Abstract
Rationale
The hallucinogen 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-MeO-DMT) is structurally similar to other indoleamine hallucinogens such as LSD. The present study examined the effects of 5-MeO-DMT in rats using the Behavioral Pattern Monitor (BPM), which enables analyses of patterns of locomotor activity and exploration, and the prepulse inhibition of startle (PPI) paradigm.
Objectives
A series of interaction studies using the serotonin (5-HT)1A antagonist WAY-100635 (1.0 mg/kg), the 5-HT2A antagonist M100907 (1.0 mg/kg), and the 5-HT2C antagonist SER-082 (0.5 mg/kg) were performed to assess the respective contributions of these receptors to the behavioral effects of 5-MeO-DMT (0.01, 0.1, and 1.0 mg/kg) in the BPM and PPI paradigms.
Results
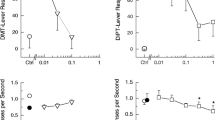
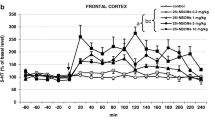
5-MeO-DMT decreased locomotor activity, investigatory behavior, the time spent in the center of the BPM chamber, and disrupted PPI. All of these effects were antagonized by WAY-100635 pretreatment. M100907 pretreatment failed to attenuate any of these effects, while SER-082 pretreatment only antagonized the PPI disruption produced by 5-MeO-DMT.
Conclusions
While the prevailing view was that the activation of 5-HT2 receptors is solely responsible for hallucinogenic drug effects, these results support a role for 5-HT1A receptors in the effects of the indoleamine hallucinogen 5-MeO-DMT on locomotor activity and PPI in rats.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams LM, Geyer MA (1982) LSD-induced alterations of locomotor patterns and exploration in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 77:179–185
Adams LM, Geyer MA (1985a) Effects of DOM and DMT in a proposed animal model of hallucinogenic activity. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 9:121–132
Adams LM, Geyer MA (1985b) A proposed animal model for hallucinogens based on LSD’s effects on patterns of exploration in rats. Behav Neurosci 99:881–900
Arnt J, Hyttel J (1989) Facilitation of 8-OH-DPAT-induced forepaw treading of rats by the 5-HT2 agonist DOI. Eur J Pharmacol 161:45–51
Bakshi VP, Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1998) Reversal of isolation rearing-induced deficits in prepulse inhibition by seroquel and olanzapine. Biol Psychiatry 43:436–445
Berendsen HH, Jenck F, Broekkamp CL (1989) Selective activation of 5HT1A receptors induces lower lip retraction in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 33:821–827
Bervoets K, Millan MJ, Colpaert FC (1990) Agonist action at 5-HT1C receptors facilitates 5-HT1A receptor-mediated spontaneous tail-flicks in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 191:185–195
Boulenguez P, Chaveau J, Segu L, Morel A, Lanoir J, Delaage M (1991) A new 5-hydroxy-indole derivative with preferential affinity for 5-HT1B binding sites. Eur J Pharmacol 194:91–98
Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990) Sensorimotor gating and schizophrenia: human and animal model studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:181–188
Cunningham KA, Appel JB (1987) Neuropharmacological reassessment of the discriminative stimulus properties of d-lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Psychopharmacalogy (Berl) 91:67–73
Darmani NA, Martin BR, Glennon RA (1990) Withdrawal from chronic treatment with (+)-DOI causes super-sensitivity to 5-HT2 receptor-induced head-twitch behaviour in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 186:115–118
Dumuis A, Sebben M, Bockaert J (1987) Pharmacology of 5-hydroxytryptamine-1A receptors which inhibit cAMP production in hippocampal and cortical neurons in primary culture. Mol Pharmacol 33:178–186
Eison AS, Wright RN (1992) 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors mediate discrete behaviors in the Mongolian gerbil. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:131–137
Gammans RE, Mayol RF, Labudde JA (1986) Metabolism and disposition of buspirone. Am J Med 80:41–51
Geyer MA (1990) Approaches to the characterization of drug effects on locomotor activity in rodents. In: Adler MW, Cowan A (eds) Modern methods in pharmacology: testing and evaluation of drugs of abuse. Wiley, New York, pp 81–99
Geyer MA, Krebs KM (1994) Serotonin receptor involvement in an animal model of the acute effects of hallucinogens. In: Lin G, Glennon RA (eds) Hallucinogens: an update (NIDA Research Monograph Series). US Department of Health and Human Services, Rockville, MD, pp 124–156
Geyer MA, Russo PV, Masten VL (1986) Multivariate assessment of locomotor behavior: pharmacological and behavioral analyses. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 25:277–288
Geyer MA, Krebs-Thomson K, Braff DL, Swerdlow NR (2001) Pharmacological studies of prepulse inhibition models of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia: a decade in review. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 156:117–154
Glennon RA (1986) Discriminative stimulus properties of the 5-HT1A agonist 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT). Pharmacol Biochem Behav 25:135–139
Glennon RA, Rosecrans JA (1982) Indolealkylamine and phenalkylamine hallucinogens: a brief overview. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 6:489–497
Glennon RA, Rosecrans JA, Young R, Gaines J (1979) Hallucinogens as a discriminative stimuli: generalization of DOM to a 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine stimulus. Life Sci 24:993–998
Glennon RA, Young R, Rosecrans JA, Kallman MJ (1980) Hallucinogenic agents as discriminative stimuli: a correlation with serotonin receptor affinities. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 68:155–158
Glennon RA, Young R, Jacyno JM, Slusher M, Rosecrans JA (1983) DOM-stimulus generalization to LSD and other hallucinogenic indolealkylamines. Eur J Pharmacol 86:453–459
Glennon RA, Titeler M, McKenney JD (1984) Evidence for 5-HT2 involvement in the mechanism of action of hallucinogenic agents. Life Sci 35:2505–2511
Hoffman HS, Ison JR (1980) Reflex modification in the domain of startle: I. Some empirical findings and their implication for how the nervous system processes sensory input. Psychol Rev 87:175–189
