edmunds SM (1980) Volume and surface area estimates of astrocytes in the sensorimotor cortex of the cat. Neurosci 5:115–1151
Williams RS, Cheng L, Mudge AW, Harwood AJ (2002) A common mechanism of action for three mood-stabilizing drugs. Nature 417:292–295
Wolff J, Chao TI (2004) Cytoarchitectonics of non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system. In Hertz L (ed) Non-neuronal cells of the nervous system: function and dysfunction. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–52
Wolfson M, Bersudsky Y, Zinger E, Simkin M, Belmaker RH, Hertz L (2000) Chronic treatment of human astrocytoma cells with lithium, carbamazepine or valproic acid decreases inositol uptake at high inositol concentrations but increases it at low inositol concentrations. Brain Res 855:158–161
Xu J, Weng YI, Simonyi A, Krugh BW, Liao Z, Weisman GA, Sun GY (2002) Role of PKC and MAPK in cytosolic PLA2 phosphorylation and arachidonic acid release in primary murine astrocytes. J Neurochem 83:259–270
Yang KT, Chen WP, Chang WL, Su MJ, Tsai KL (2005) Arachidonic acid inhibits capacitative Ca2+ entry and activates non-capacitative Ca2+ entry in cultured astrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 331:603–613
Zhao Z, Hertz L, Code WE (1996) Effects of benzodiazepines on potassium-induced increase in free cytosolic calcium concentration in astrocytes: interactions with nifedipine and the peripheral-type benzodiazepine antagonist PK 11195. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 74:273–277
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Grant No. 30572180 and No. 30370451 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China. We thank Mrs. Xiaolin Yang for her valuable technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Gu, L., Zhang, H. et al. Up-regulation of cPLA2 gene expression in astrocytes by all three conventional anti-bipolar drugs is drug-specific and enzyme-specific. Psychopharmacology 194, 333–345 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0853-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0853-5