Holmstedt B, Lindgren JE, Plowman T, Rivier L, Schultes RE, Tovar O (1980) Indole alkaloids in Amazonian Myristicaceae: field and laboratory research. Bot Mus Leaf Harv Univ 28:215–234
Krebs KM, Geyer MA (1994) Cross-tolerance studies of serotonin receptors involved in behavioral effects of LSD in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 113:429–437
Krebs-Thomson K, Geyer MA (1996) The role of 5-HT1A receptors in the locomotor-suppressant effects of LSD: WAY-100635 studies of 8-OH-DPAT, DOI, and LSD. Behav Pharmacol 6:551–559
Krebs-Thomson K, Geyer MA (1998) Evidence for a functional interaction between 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 140:69–74
Krebs-Thomson K, Paulus MP, Geyer MA (1998) Effects of hallucinogens on locomotor and investigatory activity and patterns: influence of 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 18:339–351
Lucki I, Frazer A (1982) Prevention of the serotonin syndrome in rats by repeated administration of monoamine oxidase inhibitors but not tricyclic antidepressants. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 77:205–211
Lucki I, Nobler MS, Frazer A (1984) Differential actions of serotonin antagonists on two behavioral models of serotonin receptor activation in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 228:133–139
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1988) Dopaminergic stimulation disrupts sensorimotor gating in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 94:507–514
Matthews WD, Smith CD (1980) Pharmacological profile of a model for central serotonin receptor activation. Life Sci 26:1397–1403
McClue SJ, Brazell C, Stahl SM (1989) Hallucinogenic drugs are partial agonists of the human platelet shape change response: a physiological model of the 5-HT2 receptor. Biol Psychiatry 26:297–302
McKenna DJ, Towers GH, Abbott FS (1984) Monoamine oxidase inhibitors in South American hallucinogenic plants part 2: constituents of orally-active myristicaceous hallucinogens. J Ethnopharmacol 12:179–211
McKenna DJ, Repke DB, Lo L, Peroutka SJ (1990) Differential interactions of indolealkylamines with 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor subtypes. Neuropharmacology 29:193–198
Nanry KP, Tilson HA (1989) The role of 5HT1A receptors in the modulation of the acoustic startle reflex in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 97:507–513
Ouagazzal A, Grottick AJ, Moreau J, Higgins GA (2001) Effect of LSD on prepulse inhibition and spontaneous behavior in the rat. A pharmacological analysis and comparison between two rat strains. Neuropsychopharmacology 25:565–575
Rigdon GC, Weatherspoon JK (1992) 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor agonists block prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle reflex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 263:486–493
Schultes RE (1979) Evolution of the identification of the myristicaceous hallucinogens of South America. J Ethnopharmacol 1:211–239
Schultes RE, Raffauf RF (1995) The healing forest: medicinal and toxic plants of the northwest Amazonia. Dioscorides, Portland
Scott PA, Chou JM, Tang H, Frazer A (1994) Differential induction of 5-HT1A-mediated responses in vivo by three chemically dissimilar 5-HT1A agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:198–208
Shulgin A, Shulgin A (1997) TiHKAL: the continuation. Transform, Berkeley, CA
Sipes TE, Geyer MA (1995a) 8-OH-DPAT disruption of prepulse inhibition in rats: reversal with (+)WAY 100,135 and localization of site of action. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 117:41–48
Sipes TE, Geyer MA (1995b) DOI disruption of prepulse inhibition of startle in the rat is mediated by 5-HT2A and not by 5-HT2C receptors. Behav Pharmacol 6:839–842
Sloviter RS, Drust EG, Connor JD (1978) Specificity of a rat behavioral model for serotonin receptor activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 206:339–347
Smith LM, Peroutka SJ (1986) Differential effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A selective drugs on the 5-HT behavioral syndrome. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:1513–1519
Spencer DG, Glaser T, Traber J (1987) Serotonin receptor subtype mediation of the interoceptive discriminative stimuli induced by 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 93:158–166
Thomson KK (1996) Multiple serotonin receptor influences in the behavioral effects of hallucinogens in rats: the role of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors Psychology. UCSD, La Jolla
Titeler M, Lyon RA, Glennon RA (1988) Radioligand binding evidence implicates the brain 5-HT2 receptor as a site of action for LSD and phenylisopropylamine hallucinogens. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 94:213–216
Tricklebank MD, Forler C, Middlemiss DN, Fozard JR (1985) Subtypes of the 5-HT receptor mediating the behavioural responses to 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 117:15–24
Winter JC, Filipink RA, Timineri D, Helsley SE, Rabin RA (2000) The paradox of 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine: an indoleamine hallucinogen that induces stimulus control via 5-HT1A receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 65:75–82
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institute on Drug Abuse Award R02 DA02925 and the Veterans Affairs VISN 22 Mental Illness Research, Education, and Clinical Center. M. A. Geyer holds an equity position in San Diego Instruments. These studies were conducted while E. M. Ruiz was conducting an externship from the School of Pharmacy, University of Utrecht, The Netherlands. These experiments comply with the current laws of the United States.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krebs-Thomson, K., Ruiz, E.M., Masten, V. et al. The roles of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors in the effects of 5-MeO-DMT on locomotor activity and prepulse inhibition in rats. Psychopharmacology 189, 319–329 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0566-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0566-1